This is an automatically translated article.
This article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Nhu Thu Truc - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. Doctor has more than 8 years of experience in the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology.In most cases, breast milk will be produced based on the actual needs of the baby. The more often and efficiently your baby suckles, the more milk your body makes.
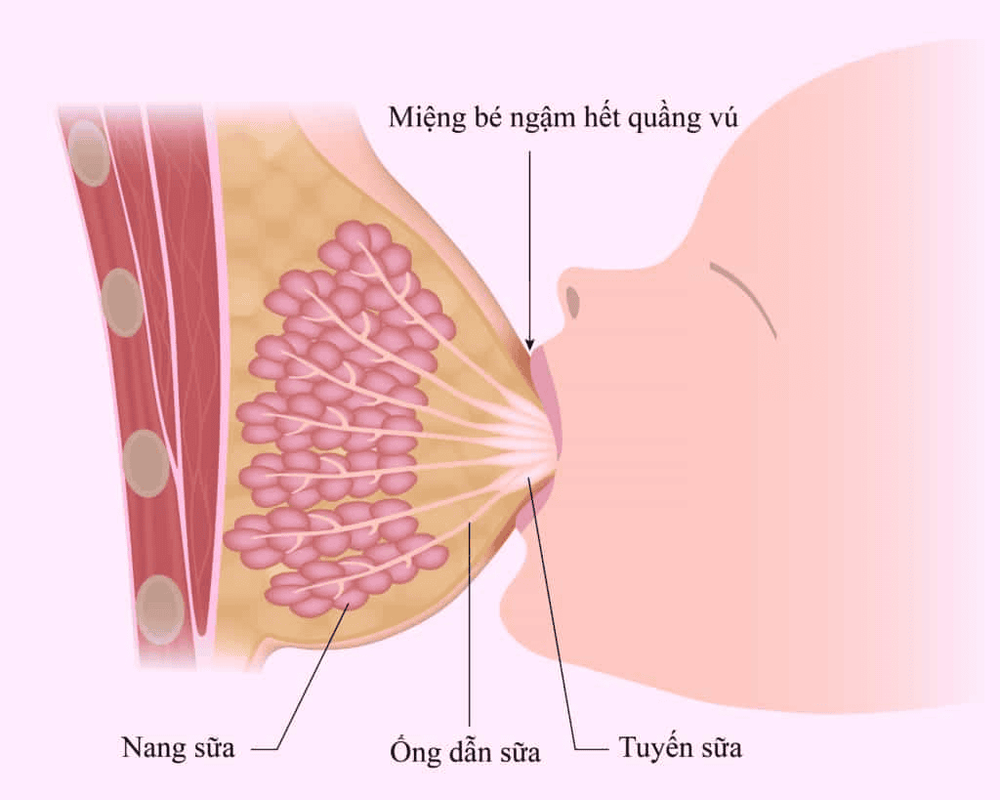
1. Anatomy of the breast
Breast structure consists of 3 main tissues: glandular tissue, adipose tissue and connective tissue. Mammary glands of mothers can be different in size depending on the composition of fat and connective tissue more or less. The amount of breast tissue is almost the same.From the outside to the inside, the breast consists of 5 layers: skin, subcutaneous fat and connective tissue, cooper ligaments suspending the breast, glandular tissue and posterior glandular tissue. The glandular tissue is divided into 15-20 lobes, arranged in a spokes shape, focusing on the nipple. Each lobe consists of 38-80 lobules and each lobule has many milk follicles.
Trắc nghiệm: Sự phát triển tinh thần, vận động của bé thế nào là đúng chuẩn?
Khi nào bé biết nói, biết hóng chuyện hay biết cầm cốc là "đúng chuẩn"? Điểm xem bạn biết được bao nhiêu mốc phát triển tinh thần, vận động "đúng chuẩn" của bé nhé!The following content is prepared under supervision of Thạc sĩ, Bác sĩ y khoa, Ma Văn Thấm , Nhi , Phòng khám Đa khoa Quốc tế Vinmec Dương Đông(Phú Quốc)
2. Breast milk production time
During pregnancy, a mother's breasts get ready to produce milk. Colostrum is produced by the mother's body from the second trimester of pregnancy until about 2-4 days after the baby is born. Colostrum is characterized by light yellow or clear, sticky consistency, rich in nutrients and antibodies. Colostrum contains more protein than mature milk. It is very important for babies to receive colostrum in the first feedings, especially in the first hour after birth. Colostrum is already present in the breast soon after the baby is born.After the baby is born, the placenta is shed, the mother's body begins to produce more milk. After about 5-14 days after the baby is born, the mother's body produces transitional milk. From day 14 onwards, the amount of milk secreted by the mother's body will continue to increase, turn white and thinner, called mature milk. More milk makes the mother's breasts full and firm. It is called the phenomenon of “milking”.

Milk at the end of the meal: Is the milk secreted at the end of a baby's feeding. The mother's breasts are now full. The milk at the end of the meal is white because it contains more fat than the milk for the first time. Fat provides a lot of energy for the baby to help the baby grow faster, so it is important to let the baby finish the milk, not let the baby release the breast early or switch sides too soon.
3. How does the body produce breast milk?
Breast milk production is influenced by four hormones: estrogen, progesterone, prolactin, and oxytocin. The body's mechanism of producing breast milk is to self-regulate the levels of these hormones to produce milk. Specifically:Estrogen and Progesterone help develop breasts, ready for milk production. These two hormones are released by the placenta during pregnancy. Estrogen is responsible for increasing the size and number of milk ducts, while progesterone helps in the development of follicles and lobules of the milk glands. High levels of estrogen and progesterone inhibit milk production while the baby is in the womb. When the baby is born, the placenta has shed, the levels of these hormones automatically decrease, telling the body that it is time to make milk. Also, nursing mothers should not take birth control pills containing estrogen because it will reduce the amount of breast milk. Prolactin helps produce milk. (lactation reflex) When the baby sucks on the breast, it stimulates the secretion of Porlactin. Prolactin enters the bloodstream, reaches the breast, and causes the breast to produce milk. Most prolactin stays in the blood for about 30 minutes after a feed, so it helps make milk for the next feed. This shows that if the baby suckles a lot, the breast produces more milk. Prolactin is produced more at night which is very helpful to maintain milk production.
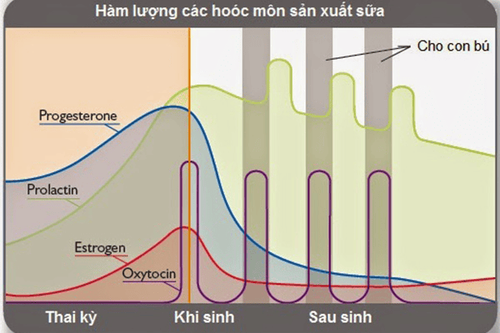
The lactation reflex may occur several times during each feeding, and the mother may feel tingling, slight discomfort in the breasts, or no other sensations. This reflex can also occur when the mother hears her baby cry or thinks about her.
Inhibition of lactation: in breast milk there is a secondary factor called lactation inhibitor. When a large amount of milk is deposited in the breast, an inhibitor is released that stops the breast from making milk. Therefore, in order for the breast to produce more milk, it is necessary to make the breast always empty by feeding the baby often or expressing milk.
4. How to make a mother have enough milk for her baby
When your baby breastfeeds, the stimulation from the baby's sucking action helps the mother release more prolactin hormone which helps the mother's body to produce more milk. This mechanism helps the mother always have enough milk for the next feeding. So, the more often a mother breastfeeds properly, the more prolactin she will have in her blood and the more milk she will produce.According to doctors, women should breastfeed or pump milk within 1 hour after giving birth, feed the baby every 2.5 - 3 hours.
Mothers need to rest, relax and eat enough nutrients; Always keep an optimistic spirit, believe that breastfeeding will bring abundant milk for the baby.
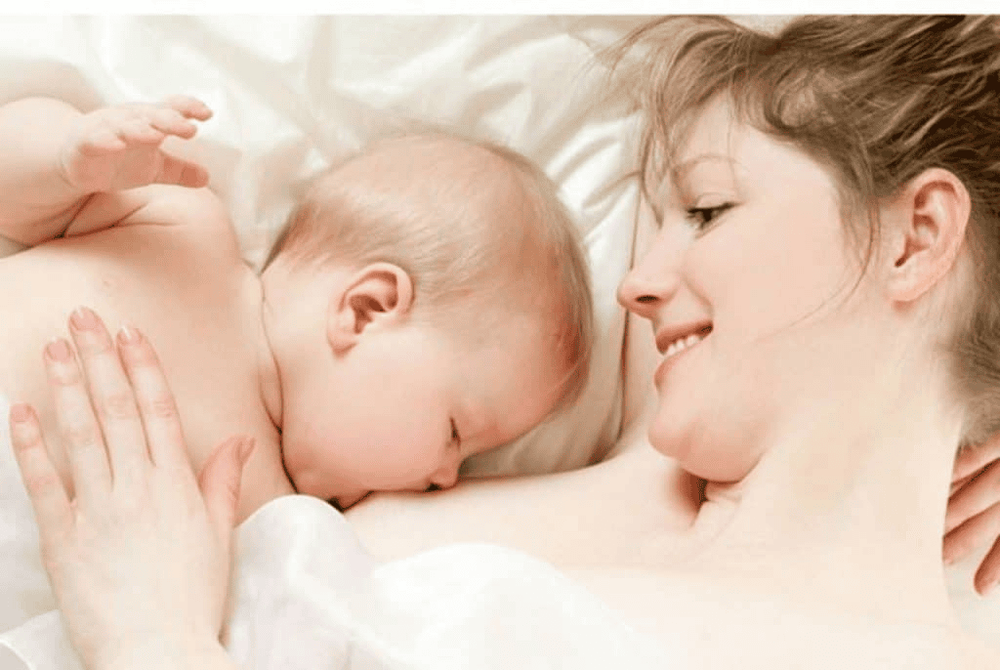

FIL determines the amount of milk in each breast separately. That means that one breast may be low on milk, but the other breast may have enough. So, even if a mother has a blocked milk duct on one breast, she can still breastfeed her baby from the other breast, and mothers of twins can still breastfeed exclusively.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.