This is an automatically translated article.
Posted by CKI Doctor Nguyen Duc Tho - Department of Surgical Anesthesia - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalLocal anesthetics act on all central nerve fibers (sensory, motor) and autonomic nerves, in turn from small to large fibers depending on the concentration of the drug. The order of loss of sensation is pain, cold, heat, shallow touch, then deep touch, and finally locomotion. When the drug is exhausted, the effect reverses.
1. Definition of anesthetic
Anesthesia is a drug capable of inhibiting the transmission of nerve impulses from the periphery to the center, causing loss of sensation (feeling of pain, heat, cold, etc.) of an area of the body. In high doses, the drug inhibits motor function.
2. Effects of anesthetics
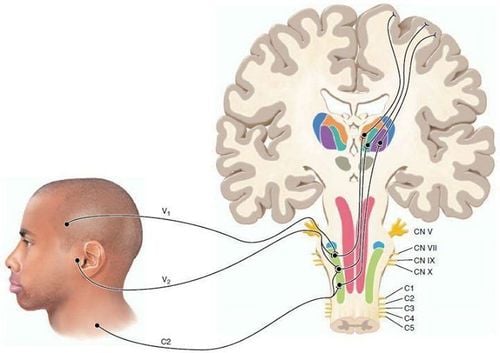
2.1 Local effects Local anesthetics act on all central nerve fibers (sensory, motor) and autonomic nerves, in turn from small to large fibers depending on the concentration of the drug. The order of loss of sensation is pain, cold, heat, shallow touch, then deep touch, and finally locomotion. When the drug is exhausted, the effect reverses.
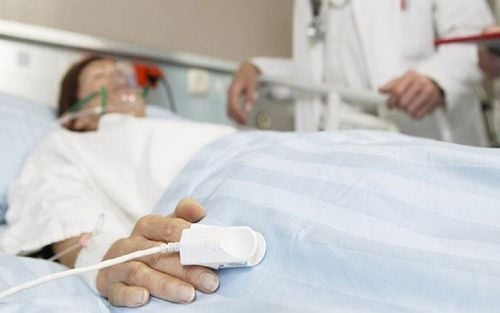
2.2 Systemic effects Central nervous system inhibitory effect: The earliest appearance with the inhibitory center should cause signs of excitement, restlessness, anxiety, muscle tremors, convulsions, disorientation. Inhibition of nerve conduction - muscle causes myasthenia gravis, respiratory paralysis. Smooth muscle relaxation due to ganglion paralysis and direct action on smooth muscle.
Effects on the heart - vessels: Due to the effect of "stabilizing the membrane", local anesthetics reduce excitability, conduction and contractility of the myocardium. May cause arrhythmia, even ventricular fibrillation. On the pulse, most anesthetics cause vasodilation and hypotension (except cocaine).
Thuốc gây tê tác dụng đến hệ thần kinh trung ương của người bệnh
3. Classification of anesthetics
Current anesthetics are classified according to their basic chemical class. Typically, local anesthetics are classified into three groups:
Esters: Includes butamben picrate, procaine, benzocaine, chloroprocaine, cocaine, proparacaine and tetracaine. These drugs are derivatives of para-aminobenzoic acid Amides class: Includes dibucaine, etidocaine, lidocaine, bupivacaine, mepivacaine, prilocaine and ropivacaine. Amides are derivatives of aniline Other: In addition, pyclonine and pramoxine are not included in the above two subclasses and can be used in patients allergic to amides or esters. Dosage and usage:
3.1 Procaine ester structure anesthetic (Novocain) Anesthesia: There is little effect of surface anesthesia due to less permeation of the mucosa, mainly used for deep anesthesia, injectable anesthetic and often must be combined with a vasoconstrictor to prolong the anesthetic effect.
On motor nerves: Reduces motor function such as reducing nerve-muscle conduction, high doses cause muscle paralysis.
On the autonomic nervous system: Reduces vegetative functions such as bradycardia, lowering blood pressure...
On the cardiovascular system: The drug has antiarrhythmic effects similar to quinidine because it reduces excitement, contraction strength and decreased intrinsic conduction. The drug causes vasodilation, reducing cardiac contractility, so it lowers blood pressure slightly.
For injectable anesthesia, a dose of 350-600 mg of procaine hydrochloride solution of 0.25 or 0.5% can be used.
Peripheral nerve blockade, the usual dose is 500mg of procaine hydrochloride with a solution of 0.5% (100ml), 1% (50ml) or 2% (25ml). A maximum dose of 1000mg may be used.

Procain là một trong các loại thuốc gây tê có cấu trúc ester
To prolong the effect of procaine in cases of injectable anesthesia or peripheral nerve block, adrenaline and procaine solution can be mixed to give a final concentration of adrenaline of 1/200000 or 1/100,000.
Other indications: Prevention and treatment of aging and some cardiovascular diseases: Arrhythmia, vasospasm, vascular sclerosis, vasculitis...
Other drugs Benzocaine: Slow absorption, little toxicity. Can be used directly on wounds and ulcers. Commonly used preparations are gels, ointments 6-20%
Tetracaine: The anesthetic effect is about 16 times stronger than procaine and also 10 times more toxic than procaine. Medicines can be used to numb the spinal cord. However, due to its high toxicity, tetracaine is mainly used for surface anesthesia and is combined in mouthwash, lozenges... to relieve pain, reduce cough, and fight inflammation.
Cocaine: It has a strong anesthetic effect on mucous membranes and causes vasoconstriction, so it is used as an anesthetic in ophthalmology and dentistry. However, due to nerve stimulation causing hallucinations and addiction, it is rarely used today.
3.2 Anesthetic with amide structure Lidocaine Local anesthetic of the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth, throat, trachea, esophagus and urinary - genital tract: Apply a solution of lidocaine hydrochloride directly (2% - 10%). The maximum safe dose for local anesthesia in an adult weighing 70 kg is 500 mg lidocaine.
Anesthesia: Inject directly into the tissue the injection of lidocaine hydrochloride (0.5% - 1%); without adding adrenaline: dose of lidocaine up to 4.5 mg/kg; when adrenaline is added: this dose can be increased by a third (7 mg/kg).
Thuốc gây tê Lidocain dạng xịt
Regional block anesthesia: Subcutaneous injection of lidocaine hydrochloride solution with the same concentration and dose as the layer anesthesia.
Nerve block anesthesia: Injection of lidocaine solution into or near nerves or peripheral nerve plexuses has a broader anesthetic effect than the techniques mentioned above. For blockade for 2 - 4 hours, lidocaine (1% - 1.5%) can be used at the dose recommended above.
Acute treatment of ventricular arrhythmias: To avoid distribution-related loss of effect, administer a loading dose regimen of 3 - 4 mg/kg over 20 - 30 minutes, eg, with an initial dose of 100 mg, followed by a subsequent dose follow for 50 mg dose, every 8 minutes for 3 times; Thereafter, steady-state plasma concentrations can be maintained by infusion of 1 - 4 mg/min, to replace drugs that are eliminated by hepatic metabolism. The time to reach steady state lidocaine concentrations is 8-10 hours.
Other drugs Bupivacaine: The anesthetic effect is similar to lidocaine but stronger, the duration of action is slower and longer lasting, can last up to 12 hours if combined with the vasoconstrictor adrenaline or noradrenalin. Therefore, bupivacaine is suitable for prolonged surgery. High doses of the drug cause muscle relaxation and inhibition of movement. The main indications are conduction anesthesia, spinal anesthesia.
Mepivacaine: The anesthetic effect is similar to lidocaine but not superficial and about 2 times weaker than lidocaine. Effects appear faster and last longer. The drug is less likely to cause varicose veins, so the anesthetic may not need to use a vasoconstrictor. The drug is mainly used for injectable anesthesia and conduction anesthesia.
Etidocaine: Has a longer duration of action than lidocaine 2-3 times, stronger anesthetic activity. Commonly used injectable anesthesia and conduction anesthesia (not using spinal anesthesia). Drugs that cause central nervous system stimulants, high doses can cause convulsions should not be used in patients with epilepsy.
4. Possible complications when using anesthetics
4.1 Systemic complications Neurological complications, due to the drug absorbed into the circulation with high concentrations, causing neurological manifestations (nausea, vomiting, disorientation, jerky movements, respiratory paralysis). Cardiovascular complications, commonly conduction disturbances and ventricular arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation

Thuốc gây tê có thể gây ra tình trạng buồn nôn và nôn ở người bệnh
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
MORE
Differentiate between epidural and spinal anesthesia Types of anesthesia commonly used Some common complications of anesthesia and anesthesia