This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Van Thanh - Obstetrician and Gynecologist - Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology - Vinmec Nha Trang International General HospitalGenetic disorder screening and diagnosis is the current advanced method in medicine to determine whether a child is born at risk of genetic diseases.
1. What is a genetic disorder?
Genetic disorders are genetic diseases that occur due to genetic or chromosomal abnormalities. Although most babies are born healthy, couples worry about the possibility of their baby being born with genetic diseases.
Genetic disorders can range from a mild illness such as color blindness to a more serious one, such as some forms of hemophilia or Tay-Sachs disease. Some genetic disorders are not harmful and do not require special treatment. For many genetic disorders, aggressive treatment and specialist care can significantly improve genetic conditions in young children.
2. Some Common Genetic Disorders
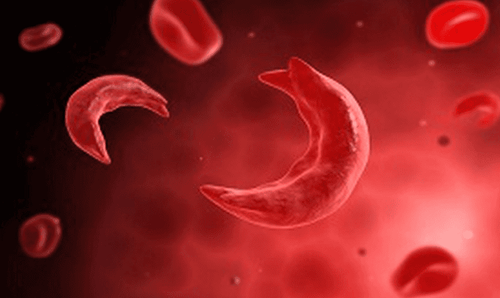
Here are some of the most common types of genetic disorders:Nerve cell disorders : Causes tumor growth. Deformity of an extra finger or foot. Thalassemia: Blood disorder. Sickle cell anemia: An inherited blood disorder caused by an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying hemoglobin molecule in red blood cells resulting in the cells having an abnormal appearance. crescent-shaped. Tay-sachs disease is a fatal genetic disorder caused by damage to nerve cells in the brain. Cystic fibrosis: An inherited disorder that affects mainly the lungs, pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestines. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is the most common inherited neuromuscular disease. Color blindness: It is a color disorder, which means that the ability to distinguish colors is reduced. Hemophilia is a blood clotting disorder caused by a deficiency of factor VIII (hemophilia A) or factor IX (hemophilia B).
3. Risk factors for genetic disorders
The risk of a genetic disorder usually increases with age, especially as women aged 35 and over are at increased risk of having a baby with Down Trisomy.Risk factors that may increase the risk of having a child with a genetic disorder include:
Aged parents. One or both parents have a genetic disorder. A couple had a child with a genetic disorder. Have a family history of a genetic disorder. One or both parents belong to an ethnic group with a high prevalence of genetic disorders.

4. What is genetic disorder testing?
Genetic disorder testing is a DNA test that allows the analysis of genes that have the potential to cause an inherited disease. In addition, the study of human chromosomes is expanded to include biochemical tests to detect inherited diseases, or mutations of important genes that increase the risk of developing genetic disorders. . In addition, genetic disorder tests help identify changes in chromosomes, genes, and proteins. From the results of the test, it is easy to detect and promptly exclude suspicions of hereditary diseases or determine the development or reduction of genetic disorders.5. Types of Genetic Disorders Tests
There are now many types of tests that are commonly used to help couples who want to have children deal with concerns about genetic disorders: Carrier screening: performed on a couple with a history of genetic disorders. genetic diseases to determine who is the carrier of the disorder gene. This test is usually done before or during pregnancy by taking a blood sample to see if the baby is at risk for genetic diseases. Tests for malformations: The test helps to screen the baby for Down syndrome, neural tube defects, and brainless babies. Diagnostic tests: used to analyze or treat specific genetic or chromosomal diseases. These tests are performed on cells obtained through amniocentesis, placental biopsy (CVS).Instead of amniocentesis, a biopsy of the placenta that directly affects the fetus, the non-invasive prenatal screening method (NIPT) is much safer because only 20ml of blood is taken from the mother's vein from the 9th week of pregnancy. onwards to proceed with DNA sequencing. This result will help experts detect fetuses at high risk of abnormalities of some chromosomes such as Down syndrome, Patau, Edward, Turner, .....
At the same time reduce the rate pregnant women with unnecessary amniocentesis. The outstanding advantage of this method is that it is non-invasive and can be carried out as early as the 9th week of pregnancy. Older pregnant women, families with children with birth defects... should choose NIPT from early pregnancy.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to the source Acog.org