This is an automatically translated article.
Choline is a nutrient that was discovered recently and was recognized as an essential nutrient in 1998. Although your body makes choline, it also needs to be obtained from your diet. However, many people do not meet the recommended intake for this nutrient.1. Concept of Choline
Compared to other nutrients, choline is found later. The body can only synthesize a very small amount of choline, so choline also needs to be supplemented from foods in the daily diet to avoid a deficiency that can lead to harmful effects on health. However, despite warnings, many people still do not meet the necessary choline intake as recommended by nutritionists.
Choline is an essential nutrient, which means it is necessary for the normal functions of the body. The liver is the organ that synthesizes and produces choline, but the amount of choline that the liver can synthesize is relatively limited and that is why you need to get choline from food.
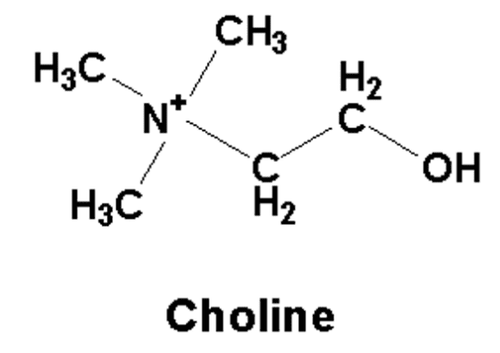
Choline is a water-soluble organic compound. Choline is neither a vitamin nor a mineral, however it is often used with vitamin B complexes due to the similarities of the two substances.
In fact, Choline and B vitamins both have an effect on many important bodily functions. Choline affects liver function, brain, motor function of muscle system, nervous system and helps the body to increase metabolism.
Choline là một chất dinh dưỡng quan trọng với sức khỏe
2. Choline uses, interactions, dosage and warnings
2.1. Uses of choline
As mentioned above, choline serves many important functions in the body, supporting many processes, including:
Aids in the formation of cell structure: Choline aids in the creation of fats for stabilize the structure of the cell membrane. Supports the functioning of cells: Choline plays an important role in the production of active cellular compounds. Fat transport and metabolism: Choline is really important in binding to transport and remove cholesterol from the liver. Choline deficiency can lead to accumulation of fat and cholesterol in the liver and other organs. DNA synthesis: Choline and other vitamins such as vitamin B12 and folate are involved in the synthesis of DNA genetic material. Nurturing a healthy nervous system: Choline is involved in the synthesis of acetylcholine, an important neurotransmitter involved in memory, muscle function, heart rate regulation, and many other basic functions. .

Bệnh nhân mắc bệnh gan nên bổ sung Choline
In addition, some other benefits of choline should also be mentioned such as:
Liver disease: Although choline deficiency can lead to liver disease, experts are still unclear if choline supplements below recommended levels increase the risk of liver disease. risk of liver disease. A large study of 56,000 people found that normal-weight women who took regular choline supplements had a 28% lower risk of liver disease compared with others. Cancer: There is strong evidence that women who eat a lot of choline foods can reduce their risk of breast cancer by up to 24% compared with other women. However, too much choline intake can increase the risk of prostate cancer in men and colon cancer in women. Neural tube defects: Getting enough choline in pregnant mothers can reduce the risk of neural tube defects in their babies. Experts have warned pregnant mothers that a lack of choline can increase the risk of neural tube defects in babies by up to 51%.
2.2. Interaction of choline with organs in the body
Choline has the ability to affect many organs in the body, specifically:
2.2.1. Impact on heart health
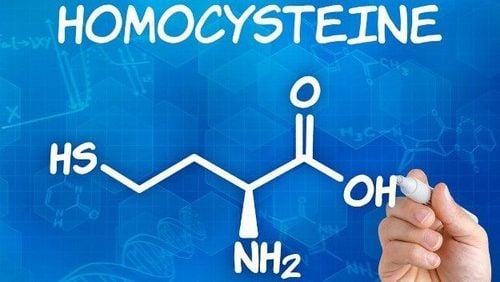
Adequate choline supplementation has been shown to be associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular disease. Folate combines with choline to help convert the amino acid homocysteine into methionine. A deficiency in either nutrient can therefore lead to a buildup of homocysteine in the blood, which increases the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke.
Although choline can reduce homocysteine levels in the blood, more research is needed to prove its effectiveness in preventing heart-related diseases.

Bổ sung Choline vào chế độ ăn uống giúp ngăn ngừa tình trạng đột quỵ
2.2.2. Impact on brain health
Choline is involved in the synthesis of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that plays an important role in the regulation of memory, mood and thinking.
Choline is also needed for DNA synthesis, which is important for brain development. Therefore, it is not surprising that choline intake is associated with improvements in several brain functions such as:
Memory: Large studies have demonstrated an association between choline levels and blood flow to the brain to improve brain functions including memory. Supplementing with 1000 mg of choline per day improves both short-term and long-term memory in adults aged 50-85 with memory impairment. In a 6-month study, giving phosphatidylcholine to people with Alzheimer's disease improved memory in about 30% of study subjects.
Brain Development: Several animal studies have shown that choline supplementation during pregnancy can enhance fetal brain development. However, human studies on this feature are limited. An observational study of 1,210 pregnant women found that choline intake was not associated with mental performance in 3-year-old children. However, another study in 99 pregnant women who took 750 mg of choline daily from 18 weeks of pregnancy showed a significant improvement in fetal brain development. Improved mental health: Some evidence suggests that choline may play a role in the development and treatment of certain mental health disorders. One study found a link between decreased blood flow and an increased risk of anxiety, and suggested a way to improve this condition with choline supplements. The results obtained are very promising.

Choline giúp cải thiện tình trạng suy giảm trí nhớ
2.3. Choline dosage
Experts do not give a specific amount of choline to supplement each day. However, the American Institute of Medicine has established a value for the recommended daily choline intake. This value is confirmed to be suitable for most healthy people to limit the risk of diseases related to choline deficiency.
Here are the values for choline required for different age groups per day:
It is important to note that choline requirements vary from person to person. Many people who are given choline levels in excess of the recommended levels can still develop a choline deficiency.
2.4. Choline abuse warning
Excessive use of choline has been associated with a number of harmful side effects to the body including low blood pressure, excessive sweating, body odor, gastrointestinal diseases....
About The daily choline limit for adults is 3,500 mg. This is the highest recommended intake at which choline is unlikely to cause harm. This is also a choline content that is difficult to achieve without a person taking supplements in large doses because the amount of choline in daily foods is also not much.
Choline is a nutrient needed by the body to ensure optimal health. Choline plays an important role in brain, cardiovascular, liver function and overall development of the fetus.
Choline deficiency often happens rarely, but it should not be subjective. To increase your daily choline intake, consider eating more choline-rich foods like salmon, eggs, broccoli or cauliflower....
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
Articles refer to sources: healthline.com, webmd.com