This is an automatically translated article.
Acute adrenal insufficiency is one of the emergency diseases of endocrinology. The disease progresses rapidly and is sometimes life-threatening if not treated promptly. Recognizing the signs of the disease and early intervention is very important, especially in subjects with known chronic adrenal insufficiency.
1. What is acute adrenal insufficiency?
Adrenal gland is conical, located on two kidneys, in the bundle layer secretes glucocorticoids. These are hormones that play an important role in the energy metabolism of cells in the body. In addition, glucocorticoids also partially assist in stabilizing hemodynamics, keeping homeostasis through control of secretion or reabsorption of salt and water. At the same time, this hormone helps the body to increase resistance to internal and external stress.
Acute adrenal insufficiency is an endocrinology emergency. The cause of this condition is acute corticosteroid deficiency. Diagnosis is usually easy because the patient has a long history of previous long-term adrenal insufficiency. However, sometimes the diagnosis can be difficult if the clinical and biological symptoms are nonspecific, especially in the setting of unexplained cardiovascular collapse. At this time, if the diagnosis is missed and the treatment is inadequate, the patient's life is very dangerous.
Acute adrenal insufficiency is common in the setting of previously unrecognized or inadequately treated Addison's disease, due to direct damage to the adrenal gland or the hypothalamus-pituitary gland, affecting the secretion of the adrenal gland. secretion of hormones on this endocrine axis. However, these conditions are very rare. In fact, products containing corticosteroids are widely available and unregulated, and can be purchased and used very easily, leading to acute adrenal insufficiency - a complication if a person suddenly stops taking them. sudden or just lower dose than usual.
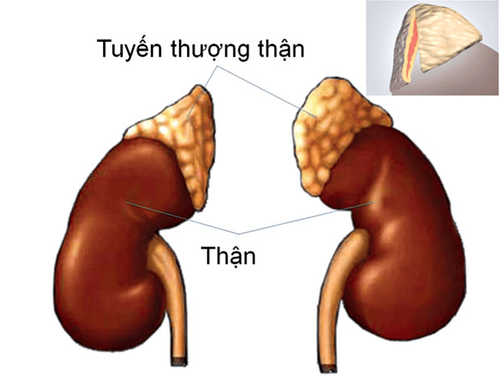
Tuyến thượng thận có hình mũ, nằm trên hai quả thận, ở phần lớp bó bài tiết ra các glucocorticoid
2. Symptoms of acute adrenal insufficiency
Different from chronic adrenal insufficiency, when the adrenal gland is acutely impaired, the hormone levels secreted into the circulation are not enough to meet the needs, the symptoms are very prominently observed. turn on in many organ systems:
Cardiovascular system: The patient suddenly had cardiovascular collapse, blood pressure dropped rapidly, cold hands and feet, small pulse, fast, difficult to detect and poorly responsive to fluid replacement and vasopressors; Digestive system: The patient complains of epigastric pain, then spreads to the whole abdomen, but the abdominal examination is still soft, sometimes accompanied by nausea and vomiting. The above manifestations can be confused with surgical abdominal diseases; Central Nervous System: Patients may complain of fatigue, weakness, malaise, restlessness, agitation, delirium to confusion, somnolence, lethargy, and coma.
3. How to diagnose acute adrenal insufficiency?
The way to diagnose acute adrenal insufficiency is not only based on the symptoms mentioned above, but also based on a history of having used pain relievers, traditional medicine... for a long time and not being able to quit smoking. In addition, it is necessary to screen for some diseases with chronic corticosteroid treatment such as autoimmune system disorders, degenerative joint diseases, uncontrolled asthma, eczema...
Also, before having the disease. With the above manifestations of an acute episode, the patient may also have symptoms of chronic adrenal insufficiency if due to excessive use of glucocorticoids such as hirsutism, weight gain, hypertension, hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, facial round, central fat, fat accumulation in the neck, back of the neck, red round face, thin skin, stretch marks...
If it is imperative to stop taking the drug suddenly or just reduce the dose, the patient will have symptoms of withdrawal syndrome such as irritability, fatigue, continuous sluggishness, lack of vitality, loss of appetite, musculoskeletal pain... Even in some cases, very high and prolonged doses were used, when stopped. Corticosteroids are provided, patients are prone to exacerbations, hemodynamic status is affected, cardiovascular and circulatory collapse, the risk of death is increased.
Regarding the paraclinical tests used to diagnose, usually only retrospectively confirmed because the patient has been treated promptly, on the spot even when the diagnosis has not been confirmed, only a few suspicious symptoms. Accordingly, taking samples for testing is only conducted when the patient is more stable; At the same time, the drugs used can affect the test results. The first indication of concern is to measure the level of cortisol in the blood and see if there is a decrease. In addition, patients also have disorders of electrolytes in the blood such as decreased sodium, increased potassium, increased HCT due to hemoconcentration due to dehydration, hypoglycemia due to decreased cellular metabolism,...
4. How to treat acute adrenal insufficiency
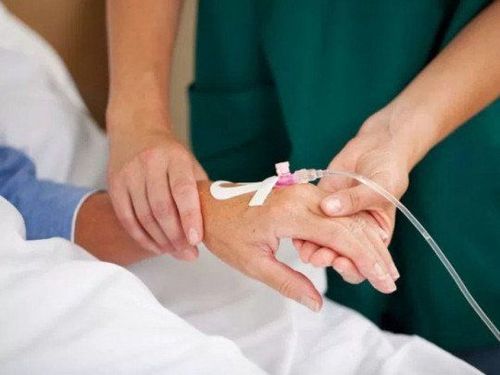
Khi nghi ngờ suy tuyến thượng thận cấp ở người bệnh với bệnh cảnh cấp cứu, trụy tuần hoàn mà chưa rõ nguyên nhân, điều đầu tiên cần làm là thiết lập một đường truyền dịch để giữ vein
When acute adrenal insufficiency is suspected in a patient with an emergency, circulatory collapse of unknown cause, the first thing to do is to establish an intravenous line to maintain the vein. The solution selected was initially physiological saline at maximum speed.
Then, if pulse and blood pressure do not improve with fluid resuscitation and the cause of shock is still unclear, a rapid injection of hydrocortisone 100 mg by intramuscular or intravenous route is recommended. If the right cause of shock is acute adrenal insufficiency, the patient's condition will quickly recover. On the contrary, it is necessary to search for other causes or initiate treatment with vasopressors.
Follow-up treatment of patients with acute adrenal insufficiency is to continue to maintain hormone replacement therapy by parenteral route, switch to oral route in parallel with resuscitation, fluid and electrolyte adjustment and close monitoring. vital signs in the first 24 hours. Give the patient absolute bed rest in a quiet, cool environment, avoid moving a lot. Ensure adequate nutrition and energy.
In addition, the doctor also needs to do a general examination, perform paraclinical tests to look for diseases that cause damage to the adrenal gland, hypothalamus - pituitary gland or other acute diseases that promote diabetes. In acute adrenal insufficiency, the body does not excrete enough cortisol to help the body cope with stress on the basis of pre-existing chronic adrenal insufficiency.
In summary, acute adrenal insufficiency is a relatively rare condition that is life-threatening if not recognized and managed properly. In patients who have been diagnosed with corticosteroid-dependent chronic adrenal insufficiency, they should be closely monitored for any suspicious signs of corticosteroid deficiency in order to promptly supplement, to avoid progression to acute adrenal insufficiency. the.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Reference source: Documents of the Medical Examination and Treatment Administration - Ministry of Health