This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor II Dinh Van Loc - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Cerebrospinal fluid leak is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid escapes into the skull base, when the cerebrospinal fluid leaks into the skull base, it can compress and damage nerve cells, if not treated, it can cause complications. dangerous disease. Endotracheal anesthesia is a general anesthetic method commonly used in surgery to treat cerebrospinal fluid leaks in the skull base.
1. Outline
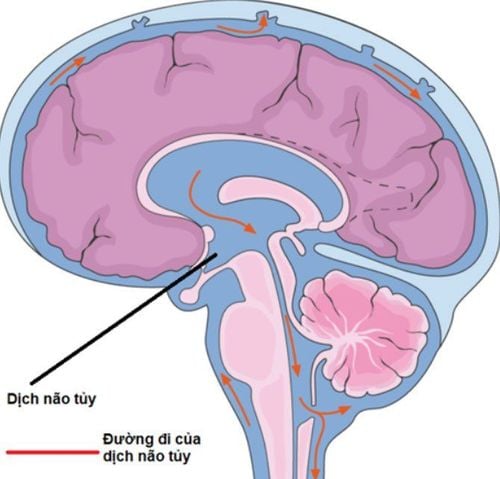
Cerebrospinal fluid is a colorless fluid made from a group of cells, flowing around the brain and spinal cord with the function of participating in the nutritional and metabolic tasks of the central nervous system; It is a buffer between the brain and spinal cord, helping to reduce mechanical trauma directly affecting the brain and spinal cord.CSF leak is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid leaks out of the skull base through a tear in the dura mater. Cerebrospinal fluid leaks at the base of the skull may occur after trauma. CSF leakage is indicated for surgery when medical treatment fails.
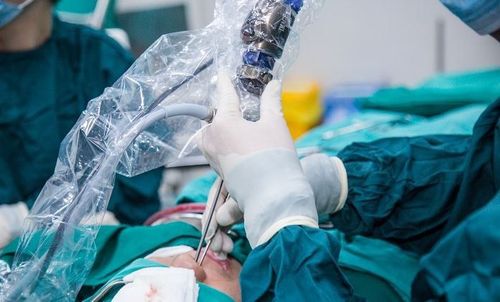
Endotracheal anesthesia is a method of general anesthesia with endotracheal intubation with the aim of controlling breathing during surgery and resuscitation after surgery to treat cerebrospinal fluid leakage.
Indications: Endotracheal anesthesia is indicated in case of endoscopic surgery to treat cerebrospinal fluid leak in the skull base or to seal the fistula of cerebrospinal fluid.
Contraindications:
Patient does not agree to cooperate. Insufficient means and not technically proficient.
2. Endotracheal anesthesia procedure
2.1 Preparation
Performer: Doctor and nurse of the department of anesthesiology and resuscitation. Facilities: Anesthesia machine system with ventilator; hand squeeze oxygen source; monitor vital functions (electrocardiogram, arterial blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2, breathing rate, temperature); defibrillator, phlegm aspirator.Laryngoscope, endotracheal tube of various sizes, suction tube, mask, abu squeezing ball, oropharyngeal cannula, Magill pliers, soft mandrin.
Drugs: Used in anesthesia resuscitation and treatment of possible complications.
Prophylaxis in case of difficult intubation: Cook tube, laryngeal mask, flexible bronchoscope, tracheostomy kit, mouth opener...
Patient: Full anesthetic examination before during surgery to detect and prevent possible complications.
Advice and explanation of possible complications during laparoscopic anesthesia.
Evaluation of cases at risk of difficult intubation.
Use sedation the night before surgery if the patient is too nervous.
2.2 Steps to take
Patient:Patient position: Lie on back, breathe 100% oxygen 3-6 l/min before induction of anesthesia for at least 5 minutes. Install a vital signs monitor, pay attention during laparoscopic surgery to have EtCO2 parameters. Establish effective communication. Pre-medication. Anesthesia:
Patients can be induced by intravenous anesthetic, inhalation anesthetic or a combination of both. Combine some drugs to increase the effect of anesthetics, including: Opioid pain relievers, muscle relaxants if needed. Oral endotracheal intubation: The condition for intubation is that when the patient is in deep sleep, muscle relaxation is sufficient in most cases to avoid stimulation causing increased intracranial pressure.
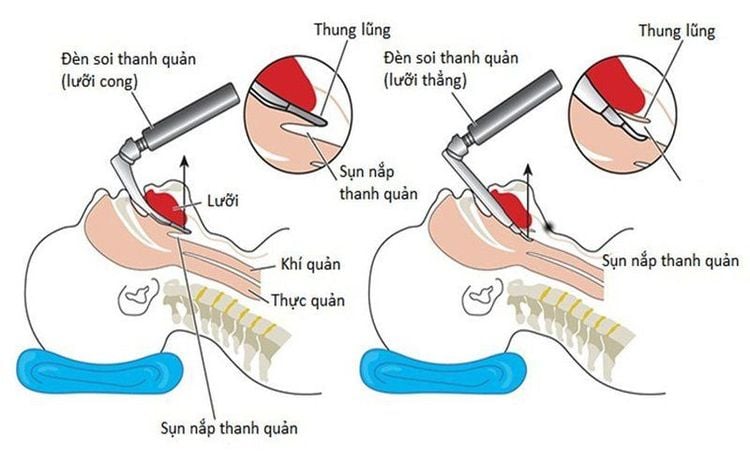
Open the patient's mouth, put one hand under the neck to help straighten the neck, insert the laryngoscope to the right of the mouth, move the tongue to the left, push the lamp deeply, coordinate with the right hand to press the cricoid cartilage to find the epiglottis and glottis hole. Perform rapid induction of anesthesia and the Sellick maneuver in cases where the patient's stomach is full (press the cricoid cartilage 20-30 kg as soon as the patient loses consciousness until the intubation is complete) Intubate the endotracheal tube gently through glottis, stopping when the balloon of the endotracheal tube passes about 2-3 cm through the vocal cords. Remove the laryngoscope and inflate the endotracheal balloon. Check the correct position of the endotracheal tube with auscultation and EtCO2 results. Secure the tube with tape and place the cannula in the mouth to avoid biting the tube (if necessary). In the case of difficult intubation, the difficult intubation procedure is applied. Maintenance of anesthesia: Maintain anesthesia with intravenous or inhalation anesthetics, analgesics and muscle relaxants (if necessary).
Monitor:
Need to control breathing with anesthetic ventilator Monitor depth of anesthesia based on heart rate, blood pressure, sweating, lacrimation... Monitor vital signs: heart rate , blood pressure, SpO2, EtCO2, body temperature. Preventing cases of endotracheal intubation in the wrong position, folding, and obstruction.
2.3 Standards for extubation
When surgery is completed, the endotracheal tube should be extubated when the following criteria are met:The patient is awake and able to follow orders. The patient raised his head on his own for more than 5 seconds, TOF > 0.9 . Breathe spontaneously, breathing rate within normal limits. Pulse and blood pressure are stable. Body temperature > 36 degrees C. No complications of anesthesia and surgery.
3. Complications and how to deal with them
3.1 Reflux of gastric juice into the airway
Signs: There is digestive juices in the oral cavity and airways. Treatment: Remove the fluid in the oral cavity, the patient lies with his head low, tilting his head to one side; Rapid intubation of the endotracheal tube and aspiration of gastrointestinal fluid from the airway; Monitor and prevent respiratory infections.3.2 Hemodynamic disorders
May experience hypotension or hypertension , arrhythmias (bradycardia, tachycardia, arrhythmia). Depending on the signs of the disorder to take measures to handle.3.3 Complications due to intubation
Intubation is not possible: It should be handled according to the difficult intubation procedure or if still unable to be intubated, need to switch to another method of anesthesia. Misplaced in the stomach: Signs: Auscultation of the lungs without alveolar murmurs, no measurement of EtCO2. Treatment: Reinsert the endotracheal tube. Vocal, air, bronchial spasms Difficult or impossible to auscultate pulmonary ventilation, auscultation with rales or muted lung. Management: Provide adequate oxygen, add hypnotics and muscle relaxants, ensure ventilation and give bronchodilators and corticosteroids; If breathing is not controlled, a difficult intubation procedure should be used. Trauma when intubation: Hemorrhage, tooth fracture, vocal cord injury, foreign body falling into the airway... Treatment depends on each specific injury.3.4 Respiratory complications
Bend or retract the endotracheal tube causing the endotracheal tube to be pushed deep into one lung, collapse or open the respiratory system, running out of oxygen...Treatment: Need to immediately ensure ventilation and provide 100% oxygen , solve the cause of endotracheal tube collapse and retraction.
3.5 Complications after extubation
After extubation, the patient may experience conditions such as: Respiratory failure, hoarseness, laryngotracheal-bronchospasm, respiratory inflammation ...Depending on each case to take measures handling.
Endotracheal anesthesia in endoscopic surgery to treat cerebrospinal fluid leaks in the skull base is a technique that requires a system of modern equipment and skilled technicians. To limit the complications caused by surgical anesthesia, patients should choose reliable treatment sites.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.