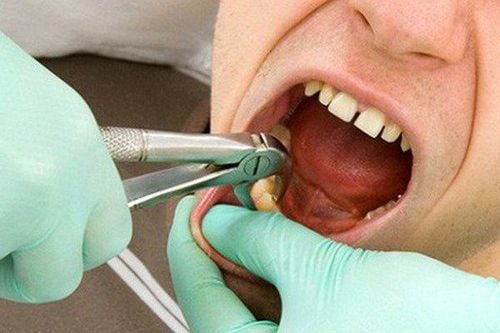
This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Pham Thieu Trung - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Phu Quoc International General Hospital, Specialist Doctor I Tran Thi Anh Hien - Department of Surgical Anesthesia - Hospital Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.The mouth contains many sensory nerve endings, and also contains many mucous membranes, so it is very sensitive to any dental intervention. Therefore, anesthesia, especially local anesthesia, is an important stage in reducing the patient's pain during tooth extraction.
1. What is local anesthesia?
Local anesthesia is a form of regional analgesia using a local anesthetic that specifically and temporarily inhibits the flow of nerve impulses from the periphery to the center, causing temporary loss of pain sensation. In tooth extraction, local anesthetic methods include surface anesthesia and local anesthesia by injection.
Surface anesthesia: An anesthetic method by placing a certain amount of anesthetic directly on the oral mucosa surface with the ability to penetrate or create cold to numb the peripheral nerve endings. This method will help numb in a short time, applied to easy and fast cases such as extracting a lot of loose teeth or removing tartar, injecting abscesses.
Local anesthesia by injection: Use local anesthetics such as Bupivacaine, Lidocaine, Prilocaine to numb the mucous membranes or numb the ligaments.

Thuốc Lidocaine được sử dụng trong gây tê
2. How is local anesthesia for tooth extraction performed?
For superficial anesthesia: There will be numbing and spraying.
Anesthesia: Disinfect, dry the numbed area, and then use a cotton ball to absorb the drug with rapid penetration through the mucosa such as 10% Lidocaine solution, or 4% or 10% Benzocaine solution, apply around the mucosa around the foot. When the tooth is extracted, wait a few minutes for the anesthetic to absorb, then intervene quickly
Anesthesia: Includes 2 types: With 10% Lidocaine in a bottle with a solution nebulizer, it is used by spraying local anesthetic for the right injection. mucosal area to be anesthetized, wait a few minutes and then intervene.
With Ethyl Chloride with the mechanism of numbing by rapidly evaporating, lowering the temperature to a low level to create anesthesia, use by holding the bottle upside down and the head towards the anesthetic, spray 2 cm from the mucosa and then put it away. slowly to 15 cm. Wait for this layer to dissolve, then spray a second time and the numbed area is white to begin intervention.

Thuốc phun tê Lidocaine 10%
For local anesthesia by injection:
Mucosal anesthesia: For single-rooted teeth: Inject 2 injections on the outer surface, 1st nose is 3-5 mm from the neck of the tooth, the needle must touch the straight bone with the crown of the tooth. With the gums at a 45 degree angle, inject 0.25 ml of anesthetic solution slowly. The second dose is injected right after that at the neck of the tooth at a distance of 15 mm into the gingival niche corresponding to the root of about 0.5-1 ml. An additional injection can be injected into the inner surface of the tongue about 0.5 ml at a distance of 3-5 mm from the neck of the tooth. Then wait 5-10 minutes for the anesthetic to take effect, the numbing effect can last 30-40 minutes.
For multi-rooted teeth: 3 injections on the outer surface. The 1st is in the mesial side, the 2nd is in the distal side of the crown, 3-5 mm from the neck, each injection is about 0.5-1 ml. The 3rd injection is administered immediately, about 0.5-1 ml from the neck of the tooth, about 0.5-1 ml of local anesthetic. The inner side can be injected with an auxiliary injection similar to a single-rooted tooth, but the upper jaw is injected 15mm from the neck of the tooth and the lower jaw is 3-5mm from the neck of the tooth.
Ligament anesthesia: Is a technique of stabbing the needle parallel to the axis of the tooth in the proximal and distal side of the needle, pressing close to the root of the tooth to be extracted, as deep as possible and requiring strong pressure.
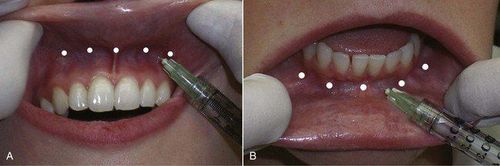
Hình ảnh gây tê nhiều chân răng
3. Possible complications in anesthesia
Anesthesia can cause the following complications:
Needle fracture, pain during injection, burning or numbness, prolonged paresthesia. Tight jaw. Infection. Edema. Exfoliation of tissue. Facial nerve paralysis. Oral injury after anesthesia. Graduating from the residency training program, Doctor Tran Thi Anh Hien has experienced many different working environments such as Binh Dan Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital, and Phap Viet Hospital before. when he returned to work at the Anesthesia and Anesthesia Unit - Department of Surgical Anesthesia - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
For detailed advice on this method, please come directly to Vinmec health system or register for an online examination HERE.
Recommended video:
Spinal plane anesthesia (ESP): Complete pain relief, no need for morphine
SEE ALSO:
Anesthesia during tooth extraction surgery Is it okay to have a tooth extracted? Should wisdom teeth be extracted before pregnancy?