This is an automatically translated article.
The glycemic index of foods shows how much a food affects blood sugar. Factors that affect a food's glycemic index (GI) include carbohydrates, glycemic load, method of preparation, and other toppings.
1. What is the glycemic index of foods?
The glycemic index (GI) of foods is a scale that evaluates the ability of foods that contain carbohydrates to raise blood sugar. The purpose of the initial development of the GI food glycemic index scale was to guide food choices for people with diabetes. Similar to calculating calories or carbs in a diet plan, the glycemic index of a food is also one of the tools to guide food choices and menu planning.There are different research methods for assigning GI values to foods. Overall, this number is based on how much a food raises blood sugar versus how much pure glucose raises blood sugar. The glycemic index value in food is generally divided into 3 categories:
Low GI: 1 to 55; Average GI: 56 to 69; High GI: 70 or more; Comparing these values can help people make healthier food choices. For example, a muffin made with white flour has a GI value of 77. While the same muffin made with whole wheat has a GI of only 45.
2. Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates, or carbs, are a nutrient found in foods. The three basic forms of carbs are sugar, starch, and fiber. When you eat or drink something with carbs, your body breaks down sugars and starches into glucose. This is the main source of energy for the cells in the body, while fiber will go in and out of the body without being digested.
The pancreas produces 2 main hormones that help regulate blood glucose:
Insulin hormone: Moves glucose from the blood into the cells; The hormone glucagon: Releases glucose stored in the liver when blood glucose levels drop. This process keeps the body refueled and ensures a natural blood sugar balance. Different types of carbohydrate-containing foods will be related to how quickly the body digests food and gets glucose into the bloodstream.
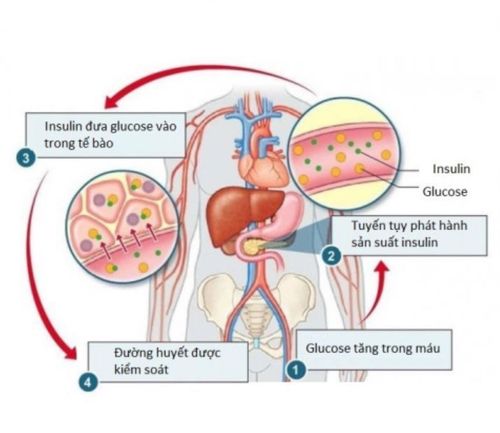
Insulin được sản xuất từ tuyến tụy và di chuyển glucose từ máu vào các tế bào
3. Glycemic load GL
A limitation of the glycemic index in foods is that it does not reflect the amount allowed to eat a particular dish. For example, watermelon has a high GI value of 80, which should be included in the list of foods to avoid. But an average serving of watermelon has relatively few net carbs, or digestible carbohydrates. Thus, you have to eat a lot of watermelon to significantly increase blood sugar levels.
To solve this problem, researchers developed the concept of glycemic load (GL). This value indicates the change in blood glucose levels when you eat a typical serving. For example, a 120-gram watermelon has a GL value of 5, and an 80-gram serving of raw carrots has a GL value of 2, suggesting these are healthy food choices.
Tables of glycemic load GL values are generally classified in the following way:
Low GL: 1 to 10; Average GL: 11 to 19; High GL: 20 or more.
4. Other influencing factors
The glycemic index of foods GI does not give information about the nutritional information of the food. For example, 1 cup (250 ml) of whole milk has a GI value of 31 and a GL value of 4. But because of its high fat content, whole milk is not a good choice for weight loss or weight control. .
Published glycemic index lists of foods are also not exhaustive of all foods. So many foods with healthy carbs are not properly researched and evaluated.
The glycemic index of foods is also affected by a number of other factors, including how it is prepared, packaged, and what other dishes are served with.
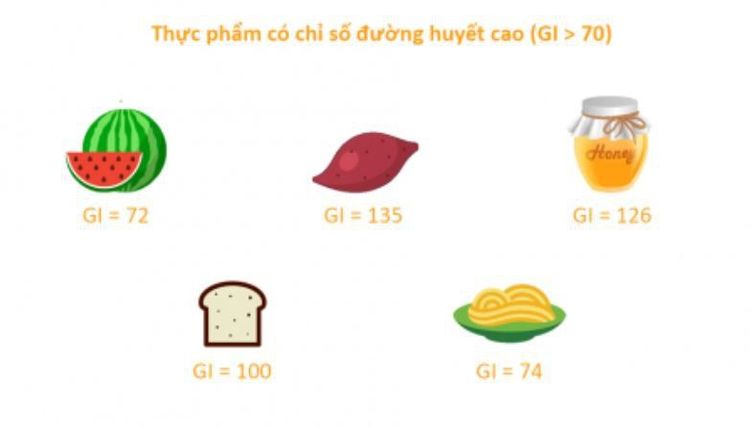
Mỗi loại thực phẩm lại có giá trị GI khác nhau
5. Low GI Diet
Examples of foods with low, medium and high GI values include:
Low GI: Green vegetables, most fruits, raw carrots, kidney beans, chickpeas, lentils and whole grains bright whole grains; Medium GI: Sweet corn, banana, raw pineapple, raisins, oat breakfast cereal or rye bread; High GI: White rice, white bread, and potatoes. In general, foods with a low glycemic index are digested and absorbed relatively slowly. In contrast, high-value items are absorbed quickly. Diets based on the food glycemic index do not specify optimal portion sizes, calorie counts, carbohydrates, or fats.
Studies show that the GI diet can help achieve the following goals:
Lose weight or maintain a healthy weight; Need to plan healthy meals; Maintain stable blood sugar levels to control diabetes. However, you can still achieve the same health benefits with an otherwise healthy diet that combines maintaining a healthy weight and getting enough exercise.
Several clinical studies have shown that a low GI diet can help people with diabetes control blood sugar. However, a low-calorie, high-fiber menu will have the same effect.
In a nutshell, the purpose of calculating the glycemic index of foods is to limit carbohydrate-containing items that cause significant blood sugar spikes. This diet also works to lose weight and prevent obesity-related chronic diseases, such as diabetes and heart disease. It is advisable to consult a doctor before starting any diet, especially if you have health problems, including diabetes.

Chế độ ăn kiêng GI thấp với những loại rau xanh giúp duy trì cân nặng khỏe mạnh
Currently, Vinmec International General Hospital is providing a Diabetes Screening Package to help patients detect the disease early and improve treatment efficiency.
To register for an examination at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact the nationwide Vinmec Health System Hotline, or register online HERE.
References: mayoclinic.org; diabetes.org