This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Tran Van Trong - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Danang International HospitalColon polyps are quite common in children. Colon polyps in children often progress silently, without many symptoms in the early stages, so early diagnosis and detection are often difficult.
1. What are colon polyps in children?
Colon polyp is an abnormal growth on the lining of the colon (large intestine). Colon polyps are mostly benign, but ductal and villi can progress to cancer. Polyps may appear singly or as multiple polyps along the colon. The disease is usually asymptomatic and is often discovered incidentally during colonoscopy, colonoscopy, or fecal occult blood tests.
There are many factors that increase the risk of children having rectal polyps such as diet, inflammation, local and genetic factors,... In children, the average age of colon polyps is 4-7 years old. . Children 1-2 years old can also get the disease but the rate is very low. The disease is also more common in boys than girls.
2. Symptoms of colon polyps in children
Passing out fresh blood or blood mixed in the stool even though the baby is not constipated; Large colon polyps can cause abdominal cramps or cause bowel obstruction; Large colon polyps, if there are small villi-like shoots, can secrete salt and water, causing diarrhea, massive watery stools, leading to hypokalemia; Children show signs of anemia due to a lot of blood loss: pale skin, pale palms, pale mucous membranes,...; Long rectal polyps may prolapse and protrude through the anal opening.
3. Some common types of colon polyps in children
Colon polyps in children are usually solitary, pedunculated, about 0.5-1cm in size. However, there are also many cases of having many polyps or having a large polyp with a size of 2-3cm in the colon;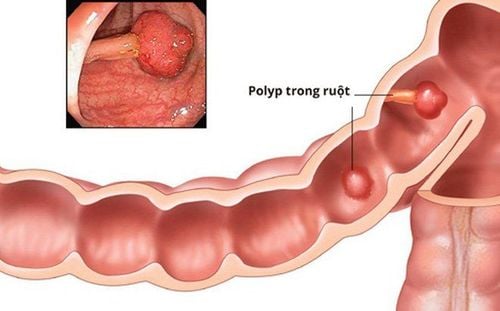
4. Are children's colon polyps dangerous?
The majority of colon polyps in children are benign. However, if not detected and treated in time, polyps will often continue to grow larger and larger, causing children to lose weight and become stunted, unable to keep up with the growth momentum.
Moreover, if left for a long time, colorectal polyps can lead to other risks such as digestive disorders, gastrointestinal bleeding or even cancer. According to research, the older the child, the higher the potential for colon polyps to become cancerous. The risk of carcinogenesis is usually after 10 years, depending on the type of polyp and the size of the polyp. Normally, polyps of ductal gland, villi, size 1 - 1.5 cm are easy to cancerous.
5. Diagnosis and treatment of colon polyps in children
Colon polyps need to be detected and treated early to avoid the risk of large growth causing intestinal obstruction or progression to cancer. Therefore, when children have symptoms of abdominal pain, digestive disorders, especially changes in bowel habits, bloody stools, etc., parents should take the child to the doctor. Diagnostic methods are based on history, physical examination, colonoscopy or performing a total colonoscopy.
The treatment of colon polyps in children is similar to that in adults, i.e. laparoscopic polypectomy. When performing, the doctor will check the area where colon polyps appear and conduct electrocautery cutting. Each excision can remove 50-60 polyps. This procedure is quite safe so the patient can be discharged immediately after the surgery. Only cases with symptoms of difficulty in hemostasis should be followed up for longer.

In children, due to the well-developed terrain, cases of colon polyp removal rarely recur. Except in the case of familial polyposis, the doctor will need to follow up after laparoscopic polypectomy to avoid complications. In addition, after 6 months of the procedure, the patient should have a follow-up examination and colonoscopy to assess the effectiveness of treatment.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.