This is an automatically translated article.
This article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Dinh Van Loc - Anesthesiologist - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital. The doctor has more than 23 years of experience in anesthesiology and resuscitation.The diaphragm is a thin layer of muscle that separates the chest and abdomen. When abdominal organs are present in the thorax, it is called a diaphragmatic hernia. Diaphragmatic hernia in adults is an uncommon disease, requiring early intervention to ensure the patient's health.
1. What is a diaphragmatic hernia?
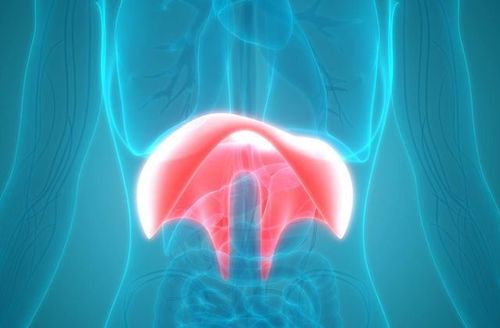
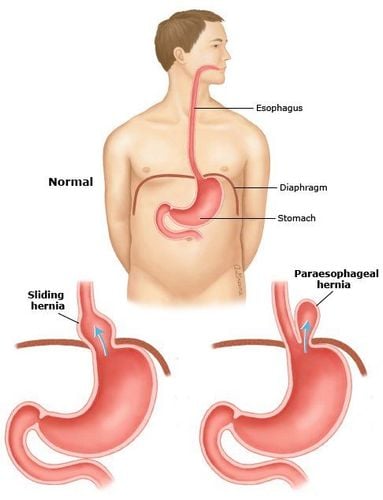
The diaphragm is a flat striated muscle that separates the rib cage from the abdomen. This is the muscle layer that plays an important role in breathing; when inhaling, the ribcage expands, the diaphragm descends, compressing the viscera in the abdomen; Conversely, when exhaling, the diaphragm lifts, helping the lungs expel the residual gas volume. The diaphragm is controlled both by the autonomic nervous system and by the human consciousness.Diaphragmatic hernia occurs when one or more abdominal organs move upward, into the thorax through any defect in the diaphragm surface. In children, this defect can occur from birth, called a congenital diaphragmatic hernia. In adults, diaphragmatic hernias are usually acquired. However, regardless of the cause, if the diaphragmatic hernia occurs acutely, the organs below go into the thoracic cavity, compressing the heart and lungs, affecting breathing, all need emergency surgery to ensure the quality of life. network.
2. What is the cause of diaphragmatic hernia in adults?
Unlike congenital diaphragmatic hernia in children, which is caused by abnormal development of the diaphragm during fetal period, diaphragmatic hernia in adults is acquired. This is usually the result of closed or open trauma directly or indirectly to the thorax and abdomen.Closed injuries can occur in daily activities such as traffic accidents, falls. On the other hand, penetrating trauma that affects the diaphragm is usually caused by a weapon such as a stab wound or a gunshot. However, during abdominal or thoracic surgery, complications of diaphragmatic hernia can also occur.
Whatever the cause, in general, it is very rare that a diaphragmatic hernia is acquired without a reason. In these cases, the diagnosis may go undetected for a long time until the diaphragmatic hernia has become sufficient to cause symptoms. Normally, the esophagus enters your stomach through an opening in the diaphragm. A diaphragmatic hernia occurs when the muscle tissue around this opening becomes weak.
Possibly the cause of diaphragmatic hernia can be caused by:
Damage to the diaphragm area; Being born with an abnormally large opening in the stomach (birth defect); Continuous and intense pressure on surrounding muscles, such as when coughing, vomiting, or straining during a bowel movement, or while lifting heavy objects. What factors increase the risk of diaphragmatic hernia?
There are several factors that increase the risk of a diaphragmatic hernia due to increased abdominal pressure such as: obesity, pregnancy, coughing, long-term constipation, abdominal constriction during defecation or abdominal trauma. In addition, people over the age of 50 are also at a higher risk of having a diaphragmatic hernia.
3. What are the symptoms of a diaphragmatic hernia?
Shortness of breath is a symptom with a very common rate but vague characteristics. Patients sometimes describe dyspnea that is intermittent, with unknown circumstances of onset and remission, or sometimes related to meals, when lying down. Besides, sometimes patients are discovered herniated diaphragm by accident when examining breathing rate, heart rate faster than normal, even at rest; bruised skin, lip color; Auscultation of the lungs shows narrowing of the lung fields. This is characteristic of dyspnea in cases of mild and progressive diaphragmatic hernia. For cases of diaphragmatic hernia due to trauma, if the defect area of the diaphragm is large, the viscera from the abdomen overflow into the chest, the patient has severe difficulty breathing, sometimes causing respiratory distress and death.
In addition to the symptoms of the respiratory system as above, the patient may also have functional digestive disorders such as eating less, anorexia, easy nausea or vomiting, frequent feeling of bloating, abdominal distension. On examination, the sound of bowel movements is heard high in the thorax. Rarely, patients have been hospitalized with bowel obstruction due to severe abdominal pain when a loop of bowel herniated through the diaphragm and became trapped.
4. How to diagnose diaphragmatic hernia in adults
While congenital diaphragmatic hernia can be detected even before the baby is born, an adult diaphragmatic hernia is only thought of after severe trauma to the thorax and abdomen or sometimes it is necessary to rely on a thorough history. meticulously exploited for a long time.The most commonly used imaging studies to diagnose diaphragmatic hernia are:
Ultrasound: uses sound waves to visualize the structure of organs in the thoracic and abdominal cavity. X-ray: signs of diaphragmatic discontinuity, presence of air-fluid level of bowel loops in the thorax Computerized tomography and magnetic resonance imaging: these imaging tools are very capable of detecting diaphragmatic hernia good, especially the small, discreet hernia.
5. How is diaphragmatic hernia treated?
For diaphragmatic hernia occurring after trauma, the patient falls into acute respiratory failure, which is life-threatening and often requires emergency surgery. The surgeon will rearrange the organs from the thorax and put them back into the abdomen. Then, repair of the diaphragm will be performed next. For cases of diaphragmatic hernia after trauma but not too severe, the patient will be given priority to stabilize other issues first such as respiratory support, circulation, bleeding control,... before during diaphragmatic repair.On the contrary, if the patient goes to the doctor because of shortness of breath and diagnoses diaphragmatic hernia, if the hernia is not at risk of re-trapping, elective surgery will be arranged. If the hernia mass has a narrow mouth, the risk of stenosis is very high, requiring early surgery. On the other hand, if the diaphragmatic hernia is stuck, there are signs of bowel necrosis, the patient is also indicated for urgent intervention, to avoid the hernia mass bursting, the risk of mediastinal and peritoneal infection is very high.
To date, there is no way to prevent diaphragmatic hernia. Mainly thanks to the caution when living in life, such as driving with concentration and always wearing a seat belt, absolutely not driving while drinking or using drugs; use protection at work as well as when playing sports that can cause injury, be careful when using sharp objects, such as knives and scissors, avoid conflicts, conflicts that cause fights, fights..
In short, a diaphragmatic hernia is when the abdominal viscera enter the thoracic cavity and this diagnosis in adults is easy to make if symptoms are severe and conversely, it is difficult if the history of dyspnea is ambiguous. . However, whatever the cause, the treatment is surgical repair of the diaphragm. Therefore, it is necessary to detect early to intervene promptly to avoid dangerous complications.

Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of leading medical doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination and consultation services. comprehensive and professional medical consultation and treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.