This is an automatically translated article.
The article was consulted with Specialist Doctor I Tran Quoc Vinh - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Department of Resuscitation - Emergency - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Circulatory arrest is a medical emergency that must be restored to circulation quickly. Prolonged circulatory arrest will cause irreversible brain damage, which can cause sequelae after restoring circulation. Along with chest compressions, airway clearance, breathing, the use of adrenaline in emergency circulatory arrest is very important.
1. What is circulatory arrest?
Circulatory arrest is a condition in which the heart stops supplying blood to the whole body, especially vital organs such as the brain, coronary circulation, lungs... There are 4 basic states of circulatory arrest that is vibration. ventricular tachycardia, pulseless ventricular tachycardia, asystole, and pulseless electrical activity.Circulatory arrest can occur suddenly on a perfectly healthy heart such as in accidents caused by anaphylaxis, electric shock, drowning, multiple trauma...
But circulatory arrest can also be a consequence. the end result of a chronic end-stage disease such as heart failure, kidney failure, cancer, cirrhosis...
In medicine, doctors also use some other terms to refer to emergency cessation Circulatory system such as:
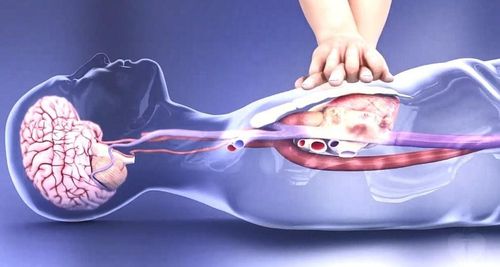
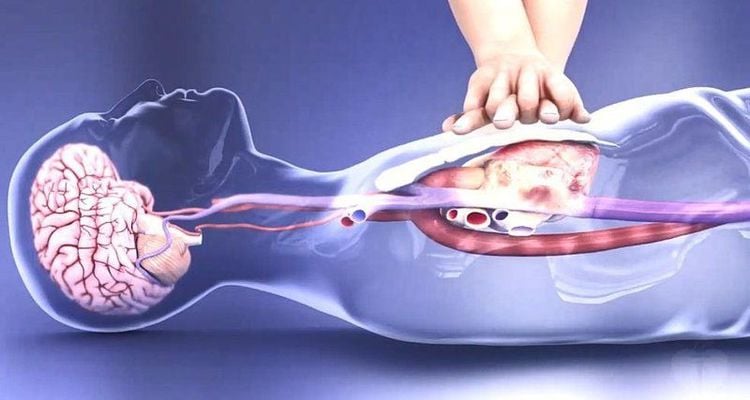
Cardiopulmonary arrest emergency Resuscitation clinical death Cardiopulmonary resuscitation Cardiopulmonary resuscitation... Normal cerebral blood flow is stable at 50ml/100gr of brain tissue in 1 minute for Although arterial blood pressure can range from 50 to 150 mmHg. The reason for this is because of the autoregulation of the cerebral vascular system, when arterial blood pressure is low, cerebral blood vessels will dilate to receive more blood and vice versa when blood pressure increases, cerebral blood vessels constrict. again.
Brain cells can live when the cerebral blood flow is below 20 ml / 100g / min, below this threshold, the cerebral vessels will be maximally dilated and the survival of brain cells is directly dependent on the duration of cerebral ischemia. It can be said that brain cells are the most special cells in the body, once damaged, they cannot regenerate and compensate like other cells.
Under normal conditions, the brain's ability to tolerate hypoxia is up to 5 minutes. This time period is also known as the clinical death phase, and emergency circulatory arrest to re-supply blood and oxygen to the brain must be carried out during this period to save the patient's life.
When circulatory arrest lasts for more than 5 minutes, brain cells will be damaged beyond repair and then the patient will enter the stage of vegetative life or brain death.
In some special cases, the brain's ability to tolerate hypoxia may last longer, such as:
Cardiac arrest in hypothermia like Barbituric Infant...
2 . What causes circulatory arrest?
Cardiac causes:Ischemic heart disease Acute coronary occlusion Cardiomyopathies Myocarditis Acute cardiac tamponade (effusion, hemopericardium) Direct stimulation of the heart, dangerous arrhythmia dangerous (ventricular fibrillation, pulseless rapid ventricular tachycardia) Circulatory causes:
Acute volume depletion (types of shock: hemorrhagic shock, dehydration shock, vasodilating shock, ..) Pulmonary embolism (due to gas, thrombosis, fat, amniotic fluid, ..) Mechanism of vagus reflex. Respiratory causes:
Severe pneumothorax (pressure pneumothorax) Acute hypoxia (usually causing asystole): Due to foreign body blocking airway. Anthrax (severe respiratory acidosis). Causes of metabolic disorders:
Disorders of potassium metabolism. Acute hypercalcemia. Increased catecholamine levels. Hypothermia. Hypoglycemia. Metabolic acidosis Drug-induced, toxic:
The direct effect of the drug causes cardiac arrest. Due to side effects of drugs (drugs, sedation, ..). Other causes:
Electric shock . Drowning.
3. Recognizing Circulatory Stopping
Circulatory arrest is diagnosed based on the following 3 basic symptoms:Loss of consciousness: determined by calling the patient unresponsive, pain stimulus unresponsive, no awakening reflex. Apnea or yawn breathing: Determined when the patient's chest and abdomen are completely without breathing movement. Cardiac arrest: When there is loss of carotid or inguinal pulse. In addition, the patient also has other symptoms such as:
Pale or cyanotic skin Dilated pupils and loss of pupillary reflexes to light If the patient is in the process of surgery, blood will be seen in the incision, purple and black and stopped. run. If the patient is on mechanical ventilation, comatose, the heart monitor will alarm, SpO2 drops suddenly.
4. Basic circulatory arrest emergency
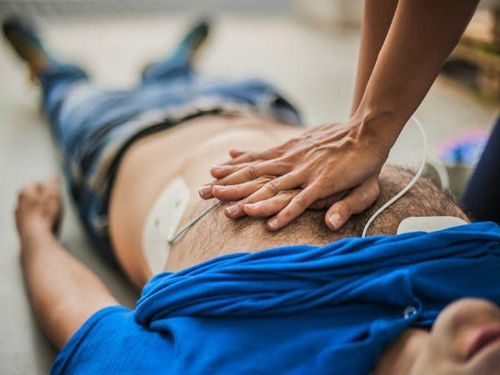
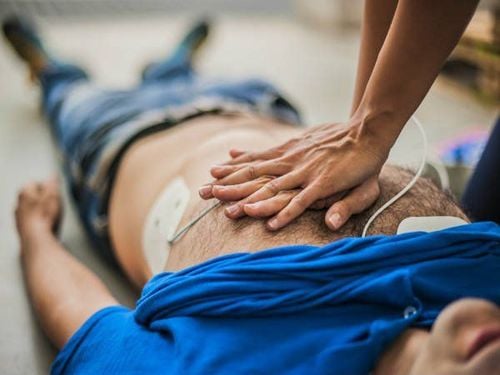
When detecting the patient's circulatory arrest, you must immediately conduct emergency with 3 things to do:A (Airway): Open the airway. B (Breathing): Artificial respiration or CPR (Chest compressions): chest compressions. In 2010 the American Heart Association (AHA) released new guidelines for primary cardiac arrest, in which the initial sequence of steps was changed from (A-B-C) airway clearance to rescue breathing. , chest compressions (C-A-B) chest compressions, open airways, rescue breaths. If there is medical equipment, give medicine and electric shock immediately.
5. How to use adrenaline in emergency circulatory arrest
The first drug used in the emergency of circulatory arrest is adrenaline tube 1mg/1ml. This medication works by stimulating adrenergic receptors on the autonomic nervous system of the heart, causing the heart to beat again.The dose of adrenaline in the emergency of intravenous (IV) or intramuscular (IO) arrest is 1 mg per injection for adults or 0.01 mg/kg for children, repeated 3-5 every minute if the heart is still not having a pulse, in the absence of an intravenous (IV) or an intra-osseous (IO) line, it can be administered through the endotracheal route at a dose of 2-2.5 mg/dose. in adults or 0.1 mg/kg/dose in children.
The best way to use adrenaline in the emergency of circulatory arrest is intravenous injection, especially injection into the central vein because this is the fastest route to deliver the drug to the sinus node. If you are injecting into a peripheral vein, you should choose the external jugular vein, the cephalic vein, or the brachial basilar vein. If an intravenous line is not available, an intra-osseous line can be used.
In adults, a dose of adrenaline 1 mg should be diluted in 10 ml of normal saline 0.9% NaCl and given rapidly intravenously, followed immediately by a rapid bolus of 20 ml of normal saline 0.9% NaCl. If injected into the brachial vein, raise the patient's arm above heart level for about 10 to 20 seconds after each injection; if an intravenous line has been placed, after the injection into the infusion line, raise the The body places the infusion line and allows the fluid to flow rapidly with the aim of making the drug return to the central circulation more quickly. The leg veins should not be used as it is less effective.
The way to prevent the introduction of adrenaline when the drug cannot be injected intravenously is to inject the drug directly into the patient's endotracheal tube. The dose of adrenaline by this route needs to be higher than that of intravenous injection, namely 2 - 2.5 mg of adrenaline mixed in 5 - 10ml of physiological saline 0.9% NaCl
Thanks to ventilation, the drug will be delivered into the alveoli. permeates the alveolar-capillary membrane into the pulmonary circulation. Then, by pressing the heart back to the heart, the heart will beat again. Do not repeat the injection of adrenaline into the trachea too many times because it will flood the patient's lungs.
Intra-osseous (IO) line has the same value as intravenous (IV) line, used in cases where an intravenous line cannot be obtained, causing delay in emergency care, especially in children . By using a specialized device, the needle is inserted into the bone marrow at one of the following locations: superior tibia, distal (lower) tibia, distal femur, anterior iliac spine.
According to statistics, the mortality rate when circulatory arrest occurs is up to 90%. Therefore, circulatory arrest is a fulminant emergency, and when circulatory arrest is detected, immediate emergency treatment is required. For cases outside the hospital, people should learn how to give chest compressions and give CPR while waiting for ambulances and paramedics to arrive. Delay can cause brain death or even death.
Vinmec is a medical system with well-trained medical staff according to the standards of the advanced respiratory arrest program ACLS in adults and PALS in children certified by the US AHA. With modern and advanced equipment to help improve survival as well as reduce the risk of brain damage, especially including a command hypothermia system, defibrillator combined with percutaneous cardiac pacing. , a device to monitor cardiac compression feedback (CPR), ... in combination with specialized support centers such as DSA coronary intervention in case of cardiac arrest due to acute myocardial infarction, ..
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.