This is an automatically translated article.
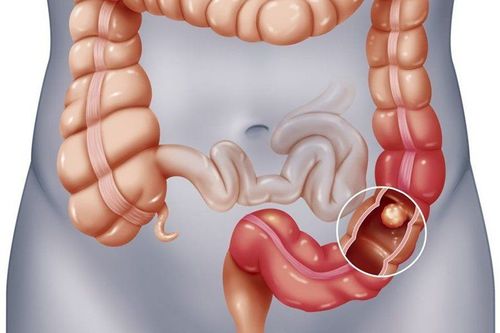
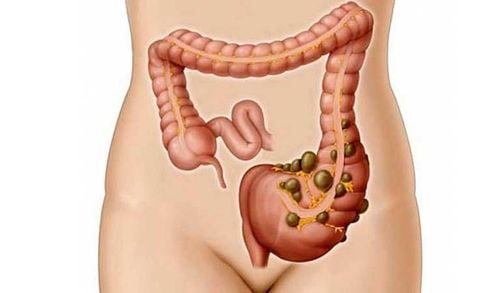
The article was written by MSc Pham Thi Mai Thanh - Department of General Internal Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Epiploic appendages are fat pockets on the outside of the colon. Usually each fatty mane is shaped like a little finger, grape or oval, and is nourished and supplied with blood by a small vein. and arteries. The number of fat pockets ranges from 50 to 100 extending from the cecum to the junction between the sigmoid colon and the rectum.
1. Inflammation of the colonic fatty mane
Epiploic appendagitis is ischemic and necrotic fatty mane caused by venous torsion or venous occlusion due to thrombosis.Epidemiology: Fatty mane of the colon accounts for 2-7% of patients with suspected diverticulitis and about 0.3-1% of patients with appendicitis. The disease usually appears in middle-aged people with an average age of 40, men are affected 4 times more often than women. Obesity and strenuous exercise are risk factors for fatty mane.
Pathophysiology: Fatty mane often occurs because the large and long fatty mane is suddenly twisted, causing ischemia, leading to aseptic fat necrosis and venous occlusion due to thrombosis. If the fatty mane is slowly twisted, it causes chronic inflammation and very few symptoms.
Clinical manifestations: Patients often have acute or subacute lower abdominal pain. Less common symptoms include: Postprandial bloating, nausea, bloating, vomiting, loose stools, and low-grade fever. WBC count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein may be normal or slightly elevated.
2. Diagnosis of colonic fatty mane
Differential diagnosis of steatorrhea from other causes of acute abdominal pain such as diverticulitis or appendicitis is based on the clinical picture and abdominal CT scan. On CT, there is an oval mass next to the colon with fat density, size 2-3cm, thick peritoneal wall and surrounding fat infiltrate. The presence of a contrast-reduced nodule in the center of the inflamed fatty mane corresponds to central venous thrombosis.The inflamed fatty mane is usually located on the anterior surface of the sigmoid or descending colon, but it can be anywhere along the colon.

3. Treatment of colonic fatty mane
Colitis is recommended medical treatment with oral anti-inflammatory drugs (eg, Ibuprofen 600 mg every 8 hours for 4-6 days), or, if necessary, opiates (acetaminophen/codein 300) /30 every 6 hours for 4-7 days). Patients who do not improve with conservative treatment or whose symptoms are worsening (eg, high fever, increased pain, nausea and vomiting or inability to eat by mouth) or complications (intestinal obstruction, abscess) , intussusception ) required surgery.Conclusion: Colitis steatitis is a benign, self-limiting disease that can be resolved without surgery in 3-14 days. Complications such as intussusception, intestinal obstruction, and abscess are rare.
Vinmec International General Hospital has put an international standard ultrasound system into the examination and diagnosis of many diseases, including colonic fatty mane. Accordingly, the gastrointestinal ultrasound procedure at Vinmec is carried out methodically and in accordance with the process standards by a team of highly skilled medical professionals, modern machinery system, thus giving ultrasound images of manetritis. Accurate colon fat, contributes significantly to the identification of the disease and the stage of the disease.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.