This is an automatically translated article.
Left colectomy surgery or right colonectomy and removal of the two ends of the intestine, also known as an artificial anus, is widely used in clinical practice, bringing many benefits to patients. This is the removal of part or all of the colon. Depending on the specific case, the doctor will choose the most appropriate and accurate surgical method.1. Learn about right or left colectomy surgery to bring out the two ends of the intestine
Right colectomy is surgery including: removing 10-15cm of ileum, cecum, ascending colon, right transverse colon, and corresponding mesentery performed by open or laparoscopic technique. belly. Making an ostomy is to bring the two ends of the intestine out to let the stool out. After a period of time, the digestive tract will be restored, then 2 by connecting the ileum to the colon through a small opening in the abdominal wall. The purpose of colostomy is to avoid anastomosis in the case of dirty, heavily necrotic colon.
Left colectomy is the surgical removal of the left transverse colon, splenic flexure, descending colon and mesentery, respectively, performed by open surgery or laparoscopic surgery. Then make an artificial anus by bringing out the two ends of the intestines. Finally, after a period of time, the gastrointestinal tract can be restored by connecting the transverse colon to the sigmoid colon. Joints can be hand-stitched or mechanically spliced.
2. Indicated to cut the right or left colon, bring out the two ends of the intestine
2.1. For right colectomy The tumor is in the colon from the ileocecal valve to the transverse colon. Tuberculosis of the ileum, cancerous polyps, complicated colonic diverticulum, necrotic intussusception, mesenteric tumor. 2.2. For left colectomy, tumor on the left side of transverse colon, splenic flexure colon, descending colon. Necrotizing intussusception, mesenteric tumor, colonic diverticulum. 2.3. Contraindications The tumor is too large, the cancer has metastasized far, into the adjacent organs, especially the duodenum, the peritoneum, which cannot be resected. Patients who are elderly and weak or have severe co-morbidities cannot perform surgery
Người già yếu không nên cắt đại tràng
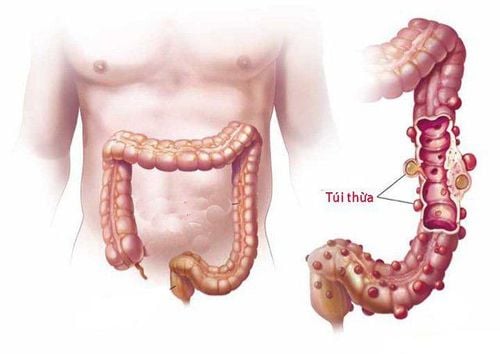
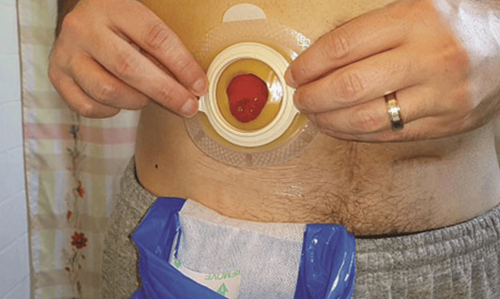
2.4. Indication to take out the two ends of the intestine Indications to take the two ends of the intestine out In the case of a dirty, necrotic colon, there is a risk of bursting the anastomosis, it is necessary to take the tip of the intestine out to make an stoma, then perform an intestinal anastomosis, then 2 to avoid the risk of anastomosis. Bringing the two ends of the intestine out or doing an colostomy here is only temporary, giving the colon time to heal, then the doctors will Re-surgery to close the stoma.
3. Steps to perform a right or left colon resection to bring the two ends of the intestine out
3.1. Colectomy technique must bring out the two ends of the intestines Insensitized with endotracheal anesthesia Open the abdomen with a knife through the midline or enter the abdomen with holes to insert the laparoscope into the abdomen Abdominal exploration Purpose: Evaluation of injuries and viscera in the abdomen. Bring the patient to a high head position, leaning to the left. Move the small intestine down, to the left to expose the right colon. Releasing the right colon: Carrying out dissection, dissection of transverse colon, hepatic flexure. Avoid damage to the stomach, duodenum, gallbladder.
Then dissect the right mesentery. The retroperitoneal viscera will be gradually exposed and separate from the posterior lateral abdominal wall. With a clear view of the duodenum, use an instrument to push the mesocolon gradually to the left, down to reveal the entire duodenal framework to close to the angle of Treitz.
Anatomy to release the ileocecal angle. In this position, the ureter and right iliac artery should be clearly exposed. Release the ileocecal angle to the lower duodenum knee. Finally, the entire right colon expected to be resected was released from the retained intra-abdominal and retroperitoneal traction components.
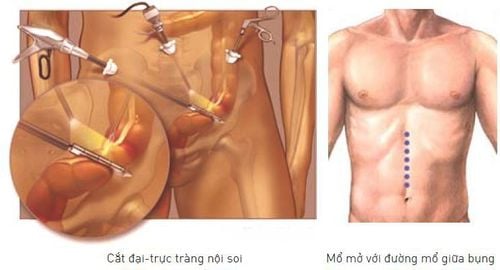
Kỹ thuật cắt đại tràng nội soi và mổ mở đường mổ giữa bụng
Laparotomy, resection of the right colon and anastomosis. Determine the location of the transverse colon to be resected to ensure a number of factors: remove all tumor tissue, including satellite nodes on the mesentery, good nutrition. Take the two ends of the intestine out to make an stoma if indicated. After a period of time, close the stoma, make an anastomosis with stitches or use a sewing machine.
3.2 Left colectomy technique to bring out the two ends of the intestines Insensitize with endotracheal anesthesia Open the abdomen with a knife through the midline or enter the abdomen with holes to insert the laparoscope into the abdomen Probe : Evaluation of lesions and viscera in the abdomen. Move the small intestine to the right to expose the left colon. Release of the left colon: Dissection of transverse colon, splenic flexure: starting from the middle of the transverse colon, using an ultrasound knife to open the oesophageal junction, dissecting the left transverse colon to the colon spleen angle.
Left mesenteric release surgery: start the surgery from the left iliac fossa to release the left mesentery. The retroperitoneal viscera are gradually exposed and the colon separates from the posterior lateral abdominal wall. The left mesenteric resection was performed to release from the traction components of the posterior abdominal wall, spleen, and large omentum and easily removed from the abdomen.
Left colectomy: Locate the transverse colon, the sigmoid colon will be removed to ensure a number of factors: remove all tumor tissue, neighboring nodes, and good nutrition. Take the two ends of the intestine out to make an stoma if indicated. After a period of time, close the stoma, make an anastomosis with stitches or use a sewing machine.
Người bệnh được gây mê nội khí quản trước khi tiến hành phẫu thuật
4. Complications after colectomy
Infection: Infection usually occurs around the incision site or deep in the abdominal cavity. Severe infections are at risk of causing peritonitis. Bleeding: Bleeding is a potential risk, with a high rate of occurrence after surgery. Injury to nearby organs: During surgery, nearby organs such as bowel and bladder can be affected. Complications of intestinal obstruction, obstruction, bladder, kidney, and urethral injury may have occurred. Anastomosis: This is a very serious complication with a high mortality rate, usually occurring about 7-10 days after surgery. Hernia at the old incision: Appearing immediately after surgery and diagnosed in the first year after surgery manifests as a bulge in the abdominal wall, the patient may present with pain, the risk of bowel obstruction,. .. After performing left colectomy or right colonectomy, the patient needs to have a reasonable care and rest regime so that the body can recover quickly as well as limit postoperative complications. may happen.
Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in examining and treating many diseases, patients can completely rest in peace. Center for examination and treatment at the Hospital.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.