This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Thai Hung - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Eyes have a very important role so eye emergency should be performed as soon as possible eye damage is suspected. Ophthalmoscopy is an important examination step, helping to detect eye injuries early for timely monitoring and treatment to avoid complications that damage the patient's vision.
1. What is ophthalmoscopy?
Ophthalmoscopy is an important examination performed by an ophthalmologist to look at the structures inside the eyeball.Ophthalmoscopy helps detect diseases of vitreous (transparent environment of the fundus), retina, optic nerve (optic nerve),... Early detection of lesions helps doctors monitor and manage timely treatment, thereby reducing the risk of complications that damage the patient's vision.
2. When is ophthalmoscopy needed?
Ophthalmoscopy is indicated when screening for eye diseases or conditions that may affect blood vessels, including:Damage to the optic nerve Retinal tear or detachment Glaucoma ( Glaucom) Loss of sharp vision due to aging (macular degeneration). Retinitis Hypertension Diabetes mellitus Melanoma skin cancer

3. When is emergency ophthalmoscopy performed?
Emergency ophthalmoscopy is performed in systemic diseases to coordinate treatment and prognosis and is a delayed emergency procedure.Ophthalmoscopy is indicated in all for emergency fundus examination in the intensive care unit or emergency bed, it is necessary to observe the condition of the retina, optic disc, and macula, with or without damage to the fundus. related to systemic emergency diseases such as: poisoning with chemicals, drugs, alcohol, asphyxiation, drowning, infectious diseases causing fundus hemorrhage....
4. Ophthalmoscopy methods?
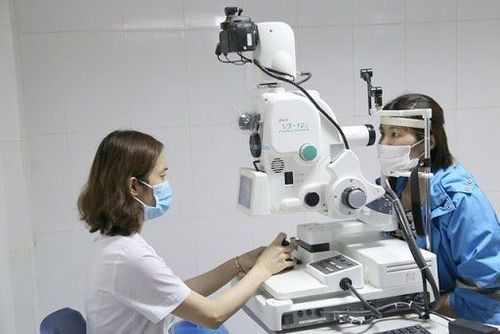
Currently, there are two main methods of ophthalmoscopy:Direct ophthalmoscopy: usually performed in a dark room. The patient will be asked to remove contact lenses (if present), keep their eyes looking straight ahead, and keep their head still. The doctor will shine the light directly into the patient's eyes. Direct ophthalmoscopy for virtual and lateral images, magnifying the image 10-15 times. Observation of the eye area is limited (10 - 15 degrees) and difficult to see if the environment is cloudy. This procedure can be done with or without dilated pupils. Indirect ophthalmoscopy, also known as inverted ophthalmoscopy. The indirect ophthalmoscope is worn over the doctor's head and the patient is asked to lie down or sit in a prone position. The indirect ophthalmoscopy method gives real and inverted virtual images, magnifying the image 2 - 5 times. This is a difficult method to perform and requires specialized tools and higher skills. However, this method has advantages over direct ophthalmoscopy, because the doctor can see better in the eye if there is a cataract. At the same time, a 3-D image of the back of the fundus can be viewed to help the doctor identify certain eye conditions such as growths, optic nerve edema, or if the retina is detached. In addition, indirect ophthalmoscopy also helps the doctor see a larger area (160 degrees) than direct ophthalmoscopy.
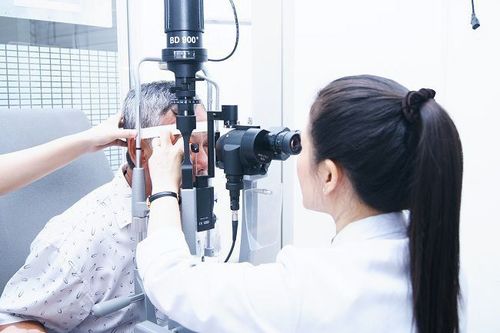
5. How is ophthalmoscopy performed?
5.1. Preparation of Personnel: Ophthalmologist Equipment: Direct ophthalmoscope or indirect ophthalmoscope, rim rim, scleral compression, pupil dilator (Mydrin-P) Before performing fundoscopy The patient was explained about the purpose and procedure and was given Mydrin-P 0.5% pupil dilator drops before ophthalmoscopy 10 - 15 minutes. If the patient is comatose, numb the eyeball with 1% dicaine solution or 0.1% tetracaine solution, after 5-10 minutes place the rim of the eyelid into the eye to be examined.5.2. Ophthalmoscopy is usually done in 5-10 minutes according to the following steps:
The doctor faces the patient, the doctor's right eye examines the patient's right eye or vice versa when looking at left eye fundus. The doctor observes the patient's retinal condition, the patient's optic disc, the patient's macula, and assesses the condition of related damage. In cases where the patient's retina cannot be seen, adjust the lens system on the ophthalmoscope to a diverging or converging lens to observe the patient's fundus image. The scope of the fundus being observed is very narrow, less than 1mm wide, so the illuminator must be placed very close to the patient and moved around the areas of the fundus. For young patients, uncoordinated can be anesthetized the surface of the eyeball and use the rim of the eyelids for ophthalmoscopy. Fundus dilation is a fairly safe procedure, with patients having almost no complications. In rare cases, the patient may experience discomfort from the eye drops or from the light of the lamp. If there is a side effect of mydriasis, the eyeball surface should be numbed, immediately stop applying the drug, wash the eyes with physiological saline. The doctor will carefully monitor the patient's progress to have appropriate treatment.
Eye Specialist - Vinmec International General Hospital always receives and handles patients who are having eye problems. With a system of modern equipment and a team of experienced doctors, they will directly examine and advise on the best treatment for the current condition. All procedures are carried out in a methodical and intensive manner, so customers can be assured of medical services at Vinmec.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.