This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Le Xuan Thiep - Radiologist - Department of Diagnostic Imaging - Vinmec Ha Long International Hospital.A coronary calcium scan is a specialized X-ray test to provide images of the arterial system in the heart. From there, the doctor can detect and measure calcium-containing plaque in the arteries that restricts blood flow to the heart muscles. By measuring calcified plaques on coronary calcium scans, coronary artery disease can be detected even before symptoms occur.
1. What is a coronary calcium scan?
Atherosclerosis is a continuous process lasting decades from the appearance of cardiovascular risk factors, the formation of fatty streaks and plaques to finally rupture, forming intravascular thrombus and forming clinical vascular events. In atherosclerotic plaques, calcium is deposited and occurs only in atherosclerotic arteries and is not present in normal artery walls. Calcium is initially present in only small amounts but will be found in greater amounts in lesions that progress with age. Therefore, coronary calcification is almost always present in people with coronary artery disease, and the degree of calcification is also referred to as "coronary age".Based on these characteristics, it has long been known that coronary artery calcification can be seen on chest X-ray, but this method cannot quantify the degree of calcification objectively. Next, the advent of computed tomography with electron beam marked a turning point in the investigation of coronary artery calcification. The machine has scanned coronary calcium by X-ray like conventional X-ray tomography with very thin slices and fast recording speed to reduce signal noise caused by movement. The number of slices performed is usually 30 to 40 slices along the length of the heart.
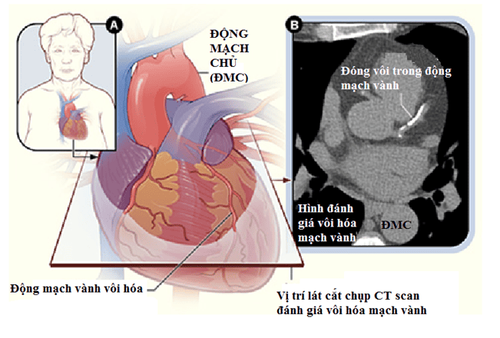
Quét canxi vành giúp phát hiện bệnh lý mạch vành
0 points: no calcifications 1 - 99 points: mild calcification (low risk, less than 1% annual mortality or myocardial infarction) 100 – 399: moderate calcification (medium risk, annual mortality or MI from 1 % to 3%) From over 400 points: severe calcification (high risk, annual mortality or MI > 3%) By coronary calcium scan, the severity of coronary artery disease remains depending on the location of the calcification. Accordingly, the lesions on the left coronary artery and the proximal coronary arteries are more dangerous than the middle and distal segments. At the same time, small calcifications are often associated with mixed atherosclerotic plaques, causing significant narrowing of the coronary lumen and may be more dangerous than large calcifications.
In addition, when the calcification score is >400 points, the patient has an indication for DSA coronary angiography or the case where the calcification score is <400 but there is a lot of calcification at one location that the patient has symptoms: Pain chest, symptoms on electrocardiogram... => indication for coronary artery DSA.
2. How can coronary calcium scan detect cardiovascular disease early?
Atherosclerosis is an inflammatory disease of the artery walls associated with metabolic changes and is a leading cause of cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease includes ischemic heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, and peripheral artery disease. It is the leading cause of death in countries around the world, including developed and developing countries. Therefore, the role of primary prevention of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is very important. In particular, the first step in primary prevention is to assess the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and from the possibility of future atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease that has an appropriate level of treatment.With the above values, the image of atherosclerotic plaque calcification observed directly on the coronary artery is calculated into the coronary calcification score, showing more and more advantages in identifying patients at risk. cardiovascular muscle. Although coronary calcification scores vary widely across gender, age, and ethnic groups, coronary calcium scanning is gradually becoming a useful alternative to existing means for assessing future atherosclerotic burden. future. Thus, coronary calcium scan for early detection of cardiovascular disease and higher coronary calcification score will be a stronger predictor of coronary heart disease, stroke and future atherosclerotic cardiovascular events.

Quét canxi vành giúp tiên đoán sớm đột quỵ
3. How is the coronary calcium scan?
When scheduling an appointment for a coronary calcium scan, there is usually no need for special preparation. Even so, you may still be asked to avoid foods containing caffeine and smoking for at least four hours before the procedure. In addition, upon arrival at the check-in, you will also be asked to remove your clothing above the waist and put on a specialized gown; you will also need to remove jewelry around your neck or near your chest to avoid creating noisy images when shooting.Before the coronary calcium scan begins, the technician will attach sensors, called electrodes, to your chest. They connect to an electrocardiogram to record the heart's activity during performance and coordinate the timing of X-ray images between heartbeats. During this process, you remain fully supine on a movable table, which automatically slides into the scanner controlled by an outside technician.
In addition, you may be prescribed medication to slow the heart rate. This helps to ensure a clear image. If you are very nervous or stressed in a hospital setting, you may be given extra sedatives to help you stay calm. However, the best thing to avoid these adverse reactions is to lie still and hold your breath for a few seconds while the CT scans are taken. The technician operates the coronary calcium scanner from the next room but can watch and talk to you the whole time, which is about 10 to 15 minutes.
After the coronary calcium scan, you can go home and resume your daily activities with no special attention. The time to return the results will be arranged with you in the following days.
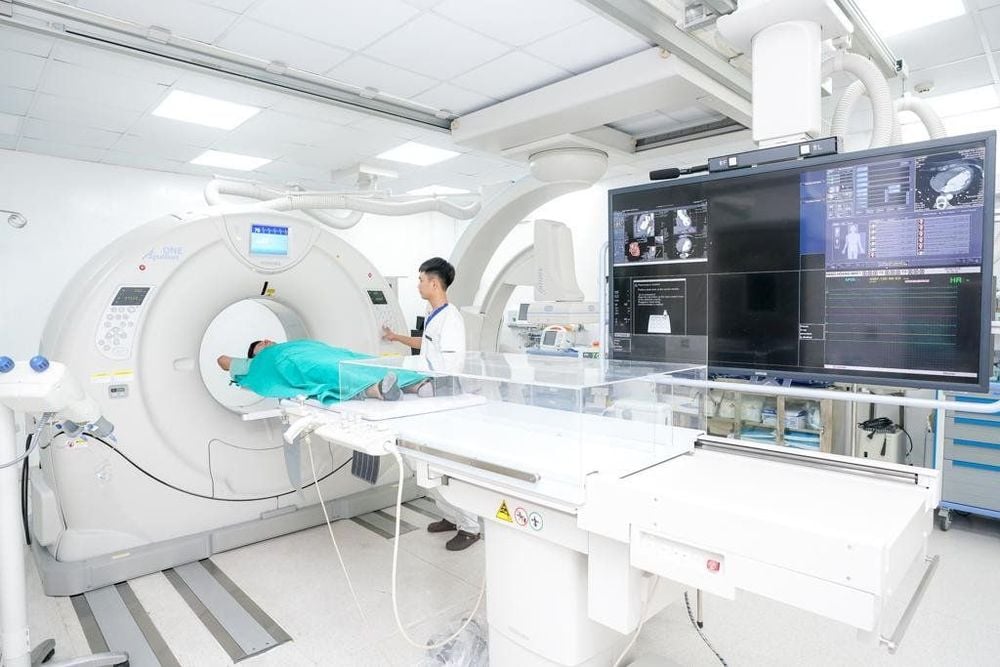
Quy trình quét canxi vành
4. What are the results of the coronary calcium scan?
The results of a coronary calcium scan are usually given as an Agatston score. These are scores against the density of calcium in your coronary arteries as well as your risk of future cardiovascular events. In the presence of calcium, you will have an Agatston score greater than 0. When the score is higher, the risk of heart disease will be proportional.At this time, based on the results of the coronary calcium scan, the doctor can plan monitoring, preventive treatment and evaluate the effectiveness of preventive treatment for cardiovascular disease. At the same time, in addition to the drug regimen, you also need to build yourself a suitable diet and lifestyle to help protect heart health in general.
Dr. Le Xuan Thiep has strengths in performing advanced and difficult magnetic resonance and computed tomography techniques such as: coronary computed tomography, cardiac function, cerebral magnetic resonance, perfusion brain and organs,..
If you notice any unusual health problems, you should visit and consult with a specialist.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Recommended video:
Cardiovascular disease: 1 person dies every 2 seconds
SEE MORE
What is coronary heart disease? Who is susceptible and how to detect early? Coronary artery disease: Manifestations, causes and treatment in Vinmec Notes on coronary angiography