This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II To Van Thai - Emergency Medicine Doctor - Emergency Resuscitation Department - Vinmec Hai Phong International General Hospital. Thai doctor has more than 34 years of experience in the field of anesthesia - emergency resuscitation.Combined spinal - epidural analgesia is a method to temporarily inhibit segmental nerve conduction through nerve roots by injecting local anesthetic into the subarachnoid and epidural spaces. .
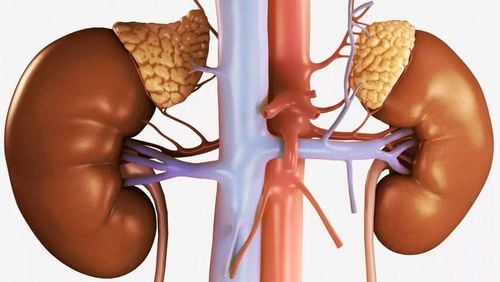
1. What is the adrenal gland?
The adrenal gland is an important endocrine gland in the human body, located deep behind the peritoneum. Hormones secreted by the adrenal glands help regulate arterial blood pressure through a complex metabolic process. Each kidney has a corresponding adrenal gland. The adrenal gland consists of two parts, the adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla.A common pathology of the adrenal gland is an adrenal tumor. The disease causes many pathological syndromes that are difficult to treat thoroughly with internal medicine due to increased hormone secretion.
Through the injection of anesthetic into the subarachnoid space and epidural space, combined spinal - epidural anesthesia for adrenalectomy to meet the requirements of anesthesia for surgery and analgesia after surgery adrenals.
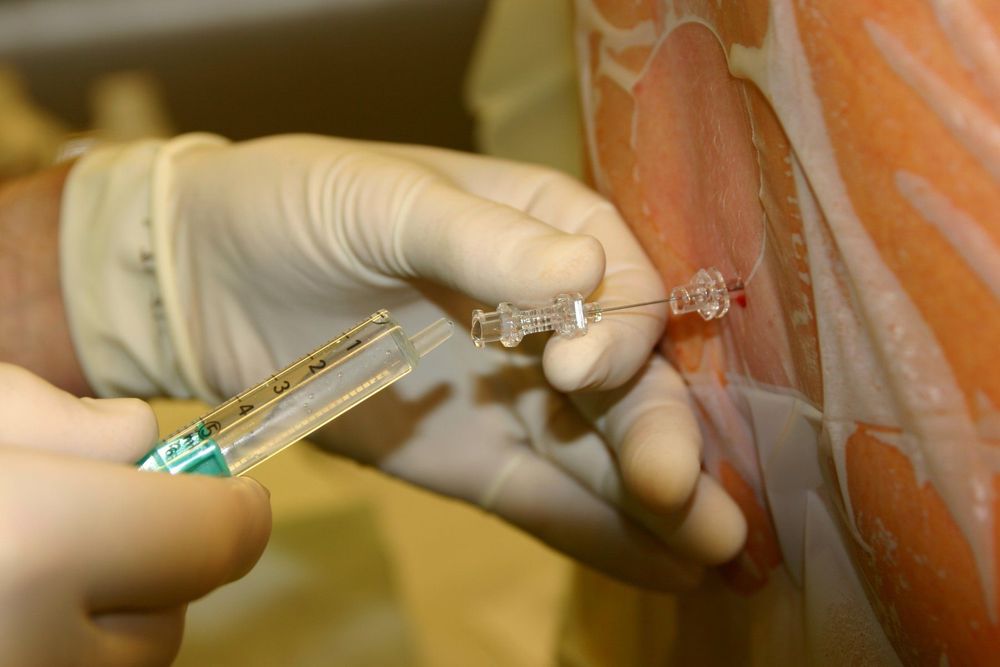
Inflammation of the needle puncture area Lack of blood volume Stopping anticoagulants for not enough time .
2. Method of combined anesthesia spinal - epidural adrenalectomy
2.1.Preparation
On the side of the hospital: To perform a combined spinal - epidural anesthesia for adrenalectomy, it is necessary to have a surgical team, a team of doctors and nurses specializing in anesthesiology and resuscitation. At the same time, the means and tools need to be fully prepared. Specifically:Resuscitation facilities: oxygen source, Ambu balloon, mask, endotracheal intubation equipment, anesthesia machine with breathing, electric shock machine, suction machine... : ephedrine, adrenaline,... Anticonvulsants: barbituric family, benzodiazepines, muscle relaxants, intralipid 10-20%,... Routine monitoring means: electrocardiogram, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, breathing rate. Needles of all sizes, gloves, sterile gauze, pince, antiseptic alcohol, sterile hole towels,... Epidural and spinal needles; Combined spinal-epidural anesthesia kit. Local anesthetics: lidocaine, bupivacaine, levobupivacaine, ropivacaine, ... can be combined with drugs of the morphine, adrenaline, clonidine family,... Dosage is based on the patient's weight, height and physical condition; Reduce dose for people > 60 years old, anemic or pregnant. On the side of the patient: Before surgery, the patient should be examined and explained to the patient to cooperate with anesthesia. Patients are instructed to clean the anesthetic area to avoid infection. In case, the patient is agitated, the doctor may prescribe a sedative from the day before surgery.
2.2. Conduct
In the process of combined spinal - epidural anesthesia, adrenalectomy requires 2 techniques: spinal and epidural anesthesia separately and spinal-epidural anesthesia once.The person performing anesthesia needs to wear a hat, mask, wash hands, wear a shirt, wear sterile gloves and disinfect the needle puncture area in the patient 3 times.
The patient will be given spinal - epidural anesthesia in a sitting or lying position. If in the lying position, have the patient lie on their side with their back bent, knees pressed against the abdomen, chin pressed to the chest. If in a sitting position, the patient sits with his back arched, head bowed, chin resting on his chest, legs stretched out on the operating table or feet on the chair. Prophylaxis of hypotension: Insert an intravenous line into the patient for effective prevention of hypotension and give fluids from 5-10 ml/kg (for adults).
2.2.1 For separate spinal and epidural techniques
Step 1: The doctor will perform spinal anesthesia in the midline (puncture between the 2 vertebrae, position L2-L3, L3-L4) or lateral line (1-2cm from the midline, direct the needle into the line). middle, up, out front).Aim the bevel of the anesthetic needle parallel to the patient's spine and insert the needle until a sensation of loss of resistance is achieved as the needle passes through the dura. Finally, to check for CSF effusion, turn the bevel of the needle toward the patient's head and inject the anesthetic.
Local anesthetics: bupivacaine, levobupivacaine, ropivacaine,... can be combined with morphine group drugs (morphine from 100-300 mcg; fentanyl 25-50 mcg, sufentanil 2.5-5 mcg,...). Dosage is based on weight, height and body condition of the patient: bupivacaine dose from 3-12mg; levobupivacaine from 5-12mg; ropivacaine dose from 5-20mg; Reduce dose for people > 60 years old, anemia, pregnancy.
Step 2: Perform epidural technique: numb the puncture site with 1-2% lidocaine. As with spinal anaesthesia, epidurals are administered in the midline or lateral line (1-2 cm midline puncture, needle in midline, upward).

Drugs used: lidocaine 2% 10-20ml; bupivacaine 0.25-0.5% 10-20ml; ropivacaine 0.25-0.5% 10-20ml; levobupivacaine 0.25-0.5% 10-20ml. Combination drugs: morphine 30-50mcg/kg; sufentanil 0.2mcg/kg should not exceed 30mcg/kg; fentanyl 25-100mcg.
Continuous infusion: bupivacaine 0.125-0.25%, running speed from 4-6ml/hour; ropivacaine 0.125-0.25% 4-10ml/hour; levobupivacaine 0.125-0.25% 4-10ml/hour. Concentrations of combination drugs: morphine 10-20mcg/ml; fentanyl 1-2mcg/ml; sufentanil 0.5 mcg/ml.
2.2.2. For one-time spinal-epidural anesthesia
One-time spinal-epidural anesthesia is performed using Tuohy needle puncture technique into the epidural space as above.The next step is to insert the 27G spinal needle into the Tuohy needle until there is a feeling of puncture through the dura, check for CSF overflow. Fix the spinal needle, inject the drug into the subarachnoid space, then withdraw the needle. Insert the catheter into the epidural space from 3 to 6 cm and fix the catheter with a sterile bandage. Continuous infusion: bupivacaine 0.125-0.25%, running rate 4-6ml/hour; ropivacaine 0.125-0.25% 4-10ml/hour; levobupivacaine 0.125-0.25% 4-10ml/hour. Concentrations of combination drugs: morphine 10-20mcg/ml; fentanyl 1-2mcg/ml; sufentanil 0.5 mcg/ml.
3. Complications that can be encountered during combined spinal - epidural anesthesia for adrenalectomy and how to manage
As with any medical treatment, patients with combined spinal - epidural anaesthesia may experience some unwanted complications. Here are some ways to deal with the complications that the patient may experience:When the patient is allergic, anaphylactic to local anesthetics, the anesthetic should be stopped; use anti-anaphylaxis regimen according to the Ministry of Health. It is necessary to stop using local anesthetics, anticonvulsants, respiratory and circulatory resuscitation, intralipid infusion when poisoning with local anesthetics bupivacaine and ropivacaine when the patient has signs Signs of anesthetic toxicity Lower blood pressure, slow pulse should be treated with vasopressors and fluid replacement. Headache: lying motionless, giving enough fluids, using pain relievers, patching the dura with autologous blood (Blood Patch). Use antiemetics when the patient feels nauseous and vomiting, and keep blood pressure under control at all times

Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.