This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Nguyen Anh Tu - Doctor of Obstetric Ultrasound - Prenatal Diagnosis - Obstetrics Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Prenatal diagnostic testing provides important information to expectant parents about the presence of genetic disorders in their unborn baby.
1. What is a genetic disorder?
Inherited disorders caused by genes are called gene mutations. Genetic disorders include sickle cell anemia, cystic fibrosis, Tay-sach disease and more. Most cases of children with these disorders are caused by both parents carrying the same abnormal gene.2. What is prenatal genetic testing?
There are two types of prenatal tests to check for genetic disorders including:
Prenatal screening tests : These tests show the baby's risk of having an aneuploidy mutation and certain other disorders. Prenatal diagnostic tests: These tests give the most accurate results possible as to whether the fetus actually has an aneuploidy mutation or other specific genetic disorder based on the test that the pregnant woman has. performance request. This test examines cells obtained from the fetus or placenta through amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS). Both prenatal screening and diagnostic testing are recommended for all pregnant women.
3. What is amniocentesis?
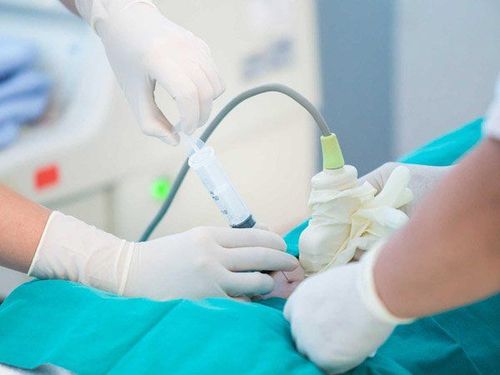
4. What is a chorionic villus biopsies?
For a placental biopsy, a tissue sample of the placenta. Performing a biopsy is superior to amniocentesis in that it can be done earlier than amniocentesis, between 10 and 13 weeks of gestation. The risk of miscarriage from a chorionic villus sampling is slightly higher than the risk of a miscarriage. muscle from amniocentesis.5. Genetic diagnosis before pregnancy?
Pre-pregnancy genetic diagnosis is available for couples undergoing in vitro fertilization (IVF) to become pregnant and who are at high risk for pregnancy with genetic and chromosomal problems. . Before transferring the embryo into a woman's uterus, it is checked for genetic disorders and mutations. Only embryos that do not test positive for the disorder are transferred into the uterus.6. How are cells analyzed in prenatal diagnostic testing?
Several technologies are used in prenatal diagnostic testing. Your obstetrician or geneticist can assess what information to look for and choose the test that best suits your condition:Karyotype test - Chromosomes: Detects chromosomes missing, redundant or damaged by taking pictures of chromosomes and arranging them in order from largest to smallest. Chromosome results are available 3 weeks after sampling. Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH): This technique is used to detect aneuploid mutations including chromosomes 13-18-21 and sex chromosomes X and Y. Results of this technique faster than traditional chromosomal assembly (usually after 1 week). Positive results are confirmed with chromosomal analysis. Microarray Chromosome Analysis: This test looks for abnormalities to a few dozen to 100 times smaller than the Karyotype test, which can find a variety of chromosomal problems, including aneuploidy mutations, complete set of chromosomes. It can find chromosomal problems that chromosomes miss. Results will be returned within 7 days. DNA testing: Specific genetic mutation testing is available upon request. If you and your partner are carriers of the gene that causes cystic fibrosis, you can expect prenatal diagnostic testing for a particular mutation.

7. What do the different results of prenatal diagnostic tests mean?
Most of the time, the result of a diagnostic test is usually negative (normal). A negative result does not rule out the possibility that the fetus has a genetic disorder. It just shows that the fetus has no specific disorder that is examined.If the diagnosis is positive (indicating the fetus has the tested disorder), your obstetrician or geneticist will explain the results and advise you on your options and possibilities. power. A specialist in the disorder can help understand life expectancy at birth, available treatments, and the care requirements your baby will need.
Support groups, counselors and social workers can also listen to concerns and answer questions. A pregnant woman may also have other tests such as an in-depth ultrasound to get more details about the defect
8. What should be considered when deciding to have prenatal genetic testing?
Pregnant women have the right to choose whether or not to have prenatal testing. Some parents want to know in advance if their baby has a genetic disorder to take the time to research the disorder and plan the medical care he or she will need. If the disorder is really severe and the life expectancy is short, nursing care for the baby should be prepared. Some parents may decide to terminate a pregnancy under certain circumstances. Other parents don't want this information before the baby is born and decide not to get tested at all.Testing done early gives parents more time to make a decision if the result is positive. If termination of pregnancy is considered, it is safer to do so during the first 13 weeks of pregnancy.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Article referenced source: Acog.org