This is an automatically translated article.
Article written by MSc Nguyen Van Huy - Emergency Department - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital
Traumatic brain injury is a condition in which the patient has damage to the skull and other structures inside the skull due to strong enough trauma causes, which can be a high fall, traffic accident, daily life accident, scuffles, and can occur at any age.
In the United States: about 30 million people are injured each year in the emergency department.
In Vietnam: no official nationwide statistics have been published yet. According to statistics of the Ministry of Health from 2010 to 2020. Traumatic brain injury is one of the top 10 causes of death in Vietnam.
I. How is traumatic brain injury divided?
1.A brief overview of anatomy related to traumatic brain injury The skull consists of 2 main parts: the base of the skull and the dome of the skull. The base of the skull has 3 layers: the anterior - middle - posterior cranial layers. The anterior cranial layer is made up of the frontal bone in front, the ethmoid bone in the middle, and the orbital bone on both sides. The middle cranial layer consists of the pituitary fossa in the middle, the two sides are the temporal fossa and the maxillary sinus. The posterior cranial layer is the posterior cerebellar fossa and the occipital bone, the occipital fossa. The dome of the skull is a large bony box, inside it is in contact with the dura mater and contains 2 cerebral hemispheres. The outer surface of the cerebral hemisphere has 3 membranes, in order from outside to the dura, arachnoid and chorionic. Composing the compartments are: the epidural space, the subdural space, and the subarachnoid space. The dura covers the inner surface of the skull and is attached to the bones at the crescent of the brain, except for one area that is easily dissected, the parietal temporal region. Injury to the skull often causes tearing of the middle meningeal artery, causing bleeding and dissection of the dura at this parietal temporal site. The dura mater is separated into the septum: the cerebellar tentacle, the cerebellar crescent, the pituitary tentacle. The arachnoid consists of 2 leaves attached to each other, between the dura and the arachnoid there is a subdural space. The chorionic membrane covers the outer surface of the brain parenchyma, has many blood vessels, between the arachnoid and the choroid is a subarachnoid space containing cerebrospinal fluid.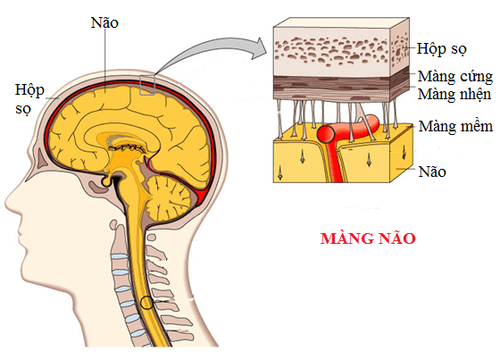
Divided according to the severity of clinical trauma, there are 3 levels according to the Glasgow scale:
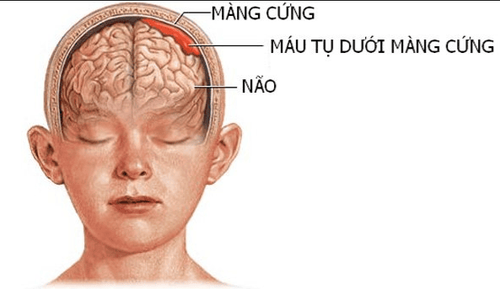
Mild traumatic brain injury when Glasgow score 12-13 points Moderate traumatic brain injury when Glasgow 8-12 score Traumatic brain injury severe and very severe when glasgow is less than 8 points Or can be divided according to specific lesions of each case such as: concussion, epidural hematoma, subdural, brain contusion...
When the patient has traumatic brain injury, the symptoms and initial manifestations of traumatic brain injury in each specific patient are more or less different depending on the degree of traumatic brain injury caused by the trauma mechanism, need to must be detected immediately, detected early, detected sufficiently to ensure the safety of the patient during emergency and subsequent treatment at the hospital.
II. Early clinical symptoms of traumatic brain injury
Symptoms and manifestations of traumatic brain injury usually manifest through two stages as primary lesions and secondary lesions. In which, the primary injury is the injury that occurs immediately after the accident, as soon as the traumatic brain injury occurs, is the earliest injury, including damage at the location where the hard object hits the head (when the head is fixed). and inertia-related injury from shaking or twisting of the skull (moving head).
The mechanism of causing severe traumatic brain injury includes direct impact or blow to the head. Depending on the place of impact, depending on the speed of the injury and depending on the cause of the injury, it will lead to skull deformity or craniofacial fissure and damage to the inside of the skull.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.