This is an automatically translated article.
Cassava is known as a vegetable in the main ingredient of many diets around the world. The nutritional composition of cassava brings many health benefits, but if processed improperly, it can have side effects caused by cassava.
1. Learn about cassava vegetables
Cassava or cassava is a root vegetable. The cassava tuber is the underground part of the cassava shrub, whose Latin name is Manihot esculenta. Like potatoes and sweet potatoes, cassava roots are also a major source of calories and carbs for humans.
So, can cassava leaves be eaten? People living along the banks of the Amazon River in South America were growing and consuming cassava hundreds of years before Christopher Columbus first got there.
Today, more than 80 countries across the tropics grow cassava, and it is a staple in the diets of more than 800 million people around the world. Cassava is favored because it is a hardy, drought tolerant crop that does not require much fertilizer, although the plant is very susceptible to bacterial and viral diseases.
In addition, cassava root is also known as a raw material, used in the production of tapioca and similar products.
People who are prone to food allergies often benefit from using cassava in their daily food preparation, because the nutritional composition of cassava does not contain gluten.

Sắn được biết đến như một loại rau trong thành phần chính của nhiều chế độ ăn kiêng
2. What are cassava vegetables used for?
Many people wonder is it good to eat cassava vegetables? Cassava is a rich, affordable source of carbohydrates. It can provide more calories per acre of crop than other grains, which makes cassava a very useful crop in developing countries.People prepare and eat cassava in different ways in different parts of the world, in which cooking methods such as baking and boiling are the most common methods. In some places, cassava is often fermented before use.
It is essential to peel the cassava and never eat it raw. Cassava contains dangerous levels of cyanide unless cooked thoroughly before eating. Dishes that you can make from cassava include:
Bread, which can contain only tapioca or both cassava and flour Chips Mashed cassava slices Sliced cassava cakes soaked in coconut milk Tapioca cakes Coconut milk cassava In addition to people eat cassava, people also use cassava to make some foods made from cassava such as:
Making tapioca flour, a common dessert Producing starch and flour products, which people can be used to make gluten-free bread. Feed to animals... Scientists have finally found an ingredient that can replace high-fructose corn syrup with tapioca starch. The researchers also hope that cassava could be a source of alcohol that manufacturers use to make polystyrene, PVC and other industrial products.

Bột sắn dây được dùng nhiều trong các món tráng miệng
3. Benefits and nutritional composition of cassava
Cassava is a calorie-rich vegetable, containing many carbohydrates, important vitamins and minerals. Cassava also provides vitamin C, thiamine, riboflavin and niacin. Cassava leaves, which can also be eaten if cooked or dried in the sun, can contain up to 25% protein. However, cassava capital stock · is evaluated as not bringing much nutritional value like many other vegetables and tubers.
Cassava is a source of resistant starch, which scientists say can boost one's gut health by helping to feed beneficial bacteria in the gut. The source of resistant starch in cassava is quite rich and their properties are similar to soluble fiber. Consuming cassava foods high in resistant starch provides health benefits. First of all, resistant starch will provide beneficial bacteria to the body's gut system, while helping to reduce inflammation and promote digestive health. What's more, resistant starch also has the potential to improve metabolism, reducing the risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes.
Nutritional composition of a bowl of raw cassava is usually assessed as follows:
Calories: 330 kcal Protein: 2.8 grams Carbohydrates: 78.4 grams Fiber: 3.7 grams Calcium: 33.0 mg Magnesium: 43.0 mg Potassium: 558.0 mg Vitamin C: 42.4 mg Thiamine, riboflavin and niacin Cassava contains only small amounts of protein and fat. Therefore, people who use cassava as a staple in their diet may need to eat extra protein or take protein supplements to avoid malnutrition.
4. Is cassava poisonous?
We should not eat raw cassava because it contains natural cyanide forms, which are very toxic when ingested. However, when soaked and cooked, this compound becomes harmless to human health.
Besides, eating cassava raw or improperly processed can lead to serious side effects. Even in places where cassava is a well-known part of the diet, reports have identified a number of dangers from eating cassava and absorbing too much active cyanide, including:
Paralyzed legs in children Children Low iodine content Increased risk of goiter
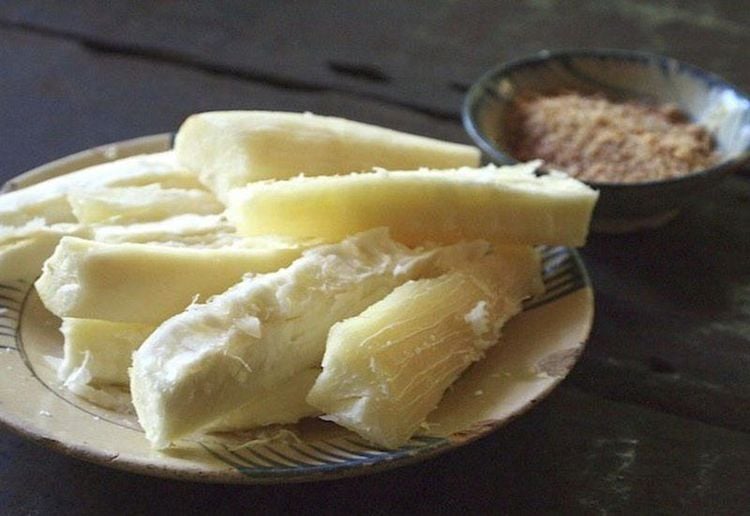

Sắn sống hoặc chế biến sai cách có thể gây ra nhiều tác dụng phụ nghiêm trọng
Not only contains natural cyanide, cassava can also absorb pollutants from the area where the tree is grown such as near factories, roads. When we eat cassava these substances can be absorbed and transmitted to humans including:
Trace metal elements Pesticides or herbicides Due to the cyanide content, people must cook cassava very carefully. First, peel the cassava tubers and slice them. Then boil, bake or fry until tender. Cassava cooking water you need to throw away and should not eat.
5. Cassava processing can reduce nutritional value
Processing by calling the peel, chopped, cooked will significantly reduce the nutritional value that cassava brings. This could be explained by the loss of many water-soluble vitamins and minerals during processing, as well as most of the fiber and resistant starch. Therefore, processed cassava has a lower nutritional value than fresh cassava.
For example, 28 grams of tapioca pellets provide only a small amount of minerals remaining mostly calories. Or boiling cassava is a proven cooking method that retains most of the nutrients. However, vitamin C is not effective, because they are quite sensitive to temperature and water evaporation.
In addition to eating directly, there are now products processed from cassava such as tapioca and tapioca, which are safe to use without pre-cooking. Cassava is a versatile, flavorful food and an important source of nutrients and energy, especially in the tropics. Cassava is similar to other types of potatoes, tapioca starch can be used to make gluten-free baked goods. As long as care is taken when handling, cassava can be a beneficial addition to the diet. Scientists are currently mapping the genetic makeup of cassava. They hope to be able to use this information to breed superior, more nutritious cassava plants that are easier to market and more resistant to disease.
Once you understand the nutritional composition of cassava as well as how to process cassava safely, you can add cassava to your daily diet or process cassava in different styles, to suit your preferences. individuals and family members.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: healthline.com - medicalnewstoday.com