This is an automatically translated article.
Currently, the 17-OHP test is considered an effective method in early detection of the risk of congenital adrenal hyperplasia in infants and adults, in order to provide timely treatment. time.
1. Hormone 17-OH-Progesterone and Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
1.1 Hormone 17-OH-Progesterone 17-OH-Progesterone (17-OHP) is an endogenous steroid hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex in the cholesterol metabolism chain and becomes cortisol, testosterone, and aldosterone. Cortisol is a hormone produced in the adrenal glands, this hormone helps to hydrolyze proteins, fats as well as glucose to regulate blood pressure and the immune system in the body. Cortisol is produced by the catalysis of several enzymes. In the event that one or more enzymes are deficient or dysfunctional, this can lead to a decrease in cortisol production, as well as a decrease in the cortisol precursor 17-OH-Progesterone, leading to consequent stasis. 17-OH-Progesterone in the blood. The adrenal glands use the excess 17-OH-Progesterone hormone to produce androgens. Excess androgens are responsible for virilization or the development of male biological characteristics in both men and women.
1.2 Congenital adrenal hyperplasia One of the most common causes of congenital adrenal hyperplasia in children is inherited mutations in the CYP21A2 gene, which leads to a deficiency of the 21-hydroxylase enzyme and causes for excess 17-OH-Progesterone hormone in the blood. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia can be severe (typical) or mild (atypical). Specifically:
Severe congenital adrenal hyperplasia Caused by a severe deficiency of the enzyme 21-hydroxylase, which in turn affects the excess androgens in the blood. This phenomenon will cause a girl to be born with a characteristic sign of unclear genitalia, making it difficult to determine the baby's initial sex. For men, this condition will appear normal at birth, but will lead to early puberty in childhood. When entering puberty, women with a deficiency of the enzyme 21-hydroxylase may experience clitoris hypertrophy, hirsutism, amenorrhea, irregular menstruation or other virilization conditions.
According to statistics, over three-quarters of patients affected by the deficiency of the enzyme 21-hydroxylase can cause aldosterone to be produced (this is an adrenal hormone that keeps salt in the body) and endanger life.
Although less common, severe forms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia can be detected by clinical symptoms as well as by 17-OHP and other neonatal screening tests.
Mild Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Mild congenital adrenal hyperplasia is more common and is caused by a partial deficiency of the 21-hydroxylase enzyme in the body.
Mild forms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia may be called late-onset or atypical congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Symptoms of the disease can appear late or anytime during childhood, adolescence or adulthood.
With mild congenital adrenal hyperplasia, symptoms may be vague, develop over time, and vary from generation to generation. Although not life-threatening, it can cause serious problems with growth and development, as well as puberty in children, and infertility in adults.
Mild congenital adrenal hyperplasia is detected mainly on newborn screening tests.
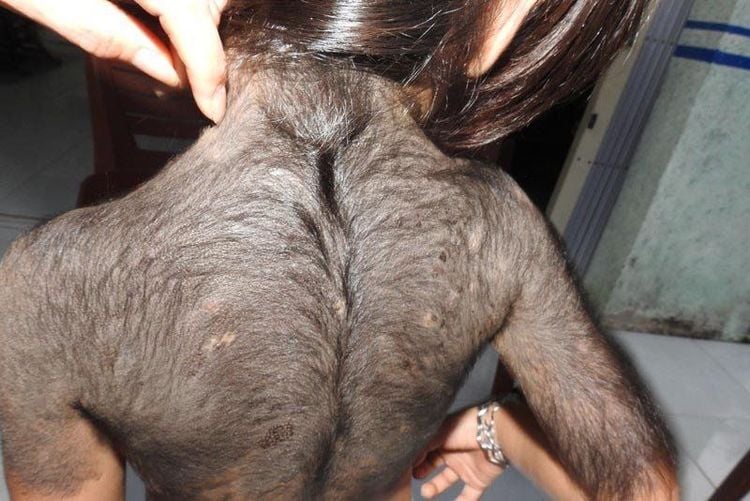
Bệnh tăng sản tuyến thượng thận bẩm sinh có thể gây rậm lông ở nữ giới
2. When is the 17-OHP test indicated?
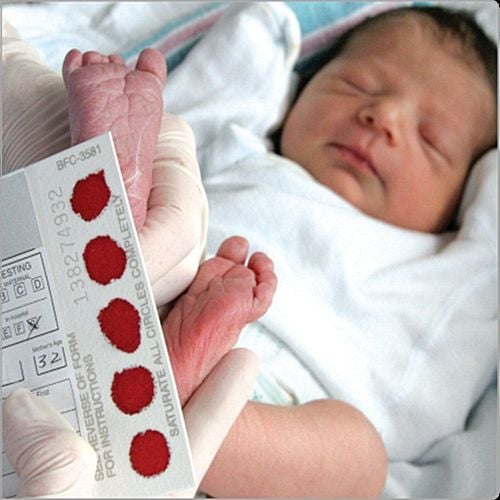
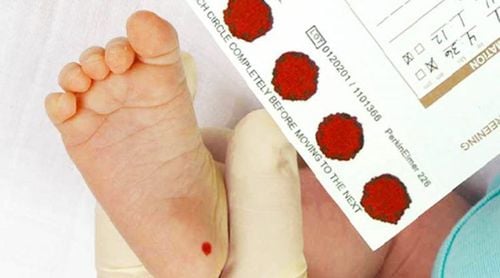
17-OHP test is a commonly used neonatal malformation screening test, this test is usually performed when the baby is 2 - 3 days old, by taking blood from the heel. leg or venous blood.
In addition, the 17-OHP test is also indicated for children or adults in cases of late-onset congenital adrenal hyperplasia, with specific symptoms:
For women: No menstrual/menstrual irregularities, hirsutism or virilization of the genitals. For men: Early puberty, abnormal development of sexual organs or men's body often fatigue, dehydration, loss of salt, low blood pressure...
3. How much 17-OHP is normal?
After testing, how much 17-ohp is normal is of great interest to many people, because it shows the current health status. However, the normal value of the 17-OHP test will vary according to whether the test is screening or diagnostic.
For newborn screening:
Children weighing > 2500g: A normal 17-ohp reading is 0 - 30 nmol/l. Children weighing > 2500g: A normal 17-ohp index is 0 - 33 nmol/l. For disease diagnosis:
Normal 17-ohp levels range from 0 - 200 ng/dl. If 17-OHP is measured > 300 ng/dl, it means that the patient is at very high risk of congenital adrenal hyperplasia. To get an accurate diagnosis, doctors will combine a number of other tests and thereby come up with an effective treatment plan.
In summary, the 17 OHP test is considered as one of the effective methods to help early detect the risk of congenital adrenal hyperplasia in children and adults to provide timely treatment methods. . Currently, many medical facilities have deployed 17-OH testing services, but you should still choose a reputable address and have a system of modern medical equipment to ensure accurate results. best.
Laboratory of Laboratory - Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the leading prestigious addresses in the country, trusted by a large number of patients to examine and conduct 17 OHP tests. Thanks to the use of modern machines and equipment to examine and analyze patient samples, it has provided accurate information, helping doctors to assess the overall health of the person being tested. Early detection of disease and timely treatment plan. In particular, with a space designed according to 5-star hotel standards, Vinmec guarantees to bring patients the most comfort, friendliness and peace of mind when visiting and receiving treatment at the hospital.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.