This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted with Doctor Nguyen Anh Tu - Doctor of Obstetric Ultrasound - Prenatal Diagnosis - Department of Obstetrics - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital.Double test is one of the routine screening tests, recommended for all pregnant women to screen for common fetal chromosomal disorders such as Down syndrome, Edwards and Patau.
1. What is a double test?
Double test is done around 11 to 13 weeks of the first trimester of pregnancy.This method is performed by quantitative testing of free β-hCG and PAPP-A - two substances present in the mother's blood during pregnancy. These two biochemical indicators are secreted by the placenta and change during pregnancy.
These indexes are then calculated together with nuchal translucency (NT), head and rump length (CRL) of the fetus and some other parameters by specialized software to calculate the Corr.MOM coefficient and fetal risk for the disease. It is to form the combined test.
Comparisons with threshold values can help health professionals assess the risk of certain birth defects for an unborn baby.
2. Purpose of Double test
The Double test prenatal screening test aims to identify abnormalities in fetal chromosomal development. Any abnormality can lead to serious health conditions, affecting fetal growth, even prolonging the life of the child being born.Double test helps to detect signs of a number of triploid chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Edwards (Trisomy 18) and Patau (Trisomy 13).
In Down syndrome
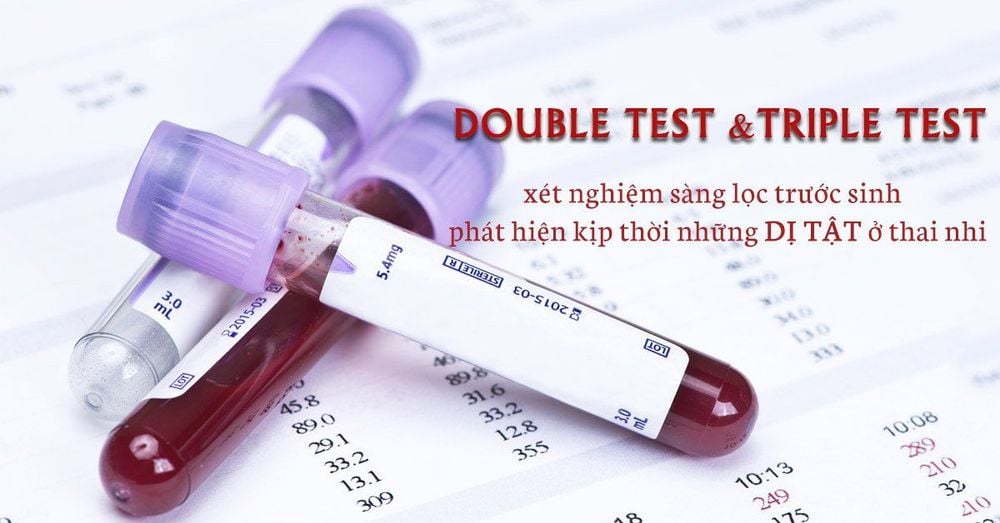
In Patau syndrome: Free β-hCG and PAPP-A are generally low.
3. Advantages and disadvantages of double test
Advantages:Accuracy of prenatal screening test Double test for pregnant women can give an accuracy of up to 80 - 90%, and is safe for both mother and baby.
Cons:
For pregnant women with twins, the Double test reduces the accuracy. In this case, the doctor may rely on morphological ultrasound to make a diagnosis.
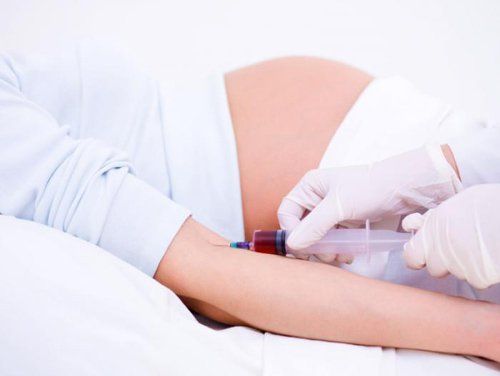
Non-invasive method NIPT or Amniocentesis (invasive): Testing fetal DNA in a sample of mother's blood or amniotic fluid to evaluate for birth defects, Accuracy can be up to 99.9%. Screening for birth defects for the fetus is extremely important, so pregnant women need to pay attention to the correct time to go to the doctor and do tests. Besides, understanding the purpose and meaning of each test will help mothers feel more secure, especially when unfortunately the screening results warn of a high risk of birth defects. To help mothers get full care during both before and after birth, Vinmec is currently implementing a Package Maternity Care Program. With this program, not only mothers and babies are examined, tested and cared for, but the family is also extremely assured to ensure that the baby is born healthy.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.