This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor I Ho Quoc Tuan - Anesthesiologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Anesthesia during traumatic brain injury surgery is the use of drugs on the brain to make the patient lose feeling in the whole body. The main purpose of this procedure is to limit or eliminate all possible causes of increased intracranial pressure, and to help closely control the patient's respiratory and circulatory status.
1. What is the role of the anesthetic step in surgery for traumatic brain injuries?
Traumatic brain injury refers to the impact from an external force on the head or the patient suffers from penetrating trauma that disrupts the basic functions of the brain.A patient can have a traumatic brain injury for many reasons, for example from a sudden and strong impact on something, or from a sharp object that pierces the skull and enters the brain tissue. In which there are many types of traumatic brain injury that require the patient to undergo surgery to ensure life such as: extradural hematoma, skull subsidence, brain contusion,...
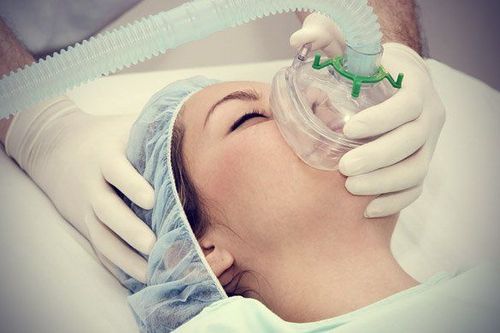
Anesthesia for trauma surgery The brain can be used to inject drugs into a vein or let the patient smell the anesthetic through the airway.
Thanks to the use of anesthesia, the patient will no longer be aware in a short time, and do not have to feel pain during surgery. The majority of anesthetics used in traumatic brain injury surgery are general anesthesia and additional intubation with the main purpose of controlling the patient's breathing during the entire surgery as well as the procedure. recovery after surgery.
Anesthesia in traumatic brain injury surgery is also to ensure that the surgical procedure goes smoothly, avoids secondary injuries and can maintain good resuscitation in the face of unexpected situations in the case. surgery such as severe cerebral edema, the patient lost a lot of blood,...

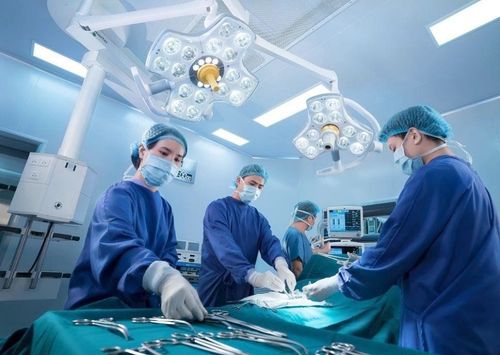
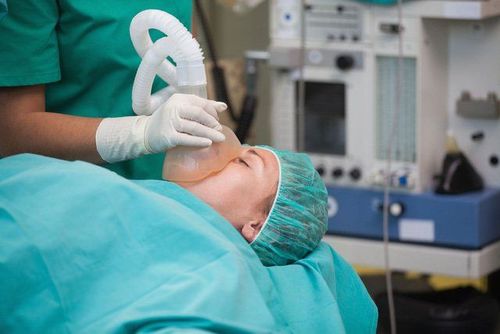
Bệnh nhân được thực hiện gây mê toàn thân trước khi phẫu thuật
2. When is anesthesia indicated for traumatic brain injury?
Patients are indicated for anesthesia in traumatic brain injury surgery in the following cases:Subdural hematoma: the amount of hematoma is determined to be located between the inner dura and the cerebral cortex, Usually due to tearing of the bridging veins, the patient will undergo decompression surgery and collect hematoma. Extradural hematoma: caused by cortical veins or meningeal artery laceration, may also be associated with concussion or tissue contusion. Leading to the formation of hematomas located inside the skull and outside the dura mater, to manage these cases, the patient will have surgery to remove the hematoma. The hematoma was identified underlying the subacute dura and the chronic region: the patient was required to use anesthesia during surgery to drill the skull to drain the hematoma. Cranial depression or concave skull: use anesthesia in surgery to lift the sunken, concave skull. Open traumatic brain injuries: many cases of traumatic brain injury are related to the communication between the structures inside the skull and the outside environment. At this time, the patient will be anesthetized to clean the foreign body. and patch the dura. Brain contusion, hematoma inside the brain: is damage to brain cells accompanied by bleeding. Contusions are more common in areas of the skull, either in the frontal or temporal lobes, because the brain touches the bony ridges of these areas. In addition, there may also be a hematoma in the brain tissue, the patient needs surgery to decompress and remove the hematoma.

Bệnh nhân bị máu tụ dưới màng cứng được chỉ định tiến hành gây mê
3. Methods of anesthesia in traumatic brain injury surgery
Pre-anesthesiaSevere traumatic brain injury: pre-anesthesia should not be used because of the risk of respiratory failure. Instead, the patient will be induced by rapid intubation to control breathing and airway. Mild traumatic brain injury: Pre-anesthesia can be used for sedation, and the airways and airways need to be continuously monitored during induction of anesthesia. Traumatic brain injury with agitation: using induction of endotracheal anesthesia instead of induction of anesthesia because induction of anesthesia is not effective at this time. Local anesthetic
Only indicated in some cases such as:
Patients with brain damage due to chronic hematoma or skull depression or concave skull. Perception: because the patient is uncooperative, agitated. Surgeon requested and indicated. Anesthesia for intubation
Includes 4 very important operations:
Induction of anesthesia: the process of intubation can be difficult due to the impact of traumatic brain injury or due to the direction and position set mandatory. In addition, the nasogastric tube or nasogastric tube cannot be inserted when the patient has a fracture of the skull base because of the risk of brain tissue damage from the fracture lines themselves. Maintenance of anesthesia: limit the use of drugs with the ability to evaporate with high flow. The patient can be given medication after artificial ventilation has been performed or after the skull has been opened. In addition, to ensure sufficient muscle relaxation, it is necessary to add pain relievers and sleeping pills to help prevent the patient from coughing or moving during surgery. Response to maintaining anesthesia: conditions that may occur during the maintenance of anesthesia such as blood loss, gas embolism or increased cerebral edema should be detected and treated promptly so as not to threaten the patient's life. . Anesthesia: In cases where the patient has severe trauma and has a GCS index of less than 9, it is necessary to maintain sedation by a ventilator immediately after surgery. In particular, when the breathing tube is removed, the patient needs to be continuously monitored to prevent respiratory or circulatory disorders. Indication of surgical anesthesia for traumatic brain injury is a necessary and special operation that cannot be subjective. This is one of the important factors for a successful operation and prevention of possible secondary injuries, and at the same time maintaining good resuscitation in the face of unexpected situations such as severe cerebral edema, heavy blood loss. ,...
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that strictly applies safe surgical anesthesia practice standards according to international guidelines. With a team of experienced anesthesiologists and nurses, along with modern equipment such as nerve detectors, ultrasound machines, Karl Storz difficult airway control system, anesthesia monitoring system GE's comprehensive AoA (Adequate of Anesthesia) including monitoring of anesthesia, pain and muscle relaxation will deliver high quality and safety, helping patients to have adequate anesthesia, not awake, no residual relaxant muscle after surgery. Vinmec Health System is also proud to be the first hospital in Vietnam to sign with the World Anesthesiology Association (WFSA) towards the goal of becoming the safest hospital for surgical anesthesia in Southeast Asia.
Doctor Quoc Tuan has many years of experience in the field of Anesthesiology - resuscitation at Hoan My Danang Hospital and Phu Yen Provincial General Hospital before being an Anesthesiologist and resuscitator at the Operating Room - Department of Medicine. General surgery at Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital as it is today.
To register for the fastest examination and treatment, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide, or register online HERE.