This is an automatically translated article.
Inflammatory diseases with bacterial infections of the eye are very common, this can be caused by direct infection or bacterial superinfection. At that time, antibiotics were the drug of first choice. Intended for local effects, antibiotic eye ointments, ointments containing antibiotics are often indicated in ophthalmology.
1. What is antibiotic eye ointment?
Antibiotics are commonly used to treat inflammatory conditions associated with eye infections. The drug is used topically, subconjunctival or systemic to treat these lesions. Some antibiotics used only in dosage form are eye ointments (small and ophthalmic) such as bacitracin, neomycin, polymyxin B...
Antibiotic eye ointments and eye drops are usually prescribed by doctors for treatment. eye infections such as: blepharitis, conjunctivitis, keratitis, corneal ulcer, eyelid inflammation, chalazion, stye...
So can eye ointment treat acne? The answer is no, ophthalmic ointments are made for bacterial infections in the eye and are not effective against infections elsewhere in the body.
Antibiotic eye ointment has the disadvantage of narrow spectrum of action, easy to cause allergies and often favors the emergence of resistant strains. To increase the effectiveness of treatment, it is necessary to combine eye ointment with an antibiotic or another antiseptic.
Like oral antibiotics, antibiotics in the form of eye drops or eye drops can still cause complications, especially when used incorrectly or in the wrong way.
MORE: Antibiotic ointment: Uses, indications and notes when using
2.Classification of antibiotic eye ointment
2.1. Group of drugs containing only antibiotics Drugs containing only antibiotics range from common drugs such as chloramphenicol, tetracycline to brand name drugs containing strong antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin, moxifloxacin...
Beta-lactam group (including penicillin and cephalosporin groups): This is These antibiotics are effective against eye infections. However, the ability of bacteria that secrete penicillinase and beta-lactamase to become resistant to antibiotics requires the doctor to choose the right group and generation of drugs. The biggest disadvantage of this group is that it is easy to cause allergic reactions (sometimes very serious) so it should be used with caution, especially for children; Chloramphenicol: The advantage of this group of antibiotic eye ointments is a wide spectrum of action (both gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria), the ability to enter the anterior chamber well, and low allergy, so the level of use is very common. variable. The side effect of Chloramphenicol is bone marrow depression, so it is contraindicated for young children; Aminoglycoside group: 1st generation drugs (such as neomycin, kanamycin, framycetin) are mainly used for prophylaxis. 2nd generation drugs (gentamycin, neomycin) are less allergenic and have a broad spectrum of action; Cyclic group (aureomycin, terramycin, tetracycline): less stable in solution form, so it is often used in the form of eye ointment. The cyclin group is effective against cocci, indicated mainly for the treatment of trachoma or for the prevention of eye inflammation in infants. The disadvantage of the drug is that it cannot penetrate the anterior chamber; fluoroquinolones (norfloxacin, ofloxacin, ciprofloxacin): These are broad-spectrum antibiotics, effective against most bacteria and less toxic to the corneal epithelium than aminoglycoside antibiotics; Polypeptide group: This group of antibiotic eye ointments is mainly polymyxin and bacitracin. Polymyxin B is effective in ulcerative colitis and is specific to gram-negative bacteria (such as Enterobacter, Klebsiella and especially P. aeruginosa). Bacitracin for use with eye infections caused by Neisseria, H influenzae, Actinomyces).

Thuốc mỡ kháng sinh tra mắt nhóm cyclin được chỉ định điều trị bệnh mắt hột
Some notes when using antibiotic-only eye drops:
Eye infections can have the same symptoms but cause different diseases and require specific antibiotics when treated. Otherwise, the disease may not be cured but also increase the resistance of bacteria; Some antibiotic eye ointments cause local side effects and eye irritation. For example, moxifloxacin eye ointment causes decreased vision, dry eyes, itchy eyes, or subconjunctival hemorrhages. Side effects will be less likely to occur at low doses, increase in proportion to the dose used and disappear when the drug is stopped; When antibiotic ointment is applied to the eye, a small part of the antibiotic can enter the general circulation of the body through the small blood vessels in the eye and have systemic effects. If the patient adheres to the usual dose, the risk of systemic side effects is not high, but if used in excess or for a long time (more than 2 weeks), the risk of side effects is similar to that of oral antibiotics. Therefore, patients need to adhere to the treatment, use the right drug, the right dose (number of times, number of drops) and not use it for a long time (more than 2 weeks); While using antibiotic eye ointment, if the patient is indicated to use another antibiotic orally or by injection, care should be taken to limit adverse drug interactions. For example, when using eye ointment containing chloramphenicol, do not drink or inject gentamicin, tetracycline, cephalosporin, polymyxin... 2.2. Group of antibiotics and corticosteroids The group of eye drops is a combination of anti-inflammatory corticosteroids and one or more antibiotics. The advantage of this combination drug is that it both fights bacteria and reduces uncomfortable symptoms caused by the inflammatory process.
However, the anti-inflammatory corticosteroid component causes some of the following risks:
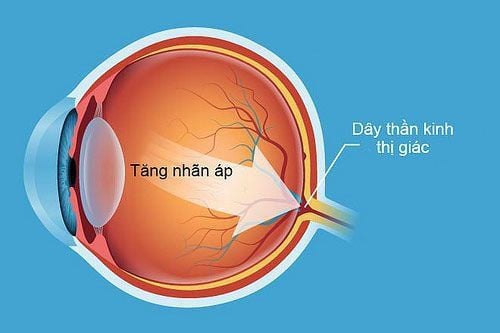
Nhóm thuốc mỡ nhỏ mắt có thành phần kháng viêm corticoid có thể gây tăng nhãn áp
Decreased resistance and inadvertently reduced the effectiveness of concomitant antibiotics, aggravated the disease and increased the possibility of secondary bacterial infections (including viral and fungal infections); Slow wound healing; Increased intraocular pressure and possible progression to glaucoma; Affects vision or reduces vision infrequently; Cataract formation; Thin sclera leads to eyeball perforation. SEE ALSO: Can chlorocina-H ointment be used for pink eye?
3. Some antibiotic ointments and notes when using
3.1. Solution - Ointment gentamicin 0.3% Gentamicin used to treat bacterial infections in the eye has two forms: solution (eye drops) and antibiotic eye ointment with a concentration of 0.3%. This is a fairly common drug. Gentamicin can be used as monotherapy or in combination with corticosteroids to treat diseases such as conjunctivitis, corneal ulcer, eyelid inflammation, lacrimal sac, stye...
For Gentamicin solution, disease eye drops 1-2 drops / time, 3-8 times / day for 5-12 days depending on the doctor's prescription. For Gentamicin eye ointment, each time apply 1.5cm of medicine to the affected eye, 2-3 times a day.
However, it should be noted if used for a long time, because it can lead to hypersensitivity in the skin and the emergence of drug-resistant bacteria. The patient should discontinue the drug if the eye discharges pus, inflammation, or pain increases.
Some notes when using Gentamicin in the eyes are as follows:
When instilled, it may cause slight burning in the eyes, itching, irritation... Discontinue the drug when there is an allergic reaction; Do not use if the cause of eye disease is viral or fungal; gentamicin eye ointment may cause blurred vision; The shelf life of Gentamicin eye ointment is no more than 15 days after opening.
Thuốc mỡ gentamicin 0,3%
3.2. 1% tetracycline ointment Indications of this eye ointment are eye infections caused by agents that are still sensitive to tetracycline such as conjunctivitis, trachoma... When using, the patient only checks a small amount of the drug. into the affected eye, 2-3 times/day.
Note when using:
Do not use for patients with a history of allergy to tetracycline antibiotics; Prolonged eye contact may increase the risk of developing drug-resistant strains of bacteria; The price of tetracycline eye ointment depends on different manufacturers, but the price of this drug is not high. 3.3. neomycin eye drops Neomycin has two forms:
0.25% eye drop solution; 0.5% Ophthalmic ointment 0.35%; 0.5%. Neomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic, which can be used alone or in combination with some other antibiotics such as polymyxin B, bacitracin... to treat eye infections. How to use: Instill 1-2 drops into the eye, every 3-4 hours depending on the degree of infection and disease condition. Some notes when using Neomycin eye ointment:
Contraindicated for use in children under 1 year old, people who are sensitive to the drug; General aminoglycoside antibiotics, including neomycin, should be used with caution because of the potential for nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity.
Thuốc nhỏ mắt neomycin
3.4. Chloramphenicol eye drops Chloramphenicol is a broad-spectrum antibiotic, capable of killing many types of bacteria both gram-negative and positive, indicated in some bacterial infections of the eyeball surface such as blepharitis, keratitis or conjunctivitis. desert.
Drugs with contraindications of the drug are children under 2 years old, patients with myelosuppression or hypersensitivity to drug components. Usage is as follows: Apply the drug to the eye every 3-6 hours, after 48 hours the dose can be reduced according to the treatment response. Rarely, chloramphenicol ophthalmic antibiotic ointment causes eye irritation. However, if irritation occurs, the patient should discontinue use and consult a physician.
3.5. Bacitracin This is a group of antibiotics usually indicated for external use. In ophthalmology, bacitracin is used as an ophthalmic ointment and is indicated in a number of conditions such as chalazion, acute and chronic conjunctivitis, ulcerative or keratitis, and lacrimal disease.
How to use: Apply a thin strip about 1cm of this eye ointment to the conjunctiva, every 3 hours. Note: The most common adverse effect of Bacitracin ophthalmic ointment is rash and patients need to stop using it immediately. Bacitracin is often used in combination with the antibiotics neomycin and polymyxin B to treat bacterial eye infections. In particular, do not use this medicine for more than 7 days.
In addition to information about precautions when using antibiotic eye drops, you can learn information about maxitrol eye ointment and weigh the benefits and risks of use. If in the case of using the drug, there is no progress and unwanted side effects, the patient should go to medical facilities for examination and treatment, to avoid dangerous complications.
Vinmec International General Hospital is the address for examination, treatment and prevention of diseases. When performing the examination process at Vinmec, customers will be welcomed and used the modern facilities and machinery system along with perfect medical services under the guidance and advice of the doctors. Good doctors, well-trained both at home and abroad.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.