This is an automatically translated article.
This article was professionally consulted by a Doctor of Radiology, Department of Radiology - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Angiography is a method of collecting images to serve as a basis for examination and diagnosis of diseases. This procedure is performed by injecting a selective iodinated contrast agent into an artery or vein to visualize the venous system.
1. Indications and contraindications for digital imaging to erase the background of the visceral venous system
1.1 Designation
Normally, digital scan to erase the background of the visceral venous system will be indicated for venous malformations such as: Venous hemangioma, pseudoaneurysm,... Other venous pathologies are also used with this procedure. This technique is similar to venous thromboembolism.In addition, digital imaging to erase the background of the visceral venous system can also be taken to check the bridge after surgery or angiography to serve for interventional radiology.
1.2 Contraindications
Digital erasure of the visceral venous system will be relatively contraindicated in cases with coagulopathy, a history of obvious allergy to iodine contrast agents, renal failure, and pregnancy.However, digitized scanning of the background of the visceral venous system has no absolute indication for any case.
Chụp số hóa xóa nền hệ thống tĩnh mạch tạng sẽ chống chỉ định tương đối với bệnh nhân suy thận
2. What do you need to prepare for a digital scan to erase the background of the visceral venous system?
2.1 The person performing the digital scan to erase the background of the visceral venous system
Specialist. Auxiliary physician. Optical technician. Nursing. Doctor, anesthesiologist (if the patient cannot cooperate).2.2 Means for digital imaging to erase the background of the visceral venous system
Digital background removal angiography (DSA). Dedicated electric pump. Lead vest, apron, X-ray shield. Film, film printer, image storage system.2.3 Medicines to prepare before the procedure
Local anesthetic. Pre-anesthesia and general anesthetic (if there is an indication for anesthesia). Anticoagulants. Anticoagulant neutralizer. Water soluble iodine contrast agent. Antiseptic solution for skin and mucous membranes.2.4 Common medical supplies
Syringe 1; 3; 5; ten; and 20ml. Syringe pump for electric pump. Distilled water or physiological saline. Gloves, shirt, hat, surgical mask. Cotton, gauze, surgical tape. Medicine box and first aid kit for contrast drug accidents. Aseptic intervention kit: knife, scissors, tongs, 4 metal bowls, bean tray, tool tray.2.5 Special medical supplies for digitization of the background of the visceral venous system
Arterial puncture needle. Three-pronged lock. Set of 5-6F muscle inlet. Microcatheter 2-3F if ultra-selective imaging is required. Micro-conductor 0.014-0.018inch. Standard conductor 0.035inch. Angiography catheter size 4-5F. Y-connector set. Instrument closure kit.2.6 What does the patient need to prepare for this procedure?
Before conducting digitized scanning to erase the background of the visceral venous system, the patient needs to understand this procedure well so that he can coordinate with the doctor.At the same time, it is necessary to fast for 6 hours before entering the process of digitizing the background of the visceral system, but the patient can still drink less than 50ml of water.
In the intervention room, the patient lies on his back, with a breathing machine, blood pressure, pulse, electrocardiogram, SpO2. Then, disinfect the skin and cover the area with a sterile cloth with holes in it. For cases of overstimulation, not lying still, sedation can be used or appropriate treatment measures can be taken.
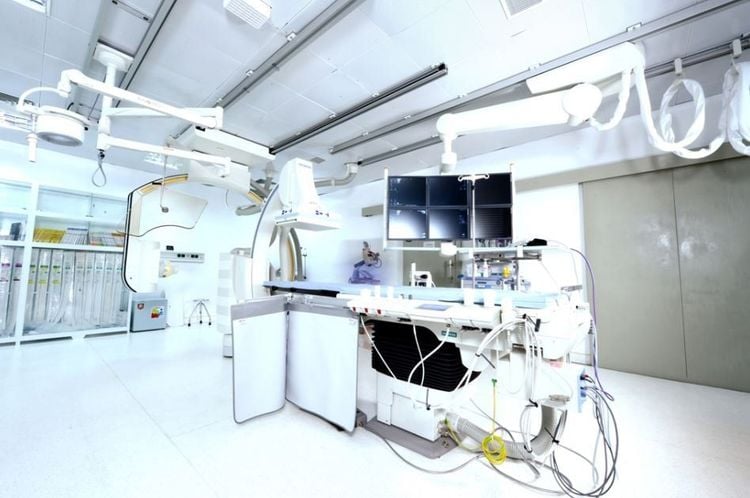
Máy chụp mạch số hóa xóa nền (DSA)
3. Steps to take digital scan to erase the background of the visceral venous system
Step 1: Anesthesia Method Place the patient supine on the table, place an intravenous line. Usually, local anesthesia will be administered, but with exceptions such as young children (under 5 years old) who are not yet conscious of cooperation or too excited to be afraid, general anesthesia is required during the procedure. Step 2: Select the technique to use and the inlet of the catheter The technique used is Seldinger, the route of the catheter can be: From the femoral artery, axillary artery, brachial artery or radial artery. Usually, the technique will use the femoral artery entrance, unless this is not possible, use other entrances. Step 3: Diagnostic angiogram Sterilize and anesthetize the puncture site. Needle puncture, catheter insertion Insert a 4-5F catheter into the superior mesenteric artery. Inject 20-30ml of contrast agent at 4-5ml/sec and then take an arterial and venous scan to study the superior mesenteric and portal vein systems. Step 4: Finish the procedure Withdraw the catheter and tube into the vessel. Apply pressure directly at the puncture site for about 15 minutes. Then, apply compression for 6 hours or use an intravascular closure device.4. Some complications and how to handle them
Bleeding or hematoma at the catheter site, in this case it is necessary to apply pressure and continue to lie motionless until the bleeding stops. Aneurysm or arteriovenous catheterization (rare), when this occurs can be treated with endovascular or surgical intervention. Post-procedural infection requires antibiotics for treatment. Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website to be served.Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.