This is an automatically translated article.
Iohexol is a non-ionized, iodide-containing contrast agent that is administered orally or by injection to reveal the structure of the body on radiographs.
1. What is Iohexol?
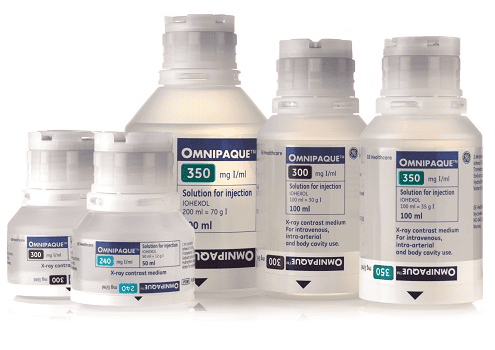
Iohexol is a non-ionizing contrast agent and contains iodine. Iohexol is mainly produced in the form of injections with many different strengths. All manufactured forms contain 1.21mg of Tromethamine and 0.1mg of calcium disodium edetat.
Iohexol is indicated for use in the following cases:
X-ray of the spinal canal such as the lumbar region, chest, neck and entire spinal canal in both adults and children. Cardiovascular X-ray includes coronary angiography and cardiac chambers. X-ray - vascular system including aorta, arteries or veins). In particular, angiography includes aortic arch, ascending aorta, abdominal aorta and its branches. Take pictures of other arteries such as the brain or peripheral arteries. Peripheral venography for the diagnosis of deep vein thrombosis, diagnosis and evaluation of tumors and vascular disease. Used in intravenous ureterography. X-ray of some hernias. Computed tomography of the brain, computed tomography of the body to evaluate and detect lesions in the liver, pancreas, kidney, mediastinum, abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal cavity,... X-ray of the pancreatic duct by retrograde pancreatoscopy. X-ray of the biliary system - pancreas through endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography using the drug Iohexol. X-ray of the joint in the synovial capsule using contrast. As contrast agent in X-ray of uterus - fallopian tubes. X-ray of the stomach and intestines.
2. Cases of contraindications to the use of Iohexol
Iohexol should not be used in the following cases:
Patients with hypersensitivity to Iohexol or allergic to any ingredient in the drug. People with a history of anaphylaxis or late skin reactions to iodine-containing injections. Patients with obvious thyrotoxicosis. Contraindications to hysteroscopy - fallopian tubes in pregnant women. Do not use Iohexol for patients with a history of allergies or asthma, people with severe kidney failure, diabetes, and iodine sensitivity, regardless of adults or children. In case of intracanal injection: Do not use Iohexol for chronic alcoholics, people with subarachnoid bleeding, history of seizures, severe systemic or local infections or diffuse sclerosis. Intravascular injection: Iohexol is not used for people with hyperthyroidism, sickle cell disease, and pheochromocytoma. In case of cerebral angiography: Iohexol should not be used for injection in patients with long-term arteriosclerosis, in patients with decompensated heart failure, in patients with severe hypertension, in senility, or in recent thromboembolic events. The patient had a recent cerebral embolism. In case of X-ray of the ureter through the vein: People with anuria, diabetes should not use Iohexol. In case of X-ray of uterus - fallopian tubes: Iohexol cannot be used during menstruation, pregnancy, bacterial infection; at least 6 months postpartum or 30 days after cervical cytology.
3. Usage and dosage of Iohexol
Iohexol can be taken orally or injected. Currently, the drug is administered intravenously is the most common.
Dosage of Iohexol by injection:
Depending on the purpose of use and the need for X-ray or CT scan, patients are used with different doses of the drug. The dosage of Iohexol used for adults and children also varies according to the prescription of the specialist. Dosage for oral administration:
For adults: Gastrointestinal scan: Patients drink 50 -100ml of 350mg iodine/ml solution, undiluted, depending on the nature of the procedure and the size of the patient. Abdominal CT scan: This case needs to be combined with intravenous injection. Take the drug 20 to 40 minutes before intravenous injection. Patients drink 500-1000ml solution of 6-9mg iodine/ml, used in combination with intravenous injection of 100-150ml solution 300mg iodine/ml. For children: Gastrointestinal scan: The dose of Iohexol used varies depending on the age of the child. Abdominal CT scan: Use oral dose 30-60 minutes before intravenous dose.
4. What side effects does Iohexol cause?
Common side effects:
Patients may experience headache, back pain, dizziness, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal or stomach pain, malaise. Meningeal irritation (neck stiffness) is present. Using medicines that cause joint pain or make joint pain worse, swollen joints, slow heart rate. Uncommon side effects:
Patients present with severe headache, erratic fatigue or muscle weakness, fever, sweating. Sometimes there is a loss of appetite, a metallic taste in the mouth, and dilation of the kidneys and renal pelvis. There is tinnitus, somnolence, erratic and mild feeling of heat. Some patients have increased sensitivity to light, blurred vision, or other visual changes. Pain or burning sensation at the injection site, urticaria, difficulty urinating. Rare side effects:
Patients develop anaphylaxis, pseudoallergic reactions with typical manifestations such as chills, persistent fever, sweating, appearance of skin rash or urticaria, sneezing. , nasal congestion, laryngeal edema, facial or skin swelling, wheezing, breathing disturbances,... Rarely severe hypotension, cardiotoxicity, ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation, thrombophlebitis , slow heart rate, even cardiac arrest. A very small percentage of patients have aseptic meningitis, convulsions, bronchospasm, or pulmonary edema.
5. Notes when using Iohexol
For patients with hypersensitivity to iodine and iodinated contrast agents may increase the risk of anaphylactoid reactions. Using Iohexol as a contrast agent in an X-ray of the uterus - fallopian tubes can increase the risk of complications in people with genital infections, worsening pelvic inflammatory disease. For surgical patients. uterus or cervix should be used with caution to avoid complications. Iohexol may cause high blood pressure in people with pheochromocytoma. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor blood pressure during the procedure. Iohexol may cause venous or arterial spasm in buerger's disease, increasing the risk of complications in people with severe ischemia. Use of iohexol in cerebral angiography may increase the risk of thrombosis and embolism in patients with hymocystinuria. Iohexol should not be used by pregnant or lactating women. In X-ray arthroscopy, Iohexol may increase the risk of complications in patients with bacterial infections at or near the examined joint. Concomitant use of Iohexol with antihypertensive agents may increase the risk of severe hypotension. Administration of intrathecal or intravascular Iohexol injection with other nephrotoxic drugs may increase the likelihood of nephrotoxicity. In summary, Iohexol is an iodine-containing drug used as a contrast agent in X-ray films to clearly visualize the structure of the body. The level of contrast of the drug is proportional to the concentration and volume of the iodized contrast agent on the X-ray line. During use, it is necessary to ensure the correct technical procedure and closely monitor the patient to prevent complications. symptoms may occur.