This is an automatically translated article.
Prenatal paternity DNA testing can determine if a man is the father of a fetus before he is born. Modern medicine is increasingly developing, in addition to accurate fetal ultrasound, blood DNA testing is also performed early. If you want to do this, from the 14th week of pregnancy, you can ask your doctor to support this desire. Currently, prenatal DNA testing is usually done by one of two methods: Amniocentesis and prenatal blood test.
1. When can a pregnant woman have a blood DNA test?
Prenatal paternity testing is a sensitive topic because of ethical issues including the risks of invasive testing. Many doctors have refused to perform prenatal paternity testing, especially if confirming the identity of the baby's father is the only reason to perform the test.
If prenatal paternity testing is done and the test results are unsatisfactory, the woman may not want to continue the pregnancy. If you're pregnant and want to consider getting a prenatal paternity test, talk to your doctor or midwife before doing it. They can help the mother review the issues involved, as well as advise on the risks to the mother and fetus.
How long it takes to have a pedigree DNA test during pregnancy depends on the type of test you choose, but can generally be done as early as 8 weeks without any risk to the mother or baby.
Women should choose a non-invasive prenatal DNA test to make sure there is no risk of miscarriage or any other risk to themselves or their developing baby. Invasive methods require further fetal development before they can be performed.

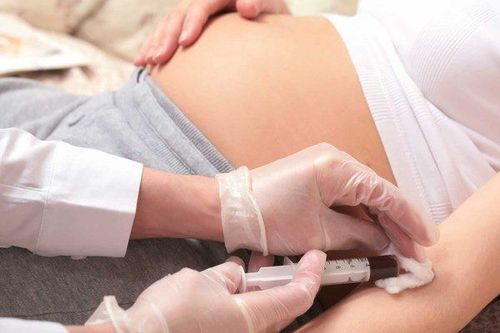
Xét nghiệm ADN huyết thống trong khi mang thai có thể được thực hiện sớm nhất vào tuần thứ 8
2. Types of prenatal DNA tests
There are three types of DNA tests that can be done while pregnant; Noninvasive prenatal DNA testing (NIPT), amniocentesis, and chorionic villus sampling or chorionic villus sampling (CVS). Testing the fetus for Down Syndrome can also be done using all three methods.
Non-invasive prenatal DNA test NIPT : DNA is collected from the mother and father to determine the bloodline. This DNA is then analyzed and compared with the baby's DNA found in the mother's blood. Amniocentesis: This is an invasive DNA test done between 14 and 20 weeks. An amniocentesis will be performed under ultrasound guidance, and amniotic fluid will be drawn through the abdominal wall with a very fine needle. , then this amniotic fluid sample will be taken for DNA testing. Normally, the amount of amniotic fluid that needs to be taken is 15-30 ml. Your body will regenerate the amount of amniotic fluid removed and your baby will not be short of amniotic fluid after the test. Some women will have mild abdominal pain after amniocentesis, the doctor will give oral medication and the pregnant woman should rest on the day of amniocentesis. The next day the abdominal pain will subside. The most important complication and risk of amniocentesis is that it can cause miscarriage, rupture of membranes, and infection. According to recent studies, the risk of miscarriage with amniocentesis is 1/500 (meaning 1 in 500 women who have amniocentesis will have a miscarriage).
Placental or chorionic villus test: This test is done between 10 and 13 weeks. A chorionic villus biopsy is the removal of a small amount of placental tissue from the uterus. The placental sample will be obtained with a needle or catheter through the abdomen. During this procedure, you will be numbed to relieve pain and stress. After the procedure, you may experience light vaginal bleeding. The risk of miscarriage with the procedure is about 1 in 500.
3. Accuracy of prenatal pedigree DNA test

Hầu hết các kết quả từ kết quả NIPT là chính xác 99,9%
Results of non-invasive prenatal DNA testing vary, depending on sample quality for pedigree DNA testing.
Most results from NIPT results are 99.9% accurate. The accuracy of amniocentesis DNA tests is about 99% accurate for checking a fetus for Down Syndrome and trisomy 18 and 98% for neural tube defects. The chorionic villus sampling test or chorionic villus biopsies detects genetic disorders and chromosomal abnormalities and has a high accuracy rate of 98 to 99%.
Experts say that to determine the bloodline of the child before birth, amniocentesis for DNA testing is more positive. The nature of amniocentesis is to cause bleeding between the mother and the baby and the only factor that can endanger both the mother and the fetus is the mother carrying the Rh blood type. If a mother with this blood type is prone to miscarriage, amniocentesis should not be performed.
4. Time to get prenatal DNA test results
Because there are 3 types of prenatal DNA tests, the time it takes to get results varies greatly with each test. It can usually take about 3 to 12 weeks to see results.
For the amniocentesis test, it can take from three days to three weeks to see the results. If you only test for one type of DNA or bloodline abnormality, the results will often be faster than when you check for many different problems. There is a chance that the results may take longer so you don't have to worry too much. Sometimes it can take a while for the growing cells to get accurate results.
The results of a chorionic villus test or chorionic villus biopsy may be available immediately or within five to 10 days. If you want to be tested for a specific disorder, you can wait a little longer for the results.
In addition to the need for prenatal gene testing to determine the blood relationship, many people want to use prenatal gene testing services to determine the risk of the fetus having genetic diseases for timely treatment. Many hospitals are now applying this method to identify many genetic diseases for timely treatment, even after the baby is born.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: NHS.UK