This is an automatically translated article.
Anesthesia is considered safe even if you have health problems. But with any medication or medical procedure, some side effects are possible.1. Short-term side effects of anesthetics
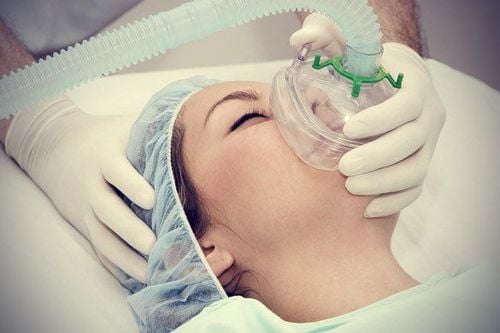
Most side effects of anesthesia happen right after you have surgery and it usually doesn't last long. Once the surgery is over and the anesthetic is stopped, you will slowly return to normal in the operating room or recovery room. However, you may feel a little wobbly. In addition, you may also feel any of the following common side effects:
Nausea and vomiting . This is one of the side effects that usually occurs right after the procedure and some people may continue to feel tired for a day or two. Nausea and vomiting are more likely to occur when you need to have prolonged procedures. In this case, anti-nausea medication can be effective. Dry mouth . You may feel a dry mouth. If you're not too nauseous, you can take a sip of water to make your mouth less dry. Sore throat or hoarseness. During surgery, a tube is inserted into your throat to help you breathe and it can cause a sore throat after it is removed. Chills and shivers. It is common for your body temperature to drop during anesthesia. The doctors and nurses will make sure your temperature doesn't drop too much during surgery, but afterward, you may feel shivery and cold. Your chills can last a few minutes to hours. Confusion and blurred thinking. After the medicine wears off, you may feel confused or drowsy. This usually lasts only a few hours, but for some people, especially older adults, the confusion can last for days or weeks. Muscle pain. During surgery, you will likely be given medications to relax your muscles, and it may cause soreness afterward.
Itchy . If you use opioids during or after surgery, you may experience itching. This is a common side effect of this class of drugs. Bladder problems. You may have difficulty urinating for a short time after general anesthesia. Dizzy . This is a common feeling the first time you stand up after surgery. Impaired coordination or judgment may be due to the effect of the general anesthetic on the central nervous system. You may feel drowsy, weak, or tired for a few days and experience blurred vision and blurred thinking. You should not drive, operate machinery, or perform other activities that could endanger yourself or others for 24 hours or longer.

Sau dùng thuốc gây tê người bệnh có thể gặp tình trạng buồn nôn
2. Long-term side effects of anesthetics
In most cases we will not experience any long-term side effects. However, older adults are more likely to experience longer-term side effects. Side effects may include:
Postoperative delirium. After surgery, some people may become confused, disoriented, or have trouble remembering things after surgery. This state can come and go, but it usually goes away after about a week. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction (POCD). After surgery, some people may experience memory problems or other forms of cognitive decline. This may be a side effect of surgery rather than medication. Some studies show that people over 60 are more likely to have POCD. You may also be more likely to develop POCD if you have:
Have a stroke Heart disease Lung disease Alzheimer's disease Parkinson's disease
3. Factors that increase the risk of side effects
For the most part, anesthesia is very safe but the surgical procedure itself puts you at risk. Older adults and those with lengthy procedures are at greater risk of side effects.
If you have any of the following conditions, tell your doctor because these conditions can affect your health during and after surgery:
History of adverse reactions to local anesthetics Apnea at Sleep Convulsions Obesity High blood pressure Diabetes Heart disease Lung disease Kidney disease Drug allergies You should also tell your doctor if you are a smoker, drink a lot of alcohol or are taking blood thinners.

Người có bệnh lý tim mạch nên thông báo với bác sĩ trước khi sử dụng thuốc gây tê
Although generally very safe, no procedure is without some risks and the anesthesiologist will discuss this with you prior to surgery. Many factors contribute to the increased safety of anesthesia including the use of safer drugs, more extensive training of anesthesiologists, and national standards of care.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to sources: healthline.com, hopkinsmedicine.org