This is an automatically translated article.
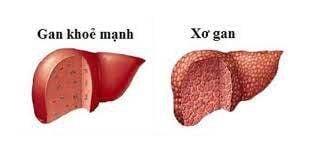
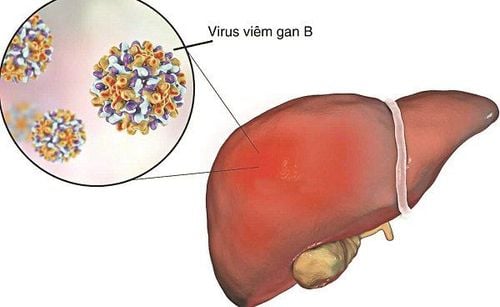
If you test positive for the hepatitis B virus for more than 6 months, this indicates that you have a chronic hepatitis B infection. Patients with chronic hepatitis B infection, including children and adults, require active antiviral therapy and regular monitoring to limit the risk of cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer.
1. Overview of chronic hepatitis B treatment
If a blood test shows that you still have hepatitis B after 6 months, your doctor will prescribe medication to reduce your risk of complications from hepatitis B.Indications for hepatitis B antiviral medication will be determined based on the following factors:
When your immune system is unable to control the hepatitis B virus on its own There is evidence of ongoing liver damage Hepatitis B drugs not only help control viruses but also prevent them from harming your liver, although sometimes they don't help clear the virus completely. Therefore, in certain subjects, the prescription for hepatitis B treatment can last a lifetime.
The main classes of drugs for chronic hepatitis B include the drugs peginterferon alfa 2-a and antivirals:
If your liver is working fairly well, the first treatment given is usually a medicine called peginterferon alfa 2-a. The drug's mechanism of action is to stimulate the immune system to attack the hepatitis B virus and regain control of them. The drug is usually given by injection once a week for 48 weeks. Common side effects include flu-like symptoms, such as fever and muscle and joint pain after you start taking the medicine, although these should improve over time. Antiviral drugs will be given when your liver is no longer working properly or peginterferon alpha-2a is contraindicated. This group of drugs is easier to use due to the form of tablets. Common side effects are feeling tired, vomiting, and dizzy. Details of hepatitis B antiviral drugs approved for use in adults and children are presented in the following sections.
Bệnh viêm gan B do virus mãn tính
2. Hepatitis B antiviral drugs for adults
There are currently five approved antiviral drugs for adults with chronic hepatitis B infection. They are taken as tablets, once a day for 1 year or so or sometimes for life, depending on the liver damage already caused by the virus.Tenofovir disoproxil (Viread) or Tenofovir alafenamide (Vemlidy) is a medicine taken by mouth once a day, with few side effects, for at least a year or longer. This is considered a first-line treatment for people with chronic hepatitis B with very low drug resistance. Entecavir (Baraclude) is a medicine taken once a day, with few side effects, for at least a year or longer. Similar to tenofovir, this is also considered a first-line treatment. Telbivudine (Tyzeka or Sebivo) is a medicine taken by mouth once a day, with few side effects, for at least a year or longer. However, it is a second-line treatment of choice. Adefovir Dipivoxil (Hepsera) is a medicine taken by mouth once a day, with few side effects, for at least a year or longer. However, similar to telbivudine, it is also a second-line agent of choice. At the same time, during the period of taking the drug, the patient must be regularly monitored for renal function. Lamivudine (Epivir-HBV, Zeffix, or Heptadin) is a medication taken by mouth once a day, with few side effects, for at least a year or longer. However, the drug is no longer commonly used because of its lower antiviral activity, most people develop resistance within a year or two, so it has been replaced by the newer drugs mentioned above.
Thuốc Zeffix kháng virus viêm gan B cho người lớn
3. Hepatitis B antiviral drugs for children
Unlike adults, chronic hepatitis B infection is considered a mild disease in children and adolescents. Most children have no obvious signs or symptoms, and they grow and develop as healthy as other children without any physical limitations.However, all children and adolescents with chronic hepatitis B infection should be seen regularly by pediatric hepatologists to see if they are indicated for treatment. The best time for each visit is every six months but can be more or less depending on the situation. During these checkups, children not only have a physical examination, blood tests, but also have additional imaging tools to help assess liver damage such as ultrasound, FibroScan [Transient tomography] or CT scan.
On the contrary, in very rare cases, children and adolescents may need earlier intervention and specific treatment if evidence of organic liver damage has been documented, in order to limit hepatic sequelae. Castle.
There are currently 3 approved antiviral drugs for children with hepatitis B :
Entecavir (Baraclude) is a medicine taken once a day, with few side effects, for at least a year or longer. This is considered a first-line treatment. Tenofovir disoproxil (Viread) is a medicine taken by mouth once a day, with few side effects, for at least a year or longer. Similar to entecavir, this is also considered a first-line treatment for children 12 years of age and older. Lamivudine (Epivir-HBV, Zeffix, Heptadin) is a medication taken by mouth once a day, with few side effects, for at least a year or longer. However, this is an older generation antiviral drug that leads to very high drug resistance. Therefore, this drug should only be considered a second-line treatment.
Thuốc Entecavir
4. Clinical guidelines for hepatitis B antiviral therapy
All patients with an indication for hepatitis B antivirals are scheduled to see their hepatologist every six months or more, depending on your health and medical condition. During these follow-up visits, you should be checked for the following:General health and liver and biliary function, digestion Blood microbiological test for hepatitis B virus Liver enzyme test (ALT/ AST) in serum Blood tests to screen for liver cancer (AFP) Imaging facilities of the liver (ultrasound, CT scan, or FibroScan) The fundamental goal of these visits is to monitor patients often regularly, early detection to actively treat from the beginning because the risk of cirrhosis, liver failure or liver cancer in this subject is very high. If these things are done well, coupled with the ability to respond to drugs effectively, patients can lead a healthy life almost as normal.
In addition, all sexual partners or family members who have close contact with an infected person should also be tested for hepatitis B and vaccinated if necessary.
Xét nghiệm vi sinh trong máu
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital has Hepatobiliary Screening packages, which help detect Hepatitis Virus at an early stage even when there are no symptoms. In addition, the comprehensive hepatobiliary screening package helps customers:
Evaluate the liver's ability to work through liver enzyme tests; Evaluation of bile function; vascular nutrition; Early screening for liver cancer; Perform tests such as Total blood cell analysis, blood clotting ability, screening for hepatitis B, C Assessment of liver and biliary status through ultrasound images and diseases that are at risk of affecting liver disease / liver disease. more severe liver disease In-depth analysis of parameters to evaluate hepatobiliary function through laboratory and subclinical tests; the risk of affecting the liver and early screening for hepatobiliary cancer
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: hepb.org; nhs.uk; mayoclinic.org