This is an automatically translated article.
With a person with diabetes, it is important for them to keep their blood sugar as stable as possible. Good blood sugar control can help prevent or slow the progression of some of the complications of diabetes. Therefore, patients with diabetes need to avoid or minimize foods that cause blood sugar spikes such as bananas.
1. How do bananas affect blood sugar?
1.1. Bananas contain Carbohydrates that raise blood sugar For patients with diabetes, it is very important to be aware of the amount and type of carbohydrates in their diet. Because carbohydrates will raise your blood sugar more than other nutrients. That means those foods can have a big impact on blood sugar control.
When blood sugar levels rise in people without diabetes, their bodies produce insulin, which helps move sugar from the blood into the cells for use or storage.
However, this process does not work effectively in patients with diabetes. These patients' bodies do not produce enough insulin or their cells become resistant to the insulin produced. Since sugar cannot enter the cells, there is a large amount of sugar in the blood.
Therefore, people with diabetes, if they do not know how to eat properly, foods containing a lot of carbohydrates can cause blood sugar spikes or make blood sugar levels rise continuously. Both of these conditions are harmful to a person's health.
About 93% of the calories in bananas come from carbohydrates. Carbohydrates in bananas are in the form of sugars and starches. One medium banana contains about 14g of sugar and 6g of starch.
Thus, bananas contain a lot of carbohydrates that cause blood sugar to rise higher than other foods.

Bên trong chuối chứa Carbohydrate gây ảnh hưởng đến chỉ số đường trong máu
1.2. Bananas also contain fiber, which can lower blood sugar. In addition to starches and sugars, a medium-sized banana contains about 3g of fiber.
Everyone, including diabetics should eat enough fiber due to its health benefits. However, fiber is especially important for people with diabetes, because it can help slow the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. This can reduce blood sugar spikes and improve overall blood sugar control.
One way to determine how a carbohydrate-containing food will affect blood sugar is by looking at its glycemic index (Gl).
The glycemic index classifies foods based on how and how quickly they raise blood sugar. This score is calculated from 0 - 100 with the following classification:
Low Gl: is 55 or less. Moderate Gl: between 56 - 69. High Gl: between 70 and 100. Diets based on low Gl foods are thought to be especially good for people with type 2 diabetes. Due to these foods Low Gl foods are absorbed more slowly and cause blood sugar to rise gradually, rather than suddenly.
Banana has a Gl index of 42 - 62 depending on its ripeness. Thus, bananas have a low to moderate glycemic index.
This way the sugar in bananas is digested and absorbed more slowly, which can prevent blood sugar spikes when eating bananas.
1.3. The effect of bananas on blood sugar depends on how ripe it is. The type of carbohydrates in a banana depends on how ripe the banana is. Green bananas contain less sugar and resistant starch.
Resistant starch is a long chain of glucose (starch) that is “resistant” to digestion in the upper part of our digestive system. This means they work similarly to fiber, so they don't raise blood sugar.
Resistant starch can help feed the beneficial bacteria in the gut, which has been linked to improved metabolism and better blood sugar control.
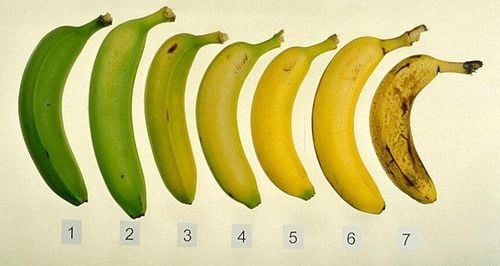
Độ chín của chuối có ảnh hưởng tới lượng đường trong máu người dùng
In fact, people with type 2 diabetes who took the resistant starch supplement had better glycemic control than those who didn't take the resistant starch for a period of 8 weeks. Resistant starch improves insulin sensitivity and reduces inflammation.
However, the role of resistant starch in type 1 diabetes is unclear.
Green bananas contain resistant starch, which does not raise blood sugar but it can even improve long-term blood sugar control.
Ripe bananas contain less resistant starch than green bananas, and contain more sugar, faster starch absorption. This means that ripe bananas will have a higher Gl index and will cause blood sugar to rise faster than green or unripe bananas.
1.4. Banana Size Affects Blood Sugar Ripeness isn't the only factor when it comes to the amount of sugar in each banana. The size of the banana also plays an important role in this regard. The larger the banana, the more carbohydrates.
Means a larger banana will have more of an effect on blood sugar. The size effect on blood sugar is known as the glycemic load. The glycemic load is calculated by multiplying the glycemic index (Gl) by the amount of carbohydrates in a serving, and then dividing it by 100. It is evaluated as follows:
A glycemic load of less than 10 is considered low. . A glycemic load of 11 - 19 is considered moderate. A glycemic load of 20 or more is high. The amount of carbohydrates will depend on the size of the banana, specifically as follows:
Extremely small banana (6 inches or less): 18.5g carbohydrates. Small banana (6-6.9 inches): 23g carbohydrate. Medium banana (7 - 7.9 inches): 27g carbohydrate. Large banana (8 - 8.9 inches): 31g carbohydrate. Extra large banana (9 inches or more): 35g carbohydrate.

Kích thước của quả chuối có thể ảnh hưởng đến lượng đường huyết khi ăn
If all of these fully ripe bananas had a Gl of 62, their glycemic load would range from 11 to 22.
So the size of the banana will determine the effect. to blood sugar levels. The larger the banana, the more carbohydrates it will have and the higher the blood sugar will be.
2. Are bananas safe for diabetics?
Most general dietary guidelines for people with diabetes recommend following a healthy, balanced diet that includes fruit in it.
This is because eating fruits and vegetables has many health benefits and lowers the risk of diseases, such as heart disease, some cancers, etc. People with diabetes are at risk. The risk of these diseases is higher than other people, so it is very important to eat enough fruits and vegetables.
Unlike refined sugar products like candy and cakes, the carbohydrates in fruits like bananas are often accompanied by fiber, antioxidants, vitamins and minerals. More specifically, bananas will provide you with fiber, potassium, vitamin B6, vitamin C and several antioxidants along with beneficial plant compounds.
Some recent studies show that eating less fruit does not improve blood sugar control, weight loss.
For most patients with diabetes, fruit including bananas is a healthy choice. You can eat bananas even if you have diabetes, but pay attention to the ripeness and size of the banana to reduce its effect on your blood sugar levels.

Sử dụng chuối đúng cách sẽ đem lại lợi ích cho sức khoẻ người dùng
3. How to eat bananas for people with diabetes
People with diabetes can absolutely eat bananas as part of a healthy diet. The following tips can help reduce the impact of bananas on blood sugar:
Keep an eye on the size of the banana you plan to eat: eat a smaller banana to reduce sugar in one sitting. eat. Choose a firm, near-ripe banana: choose a banana that's not too ripe for a slightly lower sugar content. Split your fruit intake throughout the day: dividing your fruit intake into portions helps reduce blood sugar spikes, keeping blood sugar stable. Eat bananas with other foods: Enjoy bananas with other foods like nuts and yogurt to help slow down the digestion and absorption of sugar. Customers can directly go to Vinmec health system nationwide to visit or contact the hotline here for support.
Articles refer to sources: healthline.com, webmd.com