This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by MSc Ton Nu Tra My - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalMagnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the female pelvis or female pelvis is an imaging method that uses a magnetic field, radio waves, and a computer to create detailed images of the pelvic organs. This method can be used to diagnose or monitor treatment for a variety of pelvic conditions.
1. Female subframe magnetic resonance imaging was performed to evaluate in the cases
Diagnosis of anatomical and pathological abnormalities of female pelvic organs such as bladder, uterus, ovaries, blood vessels, pelvic lymph nodes. Monitoring treatment for conditions such as: after treatment for cervical cancer, endometrial cancer, ovarian cancer...

2. What do patients need to prepare before taking magnetic resonance imaging?
You will be assigned by your doctor to do a checklist of magnetic resonance safety before the scan.
Before taking the scan, the technician or the doctor in the magnetic resonance room will check the checklist again to make sure it's safe to take the MRI. You will be asked to remove jewelry, watches, credit cards, pins, hair clips, metal zippers, phones and similar metal items before entering the studio.
Implantable medical devices can be damaged when entering the MRI room, so during the pre-exam MR safety checklist, the technician or doctor will ask you about this.
Then you need to wear a hospital gown.
Pre-exposure preparations such as eating and drinking instructions before MRI vary from case to case. If your doctor does not recommend fasting or fasting, you can eat and drink as usual before the scan.
In the case of contrast agents, you may need blood tests to determine if your kidneys are working properly. You will have an intravenous line placed in your arm or forearm before the scan. Your doctor will take your allergy history into account before deciding to use contrast agent.

In some cases, the doctor will probably give allergy prophylaxis before the scan:
Tell the technician or radiographer if you have any serious health problems or have recently had surgery . You need to inform your doctor and/or technician if you are pregnant. If you have claustrophobia (fear of enclosed spaces) or anxiety, you should talk to your prescribing doctor first, who in some cases may prescribe a sedative before the examination.
3. How does the magnetic resonance machine work?
Unlike X-rays and computed tomography (CT) scans, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) does not use radiation. Instead, radio waves rearrange the hydrogen atoms that naturally exist in the body. This does not cause any chemical changes in the tissues. When the hydrogen atoms return to their normal alignment, they emit different amounts of energy depending on the type of tissue in the body. The scanner picks up this energy and creates an image using this information.
In most magnetic resonance units, a magnetic field is created by passing an electric current through the coils. These coils send and receive radio waves, generating signals that are detected by the machine. Current does not contact the patient.
After the capture is complete, the computer processes the signals and creates a series of images of the body.
MRI can see the difference between diseased and normal tissue better than X-rays, CT scans, and ultrasounds.
4. How is female subframe magnetic resonance imaging done?
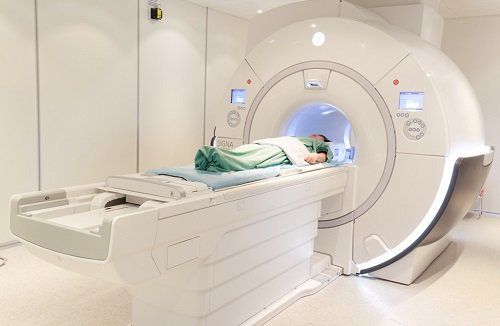
Female pelvic resonance imaging can be performed on an outpatient or inpatient basis.
The patient will be instructed to lie supine on the imaging table. The shooting table can be moved. The technician may use straps and splints to keep the patient's body still on the table.
Devices that contain coils capable of sending and receiving radio waves are placed around your pelvis. The technician will then place you on the magnetic resonance device's magnet.
Magnetic resonance imaging usually involves multiple pulses, the pulses can last from several tens of seconds to several minutes.
If contrast material is used, the nurse will place an intravenous line in your arm or forearm to inject the contrast agent. Contrast is injected into an intravenous (IV) line after the initial series of scan pulses. Subsequent pulse sequences are then taken during or after the injection.
Once the scan is complete, you may be asked to wait while the radiologist examines the existing images to decide if more scans are needed.
At the end of the examination, the nurse will remove the intravenous line.
Depending on the case, the total time can be from 30 to 50 minutes.
5. What are the benefits and risks?
5.1. Benefits
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive imaging technique that does not involve exposure to radiation.
Magnetic resonance imaging of pelvic structures has the ability to identify and describe more accurately the disease than other imaging methods to help diagnose and evaluate many diseases early, including cancer, inflammatory diseases , congenital malformations of uterus, ovaries, bladder, pelvic vascular abnormalities.
5.2. Risks
Magnetic resonance imaging has virtually no risk to the patient.
Strong magnetic field is not harmful. However, it can damage implanted medical devices. So if you have any implantable device in your body, you need to tell the technician or doctor before the scan.
Renal system fibrosis is a possible complication of gadolinium contrast agents but is rare. It usually occurs in patients with severe kidney disease. Your doctor will carefully evaluate your kidney function before considering contrast injection.
There is very little risk of an allergic reaction if a contrast agent is used. Such reactions will usually be controlled with medication. If you have an allergic reaction, your doctor will be ready to treat it right away.
6. What are the limitations of female subframe magnetic resonance?
The quality of the resulting images is sufficient regardless of the patient being able to remain still during the scan and following the instructions to hold their breath while recording the image. If you are nervous, confused, or in pain, you may find it difficult to lie still during the scan. These movements can cause the resulting image to be out of focus, limiting the diagnosis.
Implants and metal objects may cause the resulting image to be blurry.
Magnetic resonance imaging is not always able to differentiate between cancerous and benign neoplasms and/or edematous inflammatory conditions.
Magnetic resonance is often expensive and can take longer to perform than other imaging methods. Talk to your doctor and insurance company if you have concerns about the cost of magnetic resonance.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.