This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by an Anesthesiologist - General Surgery Department - Vinmec Nha Trang International General Hospital.Genital prolapse is a condition associated with pelvic floor disorders that can affect many women. Combined spinal-epidural anesthesia for genital prolapse surgery is an anesthetic technique to temporarily inhibit segmental nerve conduction through nerve roots to help patients be pain-free and awake during surgery. by injecting local anesthetic into the subarachnoid and epidural spaces.
1. What is genital prolapse?
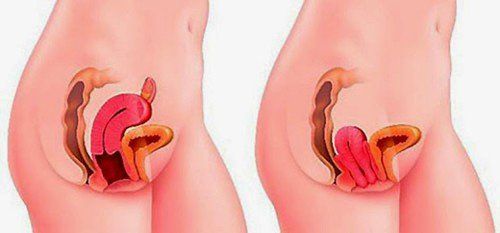
Genital prolapse is the term used to refer to the sex organs that fall or prolapse. Pelvic organ disorders are related to the prolapse of pelvic floor organs such as: bladder, uterus, vagina, etc.Most cases of genital prolapse are caused by increased pressure in the abdomen. may affect pelvic organ development. In addition, the following cases will increase the risk of genital prolapse, that is: pregnancy, labor and delivery, obesity, constipation, cancer of the pelvic organs.
Surgery is an effective treatment for genital prolapse. Combined spinal - epidural analgesia in genital prolapse surgery is one of the anesthetic methods of choice for surgical anesthesia combined with analgesia after surgery for genital prolapse.

Phụ nữ béo phì tăng nguy cơ mắc bệnh sa sinh dục
Patients allergic to local anesthetics, other contraindications to spinal, epidural anesthesia. Severe coagulopathy. Not enough time to stop anticoagulants. Closed mitral stenosis, tight aortic valve. The area where the needle was inserted is infected. Severe kyphosis, ankylosing spondylitis...
2. Method of combined anesthesia spinal - epidural for genital prolapse surgery
2.1. Prepare
On the side of the hospital: To perform spinal - epidural anesthesia for genital prolapse surgery, the surgical team needs to have a doctor, a nurse specialized in anesthesiology and resuscitation. At the same time, the means and tools need to be fully prepared. Specifically:Resuscitation facilities: oxygen source, Ambu balloon, mask, endotracheal intubation equipment, anesthesia machine with breathing, electric shock machine, suction machine... : ephedrine, adrenaline... Anticonvulsants: barbituric family, benzodiazepines, muscle relaxants, intralipid 20%,... Routine monitoring means: electrocardiogram, blood pressure, oxygen saturation, breathing rate,... Syringes and needles of all sizes, gloves, sterile gauze, pince, antiseptic alcohol, sterile gauze, spinal anesthesia needles of all sizes,... Local anesthetics: bupivacaine, levobupivacaine, ropivacaine, ... can be mixed combination with drugs of the morphine family (morphine from 100-300 mcg; fentanyl 25-50 mcg, sulfentanil 2.5-5 mcg...). Dosage is based on the patient's weight, height and body condition: bupivacaine dose is from 6-12mg; levobupivacaine from 5-12mg; ropivacaine dose from 5-20mg; Reduce dose for people > 60 years old, anemia, pregnancy. On the side of the patient: Before surgery, the patient needs to be examined and clearly explained to the patient about the method, technique, benefits, complications, and other problems that may be encountered when performing this technique. This technique allows the patient to understand, agree, and cooperate with anesthesia. Patients are instructed to clean the anesthetic area to avoid infection. In case, the patient has excessive anxiety, the doctor may prescribe a sedative from the day before surgery.

Thuốc an thần được áp dụng trong trường hợp người bệnh bị kích động
2.2. Procedure
The procedure of combined anesthesia spinal - epidural for genital prolapse surgery includes 2 techniquesSpinal and epidural anesthesia separately. One-time spinal-epidural anesthesia. Step 1: The person performing the surgery needs to wear a hat, mask, wash hands, wear a shirt, and wear sterile gloves.
First of all, disinfect the needle puncture area 3 times. The patient will receive spinal anesthesia in a sitting or lying position. If in the lying position, have the patient lie on their side with their back bent, knees pressed against the abdomen, chin pressed to the chest. If in a sitting position, the patient sits with his back arched, head bowed, chin resting on his chest, legs stretched out on the operating table or feet on the chair. Prophylaxis of hypotension: Insert an intravenous line into the patient for effective prevention of hypotension and give fluids from 5-10 ml/kg (for adults).
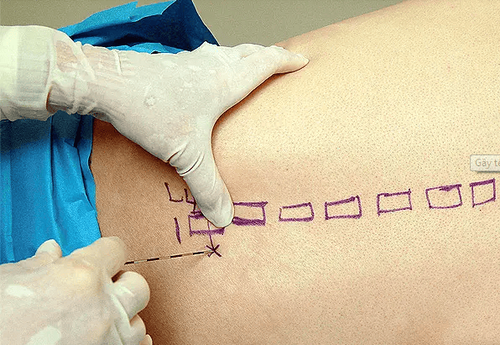
Kỹ thuật gây tê tủy sống
When administering spinal anesthesia, the doctor will perform midline (puncture between 2 vertebrae, position L2-L3 to L4-L5) or lateral line ( poke 1-2cm from midline, direct needle to midline, up, to front). Aim the bevel of the anesthetic needle parallel to the patient's spine and insert the needle until a sensation of loss of resistance is achieved as the needle passes through the dura. Finally, to check for CSF effusion, turn the bevel of the needle toward the patient's head and inject the anesthetic. Using local anesthetics: bupivacaine, levobupivacaine, ropivacaine,... can be combined with morphine drugs (morphine from 100-300 mcg; fentanyl 25-50 mcg, sulfentanil 2.5-5 mcg...). Dosage is based on the patient's weight, height and body condition: bupivacaine dose is from 6-12mg; levobupivacaine from 5-12mg; ropivacaine dose from 5-20mg; Reduce dose for people > 60 years old, anemia, pregnancy. For epidural technique with lidocaine 1-2%. As with spinal anesthesia, the doctor will perform the midline (puncture between the 2 vertebrae, the puncture location will depend on the high or low surgery) or the lateral line (1-2cm from the midline, direction needle in midline, up, out first). Assess for correct needle position by loss of resistance and absence of regurgitation of cerebrospinal fluid and blood. The next step is to turn the needle bevel towards the tip, insert the catheter slowly with a length of 3-6cm in the epidural space and withdraw the Tuohy needle. The drugs used are: lidocaine 2% 10-20ml; bupivacaine 0.25-0.5% 10-20ml; ropivacaine 0.25-0.5% 10-20ml; levobupivacaine 0.25-0.5% 10-20ml. Combination drugs: morphine 30-50mcg/kg; sufentanil 0.2mcg/kg should not exceed 30mcg/kg; fentanyl 25-100mcg. Continuous infusion: bupivacaine 0.1-0.25%, running rate from 4-6ml/hour; ropivacaine 0.08-0.2% 4-10ml/hour; levobupivacaine 0.1-0.25% 4-10ml/hour. Concentrations of combination drugs: morphine 10-20mcg/ml; fentanyl 1-2mcg/ml; sufentanil 0.5 mcg/ml.

Vị trí chọn gây tê màng cứng phụ thuộc vào phẫu thuật cao hay thấp
One-time spinal-epidural anesthesia (needle-in-needle technique) performs Tuohy needle puncture into the epidural space as above. Insert the 27G spinal needle into the Tuohy needle until there is a feeling of puncture through the dura, check for CSF exudation. Then fix the spinal needle, inject the drug into the subarachnoid space, and then withdraw the needle. Insert the catheter 3-6cm into the epidural space and secure the catheter with a sterile bandage. Continuous infusion: bupivacaine 0.1-0.25%, running rate from 4-6ml/hour; ropivacaine 0.08-0.2% 4-10ml/hour; levobupivacaine 0.125-0.25% 4-10ml/hour. Concentrations of combination drugs: morphine 10-20mcg/ml; fentanyl 1-2mcg/ml; sufentanil 0.5 mcg/ml. Step 4: Monitor
Vital signs: consciousness, heart rate, electrocardiogram, arterial blood pressure, capillary oxygen saturation. Degree of sensory and motor blockade. Adverse effects of spinal anesthesia. Criteria for transferring the patient from the recovery room: no hemodynamic and respiratory disorders, complete recovery of movement, sensory block below T12 (below the inguinal fold).
3. Complications that can be encountered during combined spinal - epidural anesthesia surgery for genital prolapse and how to manage
Like any treatment in medicine, patients with combined spinal - epidural anesthesia surgery for genital prolapse may experience some unwanted complications. Here are some ways to deal with the complications that the patient may experience:When the patient is allergic, anaphylactic to local anesthetics, the anesthetic should be stopped; using the anti-anaphylactic regimen according to the Ministry of Health. It is necessary to stop using local anesthetics, use anticonvulsants, give first aid to respiratory and circulatory resuscitation, 20% intralipid infusion according to the regimen when the patient is poisoned with local anesthetics bupivacaine and ropivacaine.
Bệnh nhân có thể bị ngộ độc thuốc tê khi gây tê kết hợp tủy sống - ngoài màng cứng
A system of modern and advanced medical equipment, possessing many of the best machines in the world, helping to detect many difficult and dangerous diseases in a short time, supporting the diagnosis and treatment of doctors the most effective. The hospital space is designed according to 5-star hotel standards, giving patients comfort, friendliness and peace of mind.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.