This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by MSc Duong Xuan Loc - Gastroenterologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. Doctor has more than 12 years of experience as a Gastroenterologist.Esophageal varices is a dangerous disease that can completely cause death for patients because esophageal varices rupture causing blood loss. To limit the risk of dangerous complications of esophageal varices. Patients need to be treated early and in accordance with each level of disease as prescribed by the doctor.
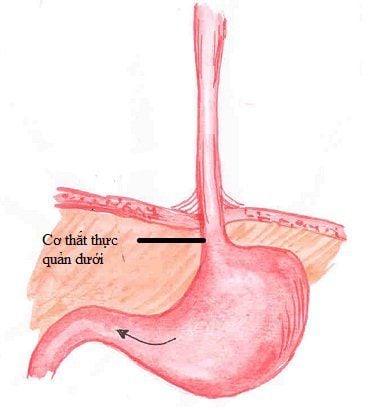
1. What is esophageal varices?
Esophageal varices are abnormalities in the lower part of the esophagus (the tube that connects the esophagus to the stomach). This is a manifestation of portal hypertension syndrome. It is produced by the splenic vein, superior mesenteric vein, and inferior mesenteric vein. The inferior mesenteric vein usually drains into the splenic vein near the confluence of the splenic and superior mesenteric veins.Esophageal varices can rupture causing bleeding, if not treated promptly, will be the leading cause of death.
2. Causes of esophageal varices
Cirrhosis is the main cause of esophageal varices. Nearly 30% of cirrhotic patients account for 80-90% of bleeding cases in cirrhotic patients.Some other causes of esophageal varices can be attributed to blood clotting , blood clots in the portal vein or in the veins that feed into the portal vein called the splenic veins can cause dilatation esophageal veins. Patients infected with parasites can damage the liver, lungs, intestines, bladder and also cause esophageal varices. In rare cases in patients with hepatobiliary regurgitation syndrome, Budd-Chiari syndrome causes blood clots to block the veins that carry blood to the liver, causing varicose veins.
3. Symptoms of esophageal varices
Black stools Frequent nausea, vomiting, vomiting blood Dizziness, loss of control, or worse, loss of consciousness Some symptoms of liver disease such as jaundice, abdominal distension, ascites, yellow eyes.4. Complications of esophageal varices
The most dangerous condition of varicose veins is indeed bleeding. When the patient has bleeding esophageal varices, there will be many other dangerous risks. In case the patient burns a large amount of blood, it is easy to cause shock and does not give emergency treatment in time, the risk of complete death occurs.Statistics show that up to 50% of patients with cirrhosis have true varicose veins, this number increases by about 5-10% every year. When esophageal varices have severe complications, the vein ruptures. At this time, if not accompanied by cirrhosis, the mortality rate is from 5 to 10%. If accompanied by cirrhosis, the mortality rate is up to 40-70%. For patients with ruptured esophageal varices, 40% of cases stop bleeding spontaneously. However, within 6 weeks there is 30% rebleeding and within 1 year, the recurrence rate is up to 70%.
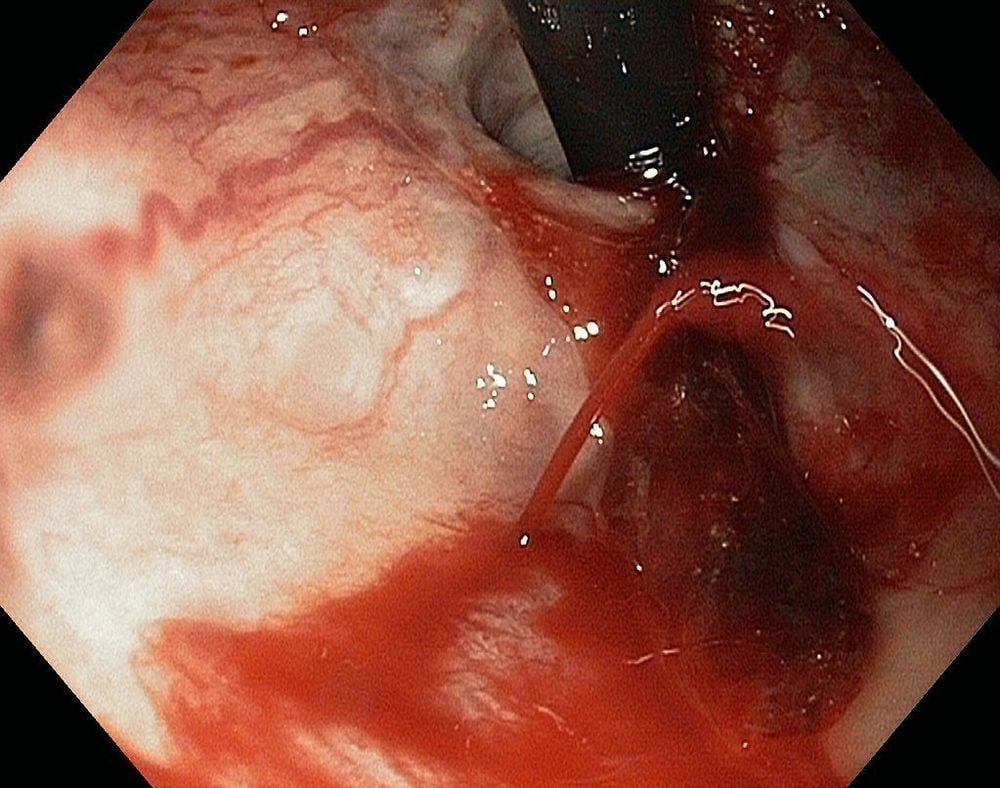
5. Treatment of esophageal varices
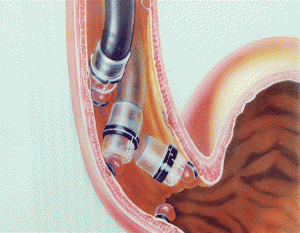
In order to limit the risk of dangerous complications of esophageal varices, the patient should be treated early and in accordance with the severity of the disease as prescribed by the doctor.In the case of patients with esophageal varices that have not yet bled, it can be treated with drugs that slow the flow of the portal vein such as propranolol and nadolol. In the case of severe varicose veins that are likely to burst, the doctor will prescribe ligation of the esophageal varices with a rubber ring to stop the bleeding.
Patients with varicose veins causing bleeding should be stopped by techniques such as ligation when bleeding is not too serious; portal vein catheterization, medication to slow blood flow, antibiotics to prevent infection, or a new liver transplant.
Depending on the patient's condition, the doctor will decide to treat with an appropriate method or combine methods together to increase the effectiveness of treatment for the patient.
If there are signs of esophageal varices mentioned above, you need to go to the hospital immediately for diagnosis, detection and treatment orientation as soon as possible.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
See also:
How long is the esophagus? Common diseases of the esophagus Esophageal atrophy: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment Gastroesophageal reflux disease: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment