This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by resident Doctor Le Thanh Tuan - Department of General Surgery - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital. The doctor has extensive experience in examination, treatment and surgery of abdominal diseases.Adrenal insufficiency is a condition in which the adrenal glands produce too little cortisol, disrupting metabolic processes in the body, seriously affecting human health.
1. Adrenal cortex physiology
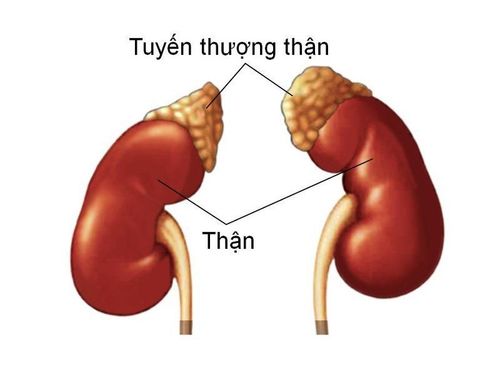
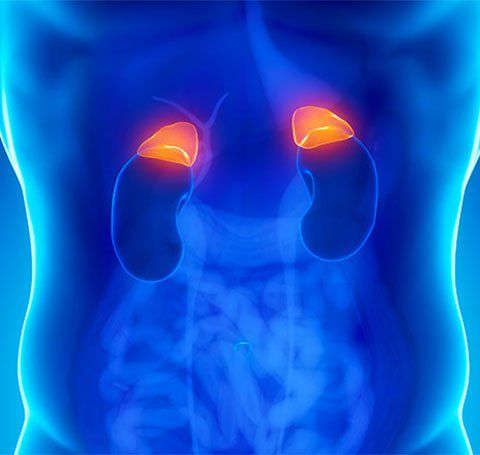
The adrenal gland is a small endocrine gland located above the two kidneys. Each gland is composed of 2 parts, the marrow secretes catechamine hormones to maintain blood pressure and heart rate; The adrenal cortex secretes the hormone aldosterone. This is the main mineral corticosteroid secreted by the glomerulus, which is the outermost layer of the adrenal cortex. Aldosterone acts on the renal tubules to increase sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion, thereby providing protection in hypovolaemia and hyperkalemia.1.1. Mechanism of secretion of adrenocortical hormone Decrease in blood volume causes indirect stimulation of aldosterone secretion. Decreased blood volume stimulates the paraglomerular cells to secrete renin; renin stimulates peripheral conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II; angiotensin II stimulates aldosterone secretion. Hyperkalemia directly stimulates aldosterone secretion. Atrial sodium-reducing factors and dopamine inhibit aldosterone secretion. Corticosteroids are the major glucocorticoids secreted by the medial and reticular layers of the adrenal cortex.
1.2. Effects of Cortisol Increases blood sugar by inhibiting insulin secretion and increasing gluconeogenesis from the liver. Inhibition of protein synthesis in muscle bundles creates a source of amino acids for that regeneration. Required for the production of angiotensin II, thus helping to maintain vascular tone. Inhibits production or activity of many inflammatory and immune mediators such as Interleukin-6 (IL-6), lymphokines, progstaglandins and histamine. Increases renal free water clearance Decreases serum calcium by inhibiting intestinal calcium absorption, tubular renal tubular calcium diffusion into cells. Cortisol is excreted in a circadian rhythm, with the highest at waking and lowest at bedtime. Normally, increased cortisol secretion during physical activity increases glucose and fatty acids needed for energy production. Cortisol secretion is increased in cases of acute trauma, infection or psychological trauma. Cortisol increases in these cases are protective, helping the body to prevent dangerous overreactions.
Androgens are produced in the adrenal cortex, most in the inner bundle. Aldosterones are the primary androgens whose function is to be secreted by the adrenal glands. The secretion of this hormone precedes the secretion of androgens by the gonads, stimulating the growth of the sex hair system during puberty.
2. Diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency

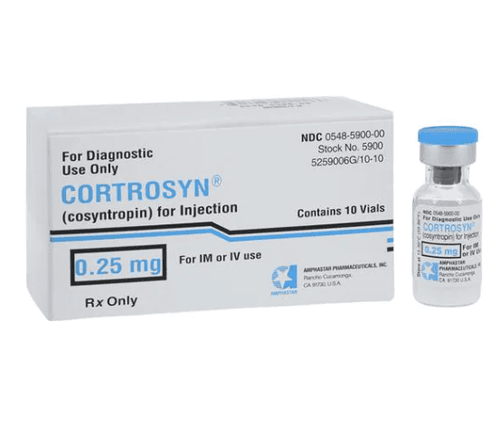
Check potassium levels through blood potassium tests bar; Check sodium levels through sodium test; Determination of blood sugar through a fasting blood glucose test; Testing cortisol levels; Adrenal cortex hormone test. 2.3. Subclinical diagnosis The number of eosinophils may increase, the number of red blood cells may decrease; hyperkalemia, decreased blood sugar. Blood cultures, sputum cultures, or urine cultures may be positive in cases of acute adrenocortical failure triggered by infection. Neutrophils are moderately reduced, lymphocytes are increased, and the number of eosinophils exceeds 300/ml of blood. In chronic adrenocortical insufficiency, hyponatremia accounts for 90%, while serum potassium is elevated (65%). In patients with diarrhea, blood potassium does not increase. Fasting blood sugar. Blood calcium may increase. The test measures the concentration of very long chain fatty acids in the blood plasma. Low plasma cortisol (< 5 mg/dl) at 8 am is diagnostic, especially with concomitant elevation of serum ACTH (usually > 200 μ/ml). The cosyntropin stimulation test was performed as described above. Anti-adrenal antibodies are found in serum in approximately 50% of cases of autoimmune Addison's disease. Anti-thyroid antibodies are 45% and antibodies to other tissues may also be present.
3. Treatment of adrenal insufficiency

The dose of glucocorticoids is also increased in cases of trauma, surgery, stress, the maximum dose of hydrocortisone used in cases of severe stress is 50 mg every 6 hours intravenously or intramuscularly.
Lower dose given orally or parenterally for milder cases of stress. This dose will be gradually reduced to the normal dose once the stress has subsided.
Patients with adrenocortical white matter disorder are treated with diet and bone marrow transplantation.
3.2. Specific treatment Alternative therapy includes a combination of both glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. In mild cases, hydrocortisone alone may be sufficient.
Hydrocortisone is the drug of choice, most patients with adrenal insufficiency take it orally at a maintenance dose of 15-25 mg/day in 2 divided doses: 2/3 of the dose taken in the morning and 1/3 of the dose taken in the morning. my afternoon. Some cases respond better to prednisolone with doses of 3 mg in the morning and 2 mg in the evening. Many patients require additional fludrocortisone or salt intake because the salt-retaining effect of hydrocortisone is insufficient.
Fludrocortisone acetate has a strong salt-retaining effect. Oral dose 0.05 mg - 0.3 mg/day. If the patient has orthostatic hypotension, hyperkalemia or emaciation, the dose should be increased. In contrast, in cases of edema due to hypokalemia or hypertension, the dose should be reduced.
Vinmec International General Hospital is one of the hospitals that not only ensures professional quality with a team of doctors, modern equipment and technology, but also stands out for its examination, consulting and service services. comprehensive and professional medical treatment; civilized, polite, safe and sterile medical examination and treatment space. Customers when choosing to perform tests here can be completely assured of the accuracy of test results.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.