This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with MSc Tran Thi Vuong - Doctor of Microbiology - Laboratory Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Hepatitis B is a form of hepatitis caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which is transmitted through blood and genital tract. Hepatitis B affects nearly one-third of the world's population, especially in developing countries. However, among them, there are people who are infected with the B virus and can clear it on their own.
1. Clinical features
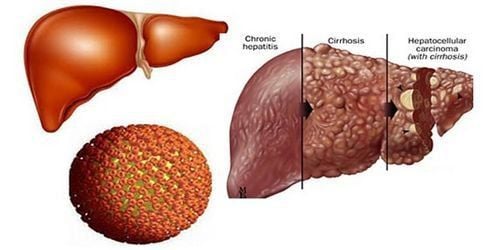
HBV causes both acute and chronic hepatitis. The clinical picture of hepatitis B is very diverse. In acute hepatitis, the disease can manifest from a clinical form without symptoms to a clinical form with typical hepatitis symptoms, sometimes the disease progresses to a severe form of fulminant hepatitis that threatens death. In the chronic phase of hepatitis, the clinical picture varies from an asymptomatic carrier to a chronic hepatitis and then progress to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer.Acute hepatitis Acute hepatitis B has an incubation period of 45-120 days 1 month - 6 months, depending on factors such as viral exposure, route of transmission, co-infection with other hepatitis viruses, and similarity. interaction between virus and host.
Clinical manifestations: low-grade fever, fatigue, restlessness, anorexia, nausea and vomiting. The patient may feel pain and heaviness in the right lower quadrant. Some patients will feel like they have a mild cold, sometimes not knowing they have HBV. Later, some patients may develop jaundice and mucous membranes. From here, the clinical picture can progress in the following directions:
(1) Favorable progress to recovery phase, jaundice gradually decreases, the patient has a better appetite
(2) Recurrence , in rare cases, the disease may recur after complete recovery. Clinical symptoms and biochemical disturbances may be present.
(3) Hepatitis flare-up, severe course, causing patients to be hospitalized, accounting for (0.5-1%) of cases
(4) Chronic conversion, concluding chronic hepatitis B when HBsAg antigens persisting for more than 6 months, clinical symptoms such as fatigue, anorexia, weakness and biochemical disturbances such as elevated liver enzymes persist for a long time.
Chronic hepatitis Most people with chronic inflammation feel completely normal. Chronic hepatitis B is often discovered incidentally through routine physical examination, pregnancy testing, military service, ordering a serological test for hepatitis B virus, or by liver enzymes are increased or the body is weak and tired. The most common symptom of chronic hepatitis is mild fatigue, but infrequently. Some patients with severe chronic inflammation continue to experience acute hepatitis-like symptoms including anorexia, loss of appetite, fatigue, abdominal pain, and jaundice.
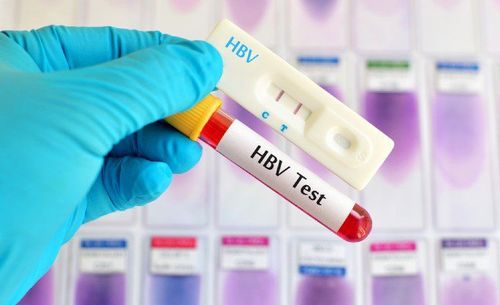
A person is considered chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection when HBV persists in the body for more than 6 months (i.e., consecutive HBsAg test more than twice positive (+) in six months). During this time, the body tries to clear the hepatitis B virus from the body.
In medicine, immunological biomarker tests such as HBsAg (viral B envelope antigen), and Anti-HBc IgM and Anti HBc total (virus B core antibody) tests are used in medicine. check if you have been infected with the virus B, what stage you are, new or old, and test for Anti-HBs (protective antibodies to the B virus) to find out if a person is immune for HBV or not.
2. Hepatitis B virus elimination rate
Elimination mechanism: Hepatitis B virus infection leads to a variety of pathological consequences depending on the host's natural or adaptive immune response. HBV infection can be excluded or persist in the form of progressive or non-progressive liver disease. The combined action of specific and nonspecific immune responses clears HBV infection and produces neutralizing antibodies, anti-HBs. Reactivation of HBV replication in the host cell nucleus is suppressed by the host's humoral and cellular immune responses.Chronic hepatitis B occurs when the body fails to produce a strong response of active immune cells to the HBsAg antigen. Immune cells in the liver do not eliminate HBV-infected liver cells. The process of non-specific inflammatory cell mobilization is maintained, prolonging the chronic inflammation.
Rate of elimination of HBV virus from the infected person's body.
In adults, the HBV clearance rate is about 90% and the chronic HBV carrier rate is 5-10%. It means that after being infected with HBV, the adult's immunity will respond well, generate Anti-HBs antibodies and completely neutralize HBsAg antigens, and completely recover from the disease, accounting for about 90%, only 10% remaining. progression to chronic hepatitis B. Children infected with HBV, most commonly infected with HBV from the mother infected with HBV, the rate of children becoming chronic accounts for 90%, the rate of complete recovery is only 10%. Therefore, in Vietnam and other countries with high rates of HBV infection, the main route of HBV transmission is from mother to child. Therefore, the program to prevent mother-to-child transmission of HBV is the core program in the campaign to reduce the prevalence of HBV infection in Vietnam and these countries. In addition, with chronic HBV infection, there is an annual natural clearance of HBV, which varies from 0.5 to 2% depending on the studies.

The hepatobiliary screening package helps customers:
Assess the liver's ability to work through liver enzyme tests; Evaluation of bile function; vascular nutrition; Early screening for liver cancer; Performing tests such as Total blood cell analysis, blood clotting ability, screening for hepatitis B, C; Assessment of hepatobiliary status through ultrasound images and diseases that have the potential to affect liver disease/exacerbation of liver disease; In-depth analysis of parameters to evaluate hepatobiliary function through laboratory and subclinical tests; the risk of affecting the liver and early screening for hepatobiliary cancer.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.