This is an automatically translated article.
The correct and prompt diagnosis of eye diseases, especially fundus disease is very important, helping to slow down the progression of the disease, improve the health and existing vision of the eye. The following article will give indications for fundus imaging for patients.
1. Fundus photography, what is ophthalmoscopy?
Diagnosis of eye diseases is made by ophthalmologists, through a comprehensive eye examination which may include visual acuity examination, fundus examination with dilated pupils, fluorescein angiography , ophthalmoscopy, OCT retinal tomography and fundus color imaging. Ophthalmoscopy is a test that allows your doctor to see the inside of the back of the eye including the retina - optic disc - blood vessels, collectively known as the fundus. With a fundus exam, doctors can also see other structures in the eye. The doctor will use a magnifying glass called an ophthalmoscope and a light source to see the inside of the eye. The test is done as part of an eye exam. It may also be done as part of a routine physical exam.
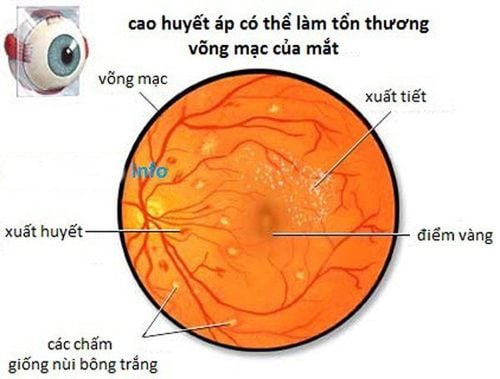
The basal region has a layer of nerve cell membranes called the retina. The retina detects the images that pass through the clear outer coating of the eye, called the cornea. The foundation also contains blood vessels and the optic nerve.
2. Indications for fundus photography or ophthalmoscopy Ophthalmoscopy is considered to have an accuracy of 90% to 95%. It can detect the early stages and effects of many serious diseases. Indicated in cases of:
Damage to your optic nerve Retinal tear or detachment Glaucoma, which is excessive pressure in your eyes Macular degeneration, loss of vision in the center of your vision your cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis, an infection of your retina Melanoma, a type of skin cancer that can spread to your eyes Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure Diabetes For conditions that cannot be detected by ophthalmoscopy, other techniques and equipment are used.

Chụp hình đáy mắt được chỉ định trong các trường hợp như thoái hóa điểm vàng, mất thị lực, viêm võng mạc,...
3. Steps to Take There are different types of ophthalmoscopy.
Direct Ophthalmoscopy : You will be seated in a dark room. An ophthalmologist will sit across from you and use an ophthalmoscope to examine your eyes. They perform this test by shining a beam of light through your pupil with an instrument called a ophthalmoscope. eye. An ophthalmoscope is an instrument with a light and several small lenses on it. Your eye doctor can look through the lens to examine your eyes. They may ask you to look in certain directions as they conduct the test.
Indirect ophthalmoscopy: You will lie down or sit in a semi-reclining position. Your doctor will keep your eye open while shining a very bright light into your eye with an instrument worn over your head. (The instrument looks like a miner's lamp). Your doctor views the back of your eye through a lens that is held close to your eye. Some pressure can be applied to the eye using a small, blunt probe. You will be asked to look in different directions. This test is often used to check for retinal detachment.
Ophthalmoscopy with a slit lamp : You will sit on a chair with a musical instrument placed in front of you. You will be asked to rest your chin and forehead on a support to keep your head stable. The doctor will use the microscope part of the slit lamp and a small lens placed near the front of the eye. They may ask you to look in different directions and use their fingers to open your eyes so they can see better. They may also put some pressure on your eye using a small, blunt probe. This allows doctors to see the same way with this technique as with indirect ophthalmoscopy, but with higher magnification.
The endoscopic fundus exam takes about 5 to 10 minutes.
4. What do I need to prepare for the ophthalmoscopy? The first thing doctors will do is use medicine to dilate your pupils, making them larger and easier to see through.
These eye drops can make your vision blurry and sensitive to light for several hours. You should bring sunglasses to your appointment to protect your eyes from glare while your pupils are dilated. And you should arrange for someone to drive you home after the test is over. If you do work that requires clear vision, such as operating heavy machinery, you should also arrange to rest during the day.
If you are allergic to any medications, tell your eye doctor. They will likely avoid using eye drops if you are at risk for an allergic reaction.
Some medications can also interact with eye drops. It's important to tell your eye doctor about any medications you use, including over-the-counter, prescription, and dietary supplements.
Finally, you should tell your eye doctor if you have glaucoma or a family history of glaucoma. They probably won't use eye drops if they know or suspect that you have glaucoma. The drops may increase the pressure in your eye too much.
5. Is ophthalmoscopy uncomfortable? Live Ophthalmoscopy
During this test, you may hear a clicking sound as the tool is adjusted to focus on different structures in the eye. The light is sometimes very strong, so you may see the spots for a short time after the test. Some people report seeing bright spots or branching images. These are really just the outlines of the blood vessels of the retina.
Indirect ophthalmoscopy
With this test, the light is much stronger. It can be a bit painful. Pressure on your eyeball with a blunt instrument can also hurt a little. The sensation of seeing images after scanning may be greater. If the test is painful, let your doctor know.
When diluting eye drops are used
Diluents can sting your eyes and give you a medicinal taste in your mouth. You will have difficulty focusing your eyes for up to 12 hours. Your distance vision is usually not affected as much as your near vision. Your eyes can be very sensitive to light.

Sau khi thực hiện soi đáy mắt, có thể đôi mắt của bạn sẽ rất nhạy cảm với ánh sáng
6. Risks of Ophthalmoscopy Ophthalmoscopy is sometimes uncomfortable but does not cause pain. You may see an afterimage after turning off the light. Those afterimages will disappear after you blink a few times.
In some cases you may experience some of the following side effects:
Dizziness Dry mouth Nausea Flushing of the face If narrow-angle glaucoma is suspected, eye drops are not usually used.
To examine and treat eye diseases, you can go to the Eye specialist - Vinmec International General Hospital. The department has a comprehensive vision and eye health care function for children, adults and the elderly including refractive error testing, general examination, diagnostic ultrasound, laser treatment and surgery. In addition, ophthalmology also has the task of coordinating with other clinical departments in the treatment of pathological complications and eye injuries caused by accidents.
Why should you choose to examine and treat eye diseases at Vinmec International General Hospital?
Simple and quick procedure. Enthusiastic advice and support, reasonable and convenient examination process. Comprehensive facilities, including a system of clinics and consultations, blood collection room, dining room, waiting area for customers... The medical staff has high professional qualifications, style. Professional, caring way of working.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: ucsfhealth.org