Hepatic flexure colon tumor is a tumor that appears in the colon at the bend between the ascending colon and the transverse colon, also known as the right colonic angle. Compared to other locations in the colon frame, hepatic flexure colon tumor is less common. Symptoms of pain in the lower right ribs when suffering from the disease can be confused with liver and biliary diseases, so patients should go to the doctor early for timely examination and treatment.
1. Risk factors for hepatic flexure colon tumor
The exact cause of colon cancer has not been determined, but there are some factors that increase the risk of the disease. Factors that increase the risk of hepatic flexure colon tumor are similar to colon cancer in general, including:
Colon polyps
Colon cancer can originate from polyps. Polyps can develop into malignant colon cancer if not removed early. A history of adenomatous polyps before the age of 60 increases the risk of developing colon cancer.
Family history of colon cancer
If a close family member has a history of colon cancer, it increases the risk of the disease, especially if the person develops the disease before the age of 45
Lifestyle and diet
Age is a significant risk factor for colon cancer, the older the age, the higher the risk. About 90% of people diagnosed with colon cancer are over 50 years old. However, recently the disease has become more common in people under 50 years old.
Colon cancer is more likely to occur in people with a sedentary lifestyle, obesity and smoking.
The colon is part of the digestive system, so diet and nutrition play an important role in the development of the disease. According to research, a diet low in fiber, high in saturated fat, and high in red meat or processed foods increases the risk of the disease.
Underlying medical conditions
Certain underlying medical conditions and treatments are associated with an increased risk of colon cancer. These include polyps, ulcerative colitis, Crohn's disease, obesity, or being overweight.
2. Symptoms and signs of hepatic flexure colon cancer
Early stages of hepatic flexure colon cancer often do not cause symptoms, but symptoms become more noticeable as the disease progresses.
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Changes in stool hardness: loose stools, flat stools.
- Blood mixed in stools makes stools dark brown or black
- Bright red blood in stools
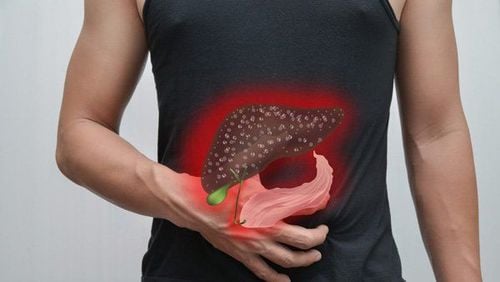
- Abdominal pain, often in the right upper quadrant
- Bloating or flatulence
- Weakness, fatigue
- Poor appetite, nausea, vomiting
- Unexplained weight loss
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Iron deficiency anemia
- If the cancer spreads to other parts of the body, it can cause other symptoms, such as metastasis to the liver, which can cause jaundice.

3. Stages of Hepatic Flexion Colon Cancer
Staging indicates the extent of metastasis of the cancer and the size of the tumor. Staging of Hepatic Flexion Colon Cancer is similar to other locations in the colon, colon cancer is often divided into the following stages:
- Stage 0: Also known as carcinoma in situ, abnormal cells are limited to the mucosal layer of the colon.
- Stage 1: Cancer has grown into the muscle layer. But has not spread to nearby lymph nodes or to other parts of the body.
- Stage 2: Cancer has invaded the serosa of the colon or some nearby organs, but has not affected the lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: Cancer has invaded the lymph nodes but has not metastasized to other organs.
- Stage 4: Cancer has metastasized to other distant organs, such as the liver or lungs.
4. Treatment methods for hepatic flexure colon tumors
Treatment will depend on the stage of hepatic flexure colon tumors. In addition, the doctor will also evaluate the age, overall health and other characteristics of the patient before deciding on the best treatment option.
The purpose of treatment is to completely remove the cancer, prevent the invasion of the tumor and reduce symptoms. Treatment methods that can be applied to hepatic flexure colon tumors include surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy.
Surgery
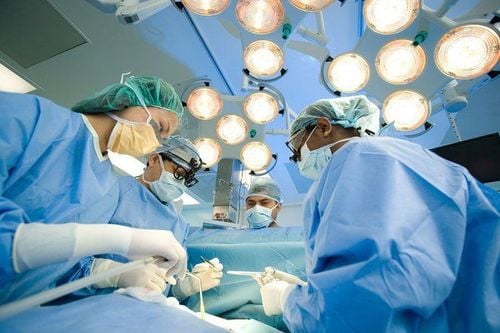
Surgery is the procedure of removing the cancerous mass and possibly surrounding healthy tissue. This is the most common treatment method for hepatic flexure colon tumors, applied at all stages of the disease. The indication for radical or temporary surgery depends on many factors of the disease.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells. For people with colon cancer, chemotherapy may be prescribed before surgery to help shrink the tumor for easier removal, and after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells. In addition, chemotherapy plays an important role in cases where the tumor has metastasized to other organs.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy kills cancer cells by focusing high-energy gamma rays on them. The drug is used to treat metastatic colon cancer or when it does not respond to other treatments.
5. Diagnosis of colon cancer
The earlier colon cancer is diagnosed, the higher the chance of curing the disease. Most colon cancer patients have no symptoms in the early stages, so the disease is detected during a routine health check.
The doctor will perform a comprehensive health check and collect information about medical and family history. In addition, some paraclinical tests are also indicated to help diagnose and stage cancer:
Fecal occult blood test
According to the American Gastroenterological Association, this test should be performed annually. This test can detect small amounts of hidden blood in the stool that cannot be seen with the naked eye, helping to determine potential gastrointestinal damage.
Colonoscopy
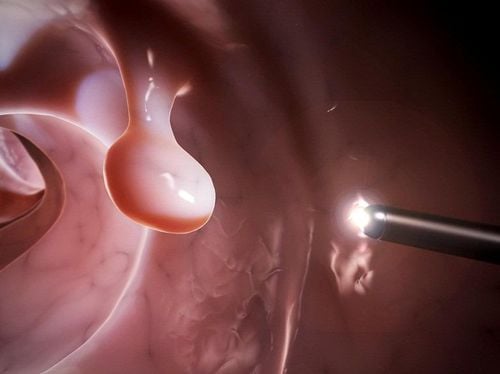
Colonoscopy is often indicated when less invasive paraclinical tests have suspicious results, or during disease screening. This procedure allows the doctor to observe the entire mucosa of the colon and rectum, detecting most lesions such as polyps, early cancer, inflammation, ulcers, etc. In addition, endoscopy can remove polyps and send them for anapathology analysis.
Double-contrast colonography
This X-ray procedure uses a contrast agent called barium to provide a clearer image of the colon and assess the extent of tumor invasion into the colon.
In addition, if the pathology results confirm the diagnosis of colon cancer, the doctor may order a chest X-ray, abdominal CT scan, etc. to assess the stage of the cancer.
6. Screening for Hepatic Flexor Colon Cancer
Symptoms may not appear until the cancer has spread and metastasized. Therefore, the American College of Gastroenterologists recommends screening for people 50 and older and earlier for those at high risk.
For people 50 and older, screening includes a fecal occult blood test every 2 years and a colonoscopy every 10 years.
The screening plan for colon cancer will depend on the risk level of each person. You should consult your doctor to have an appropriate screening plan.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.