This is an automatically translated article.
Subdural hematoma accounts for a large proportion of traumatic brain injury in humans. In particular, acute subdural hematoma is the type that accounts for the highest mortality rate, with many severe sequelae for patients.1. Definition and causes of acute subdural hematoma
A subdural hematoma is a blood clot that forms in the subdural space. A subdural hematoma is usually caused by a head injury. Head trauma causes damage and bleeding in the blood vessels in the subdural space. Blood drains from the blood vessels and coagulates in the subdural space, and head trauma also damages brain parenchyma.Acute subdural hematoma is when a hematoma is formed immediately after a head injury, rapidly and life-threatening. Symptoms can occur immediately or within hours of the injury.
2. Causes of acute dural hematoma
It is mainly caused by severe head trauma that ruptures a vein in the subdural space. This tear causes blood to flow into the cavity and coagulate into a mass that presses on brain tissue.Other causes can also be due to superficial cortical veins or sinuses in the veins.
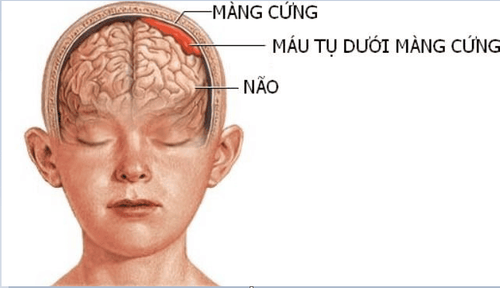
Hình ảnh mô phỏng tụ máu dưới màng cứng
3. Symptoms of acute subdural hematoma
Symptoms of an acute subdural hematoma usually appear shortly after the injury or several hours later. Specifically as follows:Because this is a severe traumatic brain injury, most of the patients are comatose right after the injury. In some cases, there will be about to wake up, a few hours later, symptoms will appear and begin to fall into a coma. Deep coma, onset of generalized spasms and convulsions Nausea and vomiting many times Severe headache Dizziness Difficulty speaking, difficulty eating Difficulty moving Confusion, forgetfulness or memory loss on the other side brain damage paralysis (weakness/paralysis of one limb) Abnormal breathing Body temperature and heart rate disturbances .
4. Treatment of acute subdural hematoma
The treatment will depend on the clinical examination, symptoms, size and location of the hematoma in the cavity. Usually, surgical intervention is required as quickly and accurately as possible to save the patient's life.If the hematoma is small or the symptoms are not serious, treatment can be indicated by careful monitoring, the hematoma is allowed to be absorbed by the body. Patients will be closely monitored and quite often to assess their level of alertness as well as monitor for any unusual symptoms that may appear.
The patient underwent CT scan several times to check the size of the hematoma. Indications for surgery to remove hematoma by craniotomy or skull hole drilling can be performed immediately if the size of the hematoma is large, symptoms of intracranial pressure gradually increase, and symptoms of unilateral weakness extremities, breathing disturbances, language disorders appear.
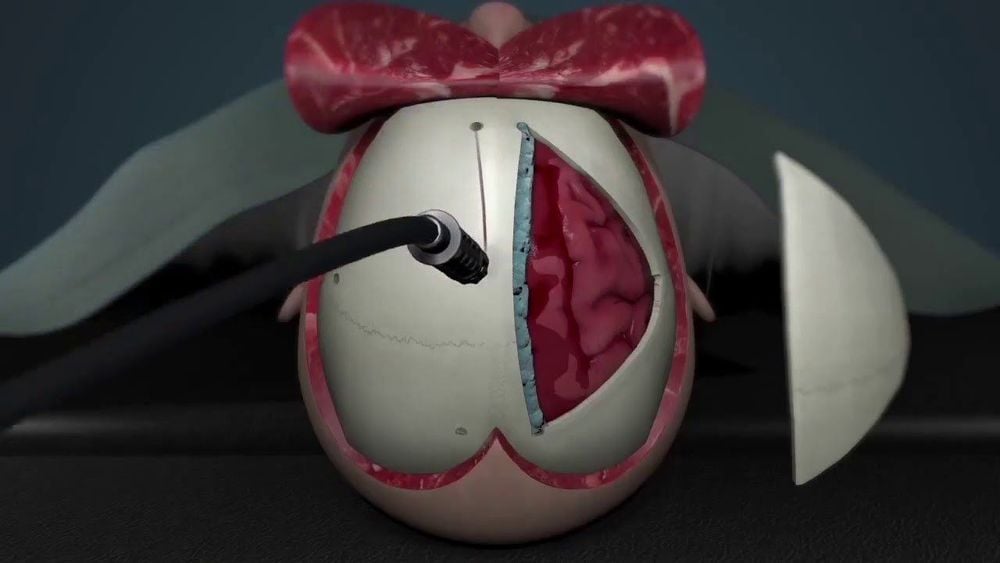
Phẫu thuật mở hộp sọ để lấy máu tụ ra ngoài
5. Complications and sequelae of people with subdural hematoma
Complications such as infection or meningitis can occur when surgically treating a person with a subdural hematoma. Due to local intracranial pressure, it can cause many serious and permanent complications for patients such as:Mental disorders Hemiplegia, irreversible hemiplegia. Plant life Epilepsy Poor memory or dementia With these sequelae can be treated with rehabilitation methods and physical therapy. However, it requires patience and long-term implementation. In addition, there are vascular complications such as blood clots, aneurysms...
The risk of subdural hematoma is reduced if:
People who are taking anticoagulants (such as warfarin) regularly go for tests. periodic blood. This test will help you see if you are taking the correct dose of medicine and make sure your blood is not too thin. In cases where the blood is too thin, the likelihood of a subdural hematoma is higher than with a head injury. Be careful and try to avoid the risk of accidents, falls and head injuries. Alcoholics should stop drinking. If participating in extreme sports, it is necessary to take measures to protect the brain such as wearing a helmet to avoid maximum serious head injuries. Vinmec International General Hospital with a system of modern facilities, medical equipment and a team of experts and doctors with many years of experience in medical examination and treatment, patients can rest assured to visit. and hospital treatment.
To register for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.
SEE MORE
Traumatic brain injury: How to recognize and treat? Structure of the meninges How dangerous is the subdural hematoma after trauma?