This is an automatically translated article.
The article was written by Specialist Doctor I Trieu Thi Hong Thai - Neonatology Department - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.
In adults, ingestion of a foreign body is rare and often accidental. Approximately 80-90% of ingested foreign bodies pass out of the body on their own without any intervention. Endoscopic foreign body removal is only necessary in 10-20% of cases and surgical intervention is less than 1%. Of the entire gastrointestinal tract, the esophagus is the most commonly obstructed site. Foreign bodies or food are often obstructed by physiological or pathological narrowing of the esophageal lumen.
1. Diagnosis of gastrointestinal foreign body
The typical clinical symptom is dysphagia that occurs suddenly. Other symptoms of esophageal obstruction may include choking, unwillingness to eat, increased salivation, fullness and pain behind the breastbone, regurgitation of undigested food, wheezing, and bloody drool.
Drooling with inability to swallow liquids suggests esophageal obstruction. Complications of foreign body ingestion include: perforation, gastrointestinal tract obstruction, aorto-oesophageal fistula, tracheoesophageal fistula.
Take the history to clarify: type of foreign body, time of swallowing foreign body, existing symptoms and progress. Drooling and inability to swallow liquids are indicative of esophageal obstruction and require evaluation for acute endoscopic intervention. Physical examination should carefully examine the oral cavity, pharynx, neck, chest, and abdomen in patients with symptoms of esophageal obstruction or perforation.
Esophageal scintigraphy is performed only in patients without signs or symptoms suggestive of esophageal obstruction, if the history is taken with the ingestion of a non-sharp, contrast-enhanced foreign body, or it is unclear what type of foreign body may be present. drug-free imaging.

Computed tomography to evaluate the following conditions:
Suspected gastrointestinal perforation based on other imaging evidence Ingestion of sharp objects Patients suspected of ingesting packets of drugs or other drugs The localization of the foreign body helps to guide the necessary interventions, but the failure to locate the foreign body does not rule out its existence. In patients with suspected ingestion of boneless food and no evidence of complications, endoscopic intervention is possible without prior radiographs. Patients with persistent esophageal symptoms should be evaluated endoscopically even if radiographic findings are unremarkable.
2. Interventional treatments
Choice of intervention method depends on the following factors:
Type of foreign body swallowed (size, sharp or not? What substance does it contain? ) Location of foreign body obstruction Symptoms and severity

In general, conservative treatment is appropriate for most cases of foreign body ingestion when the foreign body moves without incident. The timing of endoscopic intervention varies depending on the clinical picture and the type of foreign body.
All esophageal foreign bodies should be removed within 24 hours. Most foreign bodies that have reached the stomach can be out in 4-6 days, conservative treatment is appropriate for the majority of patients who have swallowed a foreign body and are asymptomatic.
Necessary endoscopic intervention for foreign bodies: sharp, magnetic, foreign bodies longer than 5cm or >2cm in diameter, disc batteries in the stomach for more than 24 hours.
Patients after successful endoscopic foreign body removal still need to be hospitalized in the following cases:
Ingestion of many foreign bodies with high risk of complications (eg, sharp objects, batteries, magnetic objects, objects with size > 5cm ... ) Extensive mucosal injury due to foreign body ingestion or removal.
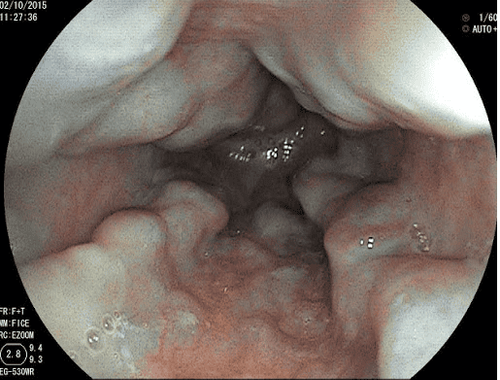
If the foreign body cannot be removed endoscopically, take daily X-rays to monitor the movement of the foreign body. Surgical intervention is only reserved for patients with complications (perforation, obstruction) and cases where the foreign body has not moved (non-sharp object remains in the duodenum for more than 1 week or sharp object does not change position in 3 weeks). day).
Foreign body or food residue has a recurrence rate of 10-20%. Repeat endoscopy is necessary to assess mucosal healing in patients with extensive mucosal lesions at initial colonoscopy.
Endoscopy for biopsies to diagnose eosinophilic esophagitis or to intervene for structural abnormalities (eg, dilation of esophageal strictures, Schatzki's ring) if initial colonoscopy has not been performed. Patients without structural abnormalities should be examined for abnormalities of esophageal motility.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.