This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Doctor Department of Gastroenterology - Endoscopy, Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
Gallstones are small stones inside the gallbladder, while common bile duct stones are when at least one gallstone is in the common bile duct. So how to recognize gallstones and common bile duct stones?
1. Distinguishing gallstones and common bile duct stones
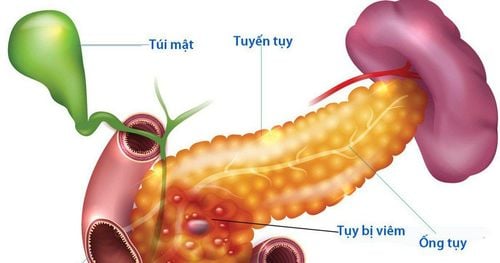
The gallbladder is a small pear-shaped sac, attached to the lower right lobe of the liver, to store and concentrate bile secreted by the liver. Bile secreted by the liver is stored in the gallbladder and then excreted into the intestines to digest fats. The gallbladder is connected to the common bile duct through the cystic duct.
Solid gallstones are formed by cholesterol, bile salts and calcium, the size of which ranges from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Quantity can be from 1 to hundreds of tablets.
Common bile duct stones , bile duct stones or gallstones in the bile duct is a condition in which there is at least one gallstone in the common bile duct. As in gallstones, stones can also be formed from bile pigments or calcium and cholesterol salts.
Gallstones are a common pathology for both gallstones and common bile duct stones. Differentiate between gallstones and common bile duct stones based on the location of the stones. Solid gallstones are formed by cholesterol, bile salts and calcium, the size of which ranges from a few millimeters to several centimeters. Quantity can be from 1 to hundreds of tablets.
Unlike gallstones and common bile duct stones in countries in Europe and America, gallstone disease in Vietnam is mostly complicated, mainly in the composition of gallstones is pigment bile, the nucleus is eggs. or roundworm carcasses. The possibility of worms entering the biliary tract is high, leading to the formation of gallstones.
2. Who is most susceptible to gallstones and common bile duct stones?
Gallbladder and common bile duct stones are more common in women because they are largely related to stimulation of the female hormone progesterone, which reduces gallbladder motility, while estrogen increases cholesterol and decreases cholesterol-soluble bile acids. Estrogen increases the concentration of cholesterol in the bile secreted by the liver, while progesterone slows down the rate of gallbladder release.
Therefore, the probability of having the disease in women usually decreases with age (compared to the tendency of men to get the disease). Before the age of 40, the rate of gallstones diagnosed in women is nearly three times higher than in men, the risk of developing the disease is especially increased during pregnancy. After age 60, the probability of having the disease in women increases slightly.
People who use hormone replacement therapy (estrogen) also have an increased risk of disease, especially if the hormone is added to the body in oral form instead of indirectly through the skin. Oral contraceptives in women also increase the risk of gallstones and common bile duct stones, especially during the first 10 years of use.
3. Gallbladder stone symptoms
Most patients have no special symptoms, gallstones are often discovered incidentally during ultrasound examination of other pathologies, only about 30% of cases with gallstones are symptomatic. If present, the symptoms of gallstones that may be encountered in the patient are biliary colic (86%), with the following characteristics:
Cyclic: distinct pain, lasting from 30 minutes to several hours. Location: pain in the epigastrium (above the navel) or the right upper abdomen, the most painful cases in the epigastrium make it easy to mistake for peptic ulcer disease. Level: severe and continuous pain, the pain can make the patient stop breathing. The pain usually occurs in the case of a sudden gallbladder contraction (usually after a fatty or meaty meal), due to increased pressure of the stones on the gallbladder wall or the contraction of the gallbladder causes them to leak. transfer, resulting in bile duct obstruction. The pain subsides, as the gallbladder returns to its normal state. Timing: Pain usually occurs within a few hours of eating, or may be nocturnal and awaken the patient. Other symptoms: back pain, left upper abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, bloating (dyspepsia with greasy food). Fever, jaundice are usually stones that have caused complications
4. Symptoms of common bile duct stones
Pain under right flank: severe, rolling, pain that radiates to the right shoulder or to the back. After eating, the pain feels worse (because the biliary tract is stimulated to contract much and strongly). The pain is usually long-lasting, painful, sometimes up to 2 to 3 hours. Fever: fever comes on at the same time or occurs only a few hours after the pain is felt. Fever can be as high as 39-40 degrees Celsius, accompanied by chills, sweating. Symptoms of infection on the face: dirty tongue, dry lips, fatigue, fast pulse, weight loss. Yellow skin, yellow mucous membranes: this is the most obvious manifestation, appearing later, initially only slightly yellow in the sclera (eyes), then gradually darker yellow in both the skin and the eye mucosa. The gallbladder is enlarged: sometimes the gallbladder is felt to rise just below the edge of the right flank, like an egg, when touched, it is round, even, smooth, when pressed, it feels painful, moving with each breath. Other warning symptoms: vomiting with pain, little urine and dark urine. Due to toxic bile salts, itching of the skin (rare cases) occurs. In particular, if the common bile duct stones cause bile obstruction, the stool will be discolored and change color. This is a distinguishing feature from gallstones, gallstones do not cause biliary obstruction if the stones are completely located in the gallbladder.
5. Test for gallstones and common bile duct stones
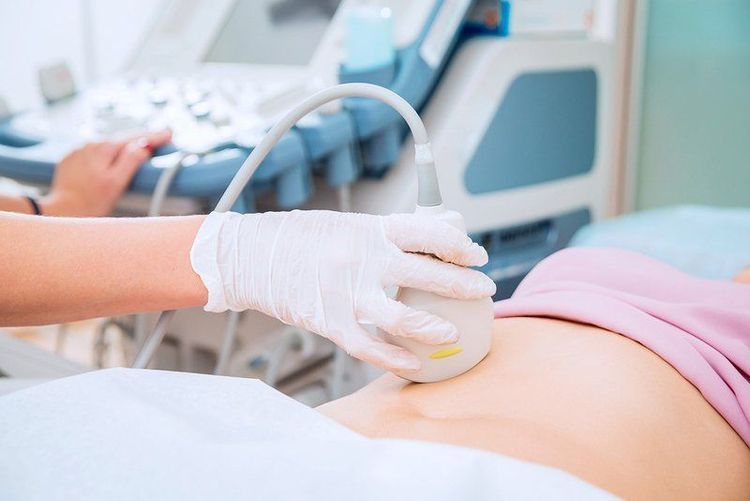
Ultrasound method: brings high value, determines the location and size of stones, shows the size of gallbladder, common bile duct with accurate results up to 95%. Ultrasound is widely used to aid in the diagnosis of hepatobiliary diseases. Through ultrasound images, common bile duct stones are often dark, appear shadowy and are located in the common bile duct. Similarly, gallstones will show a dark shadow in the gallbladder.
Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used in the diagnosis of suspected cases of gallstones (including gallbladder and biliary tract) that cannot be confirmed by ultrasound .
6. Complications of gallstones in general
Acute cholecystitis, caused by a stone stuck in the neck or cystic duct, requires emergency surgical treatment. Cholangitis is caused by gallstones falling into the common bile duct (causing choledocholithiasis), leading to biliary obstruction leading to cholangitis. This is a serious complication that requires urgent intervention to remove stones. Acute pancreatitis is caused by gallstones that fall into the common bile duct and become lodged at the end of the common bile duct, obstructing both the bile duct and the pancreatic duct. This is a very serious complication, requiring timely intervention to remove stones. Gallbladder cancer is associated with large gallstones (over 25mm), stones with gallbladder polyps, and porcelain gallbladder. The disease progresses slowly and is often diagnosed late.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.