This is an automatically translated article.
Coronary intervention is a procedure that helps to solve the narrowing and blockage of coronary arteries without the need for open thoracic surgery. Accordingly, depending on each case, doctors will prescribe different coronary intervention methods. However, percutaneous coronary intervention is a technique used to treat some common coronary diseases.
1. What are the symptoms that require urgent coronary intervention?
Coronary artery bypass surgery is a procedure that helps to solve coronary artery stenosis and blockage without the need for open thoracic surgery. Over the years, this method has achieved many advances both in terms of technique and effectiveness in treatment.
Percutaneous coronary intervention includes percutaneous angioplasty, which may or may not include stenting (coronary stents).
Percutaneous coronary intervention is indicated mainly for the treatment of the following conditions:
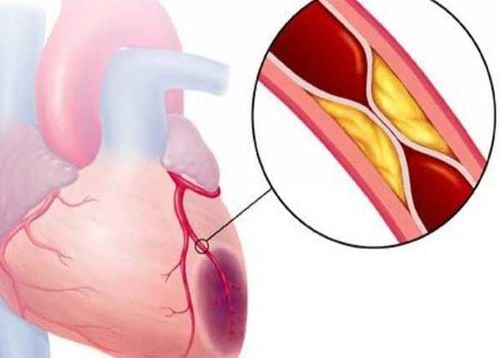
Angina : Stable angina that cannot be controlled by optimal medical therapy or unstable angina determined . Non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction with high risk. Myocardial ischemia due to coronary artery stenosis. Acute myocardial infarction is particularly indicated in patients with cardiogenic shock or progressing to cardiogenic shock. Coronary intervention with early stenting is the most optimal treatment modality for acute myocardial infarction with ST elevation. After an acute myocardial infarction, but still having chest pain despite aggressive medical treatment, it is possible to conduct preparatory coronary intervention. There are symptoms of coronary re-stenosis after percutaneous coronary intervention,... Some cases with relative contraindications to coronary intervention include:
When there are not enough facilities for cardiac surgery and support as needed Severe left main coronary artery stenosis, in the absence of collateral circulation from another branch of nourishment. In this case, bypass surgery is usually indicated. Patients with coagulation disorders. The patient's condition has increased blood clotting. The lesion is diffused throughout the coronary artery system without a fixed stenosis. There is only one vessel supplying blood to the whole heart that is narrowed. Complete occlusion of one coronary artery coronary artery stenosis < 50%, this case usually requires medical treatment. SEE ALSO: Vinmec Nha Trang successfully performed percutaneous coronary intervention in a case of severe heart disease with many complicated diseases

Chỉ định can thiệp mạch vành để điều trị các tình trạng thiếu máu cơ tim do hẹp mạch vành
2. How to prepare before coronary intervention?
Percutaneous coronary intervention is usually performed through the femoral, radial, or brachial arteries.
2.1 Preparation before performing coronary intervention
Patient:
The patient was thoroughly explained about the percutaneous coronary intervention procedure and agreed to the procedure. Do tests to evaluate and monitor the disease such as: Blood count test, complete coagulation function, Bilan blood fat, blood biochemistry, echocardiography... The patient has fully used anti-coagulant drugs. Platelet collection before the intervention. Check the accompanying medical conditions, allergy to contrast agents... Performer: Doctors and nurses trained in interventional cardiology.
Means: Vehicles used in vascular interventions and post-interventional resuscitation.
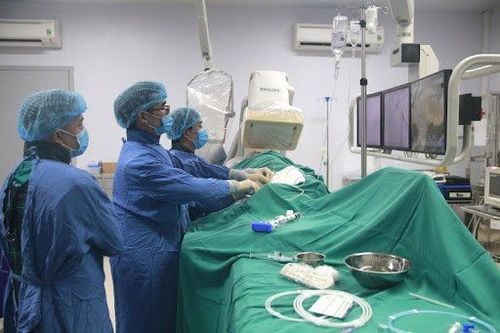
Can thiệp động mạch vành qua da thường được thực hiện thông qua đường vào ở động mạch đùi
2.2 Steps to take
Extensive disinfection of the femoral or radial artery. Anesthetize the area where the vascular access is made. Use a special needle to poke the artery and place a catheter into the femoral or radial artery. Through the catheter, the catheter is passed from the femoral or radial artery to the aorta and coronary arteries of the heart under radiological guidance. Do not enter too small of the coronary artery. Contrast is injected into the right and left coronary arteries for coronary angiography to detect stenosis or occlusion. Insert the balloon and proceed to inflate the balloon to widen the coronary stenosis. Then, depending on the purpose, whether to place a stent (stent) to keep the artery lumen from narrowing again or not to place and place a stent that is suitable for the disease condition. Once the stent has been placed, a coronary angiogram is performed to make sure there are no complications. Then, remove the catheter from the coronary artery and end the procedure. After the catheter will be removed, the puncture site is covered with a compression bandage. Coronary intervention is a technique that is unlikely to have some risks, so close monitoring is required after percutaneous coronary intervention. During the first 6 hours after the intervention, the patient should be monitored every 30 minutes. Specifically:
Monitor pulse, blood pressure, signs of hypovolemic shock. The lateral artery access site is used to detect bleeding or hematoma formation. The dorsal pulse, color and skin temperature of the legs and arms are punctured to ensure that there is no limb ischemia. SEE ALSO: Coronary artery stenosis needs early intervention
Accordingly, the patient needs to stay in bed for the first 6 hours, keeping pressure on the puncture site when coughing or sneezing. Drink extra fluids to prevent hypotension and kidney disease caused by contrast build-up. Notify medical staff when there is bleeding at the puncture site and pain in many areas of the intervention.
Coronary intervention is a procedure indicated in many cases of coronary stenosis. When there are symptoms of angina, patients need to visit a cardiologist for early diagnosis and treatment, to avoid life-threatening complications.
Percutaneous coronary intervention is a difficult technique, requiring medical facilities to have a team of highly qualified and experienced doctors and nurses in the field of Cardiology and facilities. modern equipments. Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the most prestigious medical treatment units for cardiovascular diseases in Vietnam. Vinmec's Cardiology Department has always received much praise and satisfaction from domestic and international customers, being the pioneers in successfully applying the world's most advanced techniques in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
A team of highly qualified and experienced specialists: qualified doctors from Master's to Professor's and Doctor's degrees, reputable in medical treatment, surgery, interventional cardiac catheterization. Intensive training at home & abroad. In particular, Prof. TS.BS Vo Thanh Nhan - Cardiology Director of Vinmec Central Park was recognized as the first and only expert in Vietnam to be awarded the "Proctor" certificate on TAVI. State-of-the-art equipment, comparable to major hospitals in the world: The most modern operating room in the world; The most modern silent magnetic resonance imaging machine in Southeast Asia; The CT machine has a super-fast scanning speed of only 0.275s/round without the use of drugs to lower the heart rate; The 16-sequence PET/CT and SPECT/CT systems help detect damage to the cardiovascular organs early even when there are no symptoms of the disease. Applying the most advanced intensive cardiovascular techniques in the world in treatment: Painless open-heart surgery; Percutaneous aortic intervention without general anesthesia; Treatment of mitral regurgitation through the catheter has a success rate of 95%; Ventricular-assisted artificial heart transplantation for patients with end-stage heart failure prolongs quality of life beyond 7 years. Cooperating with leading cardiovascular centers in Vietnam and the world such as: National Heart Institute, Cardiology Department of Hanoi Medical University, University of Paris Descartes - Georges Pompidou Hospital (France), University of Pennsylvania (France), University of Pennsylvania (France), University of Pennsylvania (France). United States)... with the aim of updating the most modern cardiovascular treatments in the world.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.