This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master. BSCK II Phan Thi Minh Huong - Gastroenterologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Da Nang International General Hospital.Hepatitis B is one of the dangerous diseases and is considered a "silent killer" because the symptoms are not clear but it leaves many consequences for the patient. The following articles are frequently asked questions by patients about hepatitis B that the World Health Organization (WHO) has answered. Properly understand this disease to have the right prevention and prevention methods.
1. What is Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a very serious liver infection. The disease is potentially life-threatening when acquired. Hepatitis B is caused by the hepatitis B virus.This is the most serious type of viral hepatitis among liver diseases. This disease is also one of the major problems for world health. Hepatitis B is also a cause of liver cancer and cirrhosis.
This disease can become chronic and extremely dangerous. The hepatitis B virus can always be present in the blood and body fluids of a person with chronic hepatitis B infection.
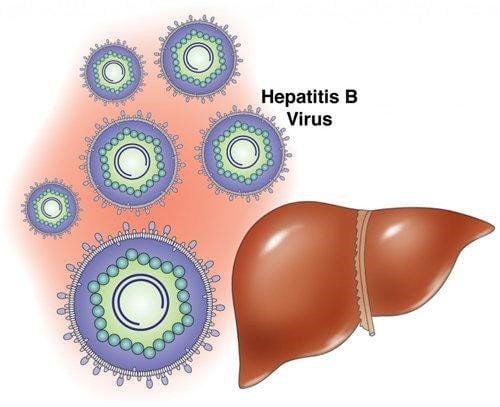
Bệnh viêm gan B và virus viêm gan B
2. How is hepatitis B spread?
Hepatitis B is a very contagious virus. Its infectivity is 50 to 100 times higher than that of HIV. This virus is transmitted through contact with blood or body fluids of an infected person, especially a chronically ill person.One of the most dangerous and common ways of hepatitis B infection is mother-to-child transmission. Babies born to mothers with chronic hepatitis B have a 90% chance of chronic infection.
Specifically, transmission routes are as follows:
Vertical transmission is transmission from mother to child: Most occur during the perinatal period (from the 28th week of pregnancy to the 7th day after birth) or In the first month after birth, this is the most common and important mode of infection. Horizontal transmission by contact: Transmission usually occurs in homes, children's hospitals, schools and kindergartens,... Mechanism of transmission may involve contact with wounds and abrasions. small in the skin, mucous membranes with bleeding, or exudate from the wound. The hepatitis B virus can also be transmitted by contact with saliva through bites and other scratches on the skin as well as by chewing food before giving it to a child. Transmission through injection and blood transfusion: Unsafe injections are the main route of transmission of hepatitis B virus and other diseases (Hepatitis C, HIV) in many countries. Transmission during sex: When there is abrasion, contact with blood or other body fluids
3. How is hepatitis B treated?
Currently, there is no cure for chronic hepatitis B in the world. Current treatments only help control and inhibit the replication of the virus, return the virus to a state of inactivation, prevent complications, and restore liver damage. Some new methods such as blood transfusion with ozone, virus filtration, targeted therapy, ... However, this is a very contagious disease, so it is important to prevent and prevent hepatitis B from spreading. is extremely important, in which vaccination is the best way today. Children as young as 1 day old can be vaccinated against hepatitis B to prevent infection. This is also the most optimal choice to deal with this dangerous disease and its consequences.4. Estimated annual burden of chronic hepatitis B due to mother-to-child transmission in Vietnam?
In Vietnam, the rate of pregnant women infected with hepatitis B virus is 10%, with this number, it is estimated that each year Vietnam will have 54,655 babies infected with this dangerous virus from their mothers.The rate of hepatitis B transmission from mother to child during pregnancy is not more than 2%, but during labor up to 90% of cases of hepatitis B virus transmission from mother to baby. If the mother is infected with HBV and has HBeAg (+), the infant has a 95% chance of becoming infected if not receiving immunoprophylaxis. In case the mother is infected with HBV and HBeAg (-), the infection rate for the baby is 32%
Even among children infected from the mother, there is a 90% chance of chronic hepatitis B virus infection. These children are at high risk for complications from chronic hepatitis B and can spread it to others, increasing the number of infected patients.
5. How can hepatitis B be prevented?
Hepatitis B can be prevented by vaccines, which are very effective and widely used vaccines to prevent hepatitis B. Hepatitis B vaccine is usually given to infants within 24 hours of birth to ensure safety and effectiveness.In addition, we should also apply other reasonable precautions to prevent hepatitis B such as not sharing toothbrushes and razors with others, especially patients with hepatitis B. Hepatitis B, regular screening for hepatitis B.
The liver and biliary screening is very important. It allows you to know the potential risks of liver disease in advance and have a treatment plan early. Currently, screening packages have been deployed at Vinmec International General Hospital, there are two standard and advanced packages for you to choose from. Both of these screening packages help customers diagnose hepatitis and plan treatment early, before the disease gets worse.
Loại virus nguy hiểm cho gan
6. Where is the hepatitis B vaccine produced in Vietnam?
All Vietnamese vaccines used under the National Program on Expanded Immunization must meet international quality and safety standards. In Vietnam, hepatitis B vaccine is produced domestically at the No. 1 Vaccine and Biological Company. Vietnam's vaccines have met the standards and have been put into common use since 1997.All vaccines are tested by the Ministry of Health and licensed for use by the National Institute of Vaccines and Medical Biologicals.
7. Why is it important to vaccinate newborn babies against hepatitis B within the first 24 hours after birth?
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that infants be vaccinated against hepatitis B within the first 24 hours after birth. Vaccination is the most effective and safest way to prevent hepatitis B (WHO)In Vietnam, 10-12% of pregnant women have chronic hepatitis B, so the transmission of hepatitis virus B from mother to child is the cause of the increasing incidence of this virus.
The sooner the hepatitis B vaccine is given, the more effective it is. Within the first 12-24 hours after birth, the vaccine is able to prevent 85-90% of cases of mother-to-child infection, this is a competition between the replication of hepatitis B virus and antibodies against hepatitis B virus. neutralize the virus present in the body. The preventive effect will decrease gradually with each day and is not reached if the injection is given after 7 days. Early vaccination against hepatitis B not only protects against mother-to-child transmission, but also helps infants to be protected by other family members.
In addition to an early injection of hepatitis B vaccine to create active immunity, children of HBsAg-positive mothers also need 1 injection of Hepatitis B Immune Globulin (HBIG), a passive immunity that helps neutralize the virus. withdraw hepatitis B while waiting for the effects of the vaccine. Two injections at 2 different sites within 12-24 hours after birth.
And to prevent infection with this dangerous virus, WHO recommends hepatitis B vaccination within the first 24 hours after birth and 2 additional doses within the next 1 year.
Vắc-xin viêm gan B
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.