This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Dr. Nguyen Anh Tu - Doctor of Obstetric Ultrasound - Prenatal Diagnosis - Obstetrics Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Edward syndrome is a rare genetic disorder in the fetus. Children with Edward's syndrome often have a hard time surviving after birth and if they are lucky enough to be born, they will develop abnormally. It is the second most common syndrome, after Down syndrome, with an incidence of 1/3000 to 1 in 8000 newborns.
1. What is Edward's syndrome?
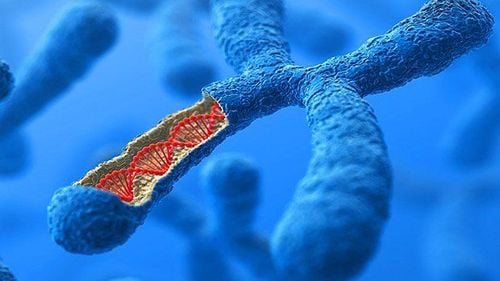
Edward's syndrome, also known as Trisomy 18 or trisomy 18, is a condition caused by an error in cell division that leaves an infected person with an extra chromosome 18 in the genome. This excess of genetic material causes birth defects in the fetus.Unlike Down syndrome, which is also caused by an extra chromosome, developmental problems caused by Trisomy 18 are potentially more life-threatening during the first months of life. Edward's syndrome occurs in about one in 5,000 births. Some studies show that many babies who survive are born girls. Many of the babies affected died before birth.
2. Effects of Edward's syndrome on the fetus
Most fetuses with Edward's syndrome have growth retardation in utero and then stop growing around the 7th month of pregnancy.Trisomy 18 syndrome not only affects the fetus, but pregnant women also experience serious abnormalities and disorders during pregnancy. These abnormalities include polyhydramnios, lack of amniotic fluid, having a single umbilical artery, intrauterine growth retardation, small placenta, fetal distress, and weak fetal movements.
For babies who are lucky to survive after birth, they can face serious health problems such as:
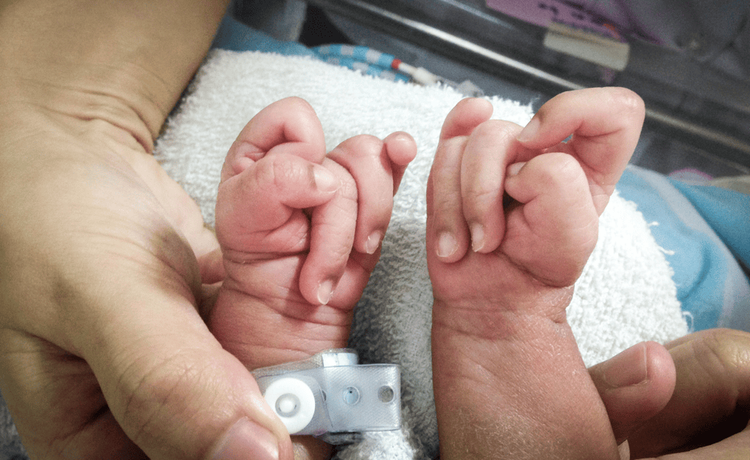
Head and face abnormalities: small head, small chin, low closed ears, vascular plexus cysts brain, cleft palate, cleft lip Short sternum Having some congenital heart disease: atrial septal defect, ventricular septal defect Aortic stenosis Split spine Herniated spinal cord Abdominal and muscular abnormalities Internal organs: umbilical hernia, abdominal wall regurgitation, esophageal atrophy, polycystic kidney or hydronephrosis, horseshoe kidney, undescended testicle. Hand cramp, hypoplastic fingernails, crooked hands, thick soles. Hands clenched into fists Deformed kidneys Undescended testicles (testicles do not descend into the scrotum)

3. Ways to diagnose Edward's syndrome
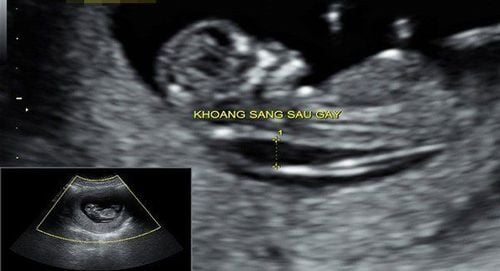
Although there is currently no cure for Edward's syndrome, it can be detected through early pregnancy screening.Prenatal diagnosis:
Two types of tests are recommended to be performed before birth, namely Screening and Diagnostic Tests for Genetic Disorders:
Screening Tests : helps to estimate the risk of having the syndrome. These are non-invasive and painless tests. However, the weakness of this test is that it cannot make an accurate conclusion whether the fetus has Edward's syndrome or not, it can only provide couples with useful information from which to make a decision. determine whether or not to perform diagnostic testing. Diagnostic test: The test can detect Edward syndrome and some other chromosomal disorders with high accuracy. Amniocentesis gave very accurate results for Edward, ~100%. However, this test requires some invasive procedures in the uterus such as amniocentesis or placenta biopsy, so there is a risk of miscarriage and other complications in the fetus. Postpartum diagnosis:
Postnatal diagnosis is made by physical examination of the newborn, looking for abnormalities that manifest on the outside of the baby, such as arced fingers or broken sternum shorten.
NIPT test
NIPT is considered one of the safe and highly accurate prenatal screening methods, helping to detect abnormalities in the number and structure of fetal chromosomes during pregnancy. The NIPT method of prenatal screening is a noninvasive test, based on testing the fetal DNA in the mother's blood.
Currently, Vinmec is deploying the NIPT non-invasive prenatal test service, which offers quality, safety and efficiency that is far superior to other traditional methods such as amniocentesis or placental biopsy. The outstanding advantage of this method is that it is non-invasive, can be performed as early as the 9th week of pregnancy, and reduces the percentage of pregnant women who are prescribed unnecessary amniocentesis.
Doctor Nguyen Anh Tu has 6 years of experience in obstetrics and gynecology ultrasound, specially researched and trained in pregnancy ultrasound - prenatal diagnosis. Dr. Tu has completed courses on ultrasound - prenatal diagnosis of the FMF International Fetal Medicine Association; trained in consulting and implementing diagnostic intervention techniques in fetal medicine and participated in many specialized conferences and seminars on Fetal Medicine
Currently working as a doctor at the Hospital's Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Trisomy18.org; Webmd.com