This is an automatically translated article.
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Huynh Khiem Huy - Cardiac Resuscitation Doctor - Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General HospitalCardiac tamponade is a serious disorder that prevents the ventricles from dilating, resulting in the inability of the heart to pump blood to the body's organs. This condition, if not diagnosed and treated promptly, can lead to heart failure or even death.
1. What is cardiac tamponade?
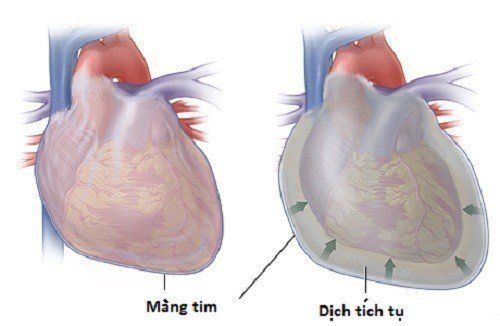
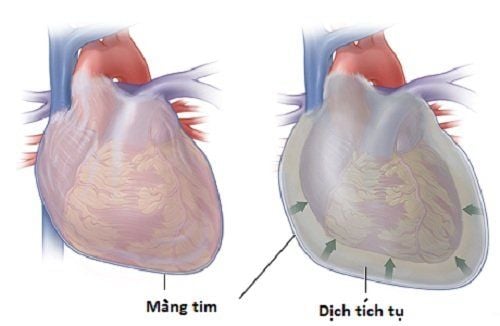
Cardiac tamponade is a compressed heart condition that occurs when blood or fluid fills the pericardial cavity (the space between the thin membrane that surrounds the heart muscle and the heart). At that time, the ventricles will be prevented from fully dilating, the organs in the body are not fully pumped by the heart, leading to organ failure, more severe will lead to cardiogenic shock and death.
Chèn ép khiến tim không bơm đủ máu tới các cơ quan trong cơ thể
2. Causes of cardiac tamponade syndrome
Causes of cardiac tamponade syndrome are divided into 2 types:2.1 Acute cardiac tamponade Acute cardiac tamponade is caused by trauma such as an accident or stab wound or gunshot wound.
In addition, acute cardiac tamponade is also caused by a number of other causes, such as: After a myocardial infarction, the heart muscle is destroyed or holes in the heart are formed after surgery (through surgery). cardiology, angiography, pacemaker placement, or central venous access).
2.2 Chronic cardiac tamponade Some common causes of this condition can be listed as: Cancer (lung cancer, breast cancer, lymphoma), lupus erythematosus, kidney failure, hypothyroidism, infections that affect the heart.
3. What are the symptoms of heart compression syndrome?
Some of the main symptoms that often occur in people with cardiac tamponade are:Decreased blood pressure, weak pulse Chest pain, mild pain in the neck, shoulder, back, abdomen Palpitations Swelling in the abdomen or some other areas Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing Dizziness, fainting, lightheadedness Feeling anxious, restless Irritability, which may be relieved by sitting upright or leaning forward

Chèn ép tim khiến người bệnh thường xuyên đau tức vùng ngực
4. Methods of treatment of cardiac tamponade syndrome
The doctor will go through a clinical examination and perform a number of tests to determine whether the patient has cardiac tamponade or not. Cardiac tamponade is a medical emergency that requires intensive treatment in a hospital.Treatment has 2 goals:
First, methods will be used to relieve pressure on the heart. For acute conditions, when pericardial effusion causes cardiac tamponade, the doctor must immediately use procedures to remove the fluid around the heart as quickly as possible. The procedure used is puncture. aspiration pericardial drainage. Patients can easily die so the procedure needs to be done quickly and with the right technique to save the patient's life and minimize the event. In addition, give the patient oxygen, use antihypertensive drugs, intravenous fluids. Then, when the patient's condition is stable, the doctor will conduct some more tests to determine the cause. Finding the cause is very important in the complete treatment of tamponade. The prognosis of treatment depends mainly on 2 factors: When you are diagnosed and the cause of the disease. Therefore, timely and prompt detection of the disease is very important.
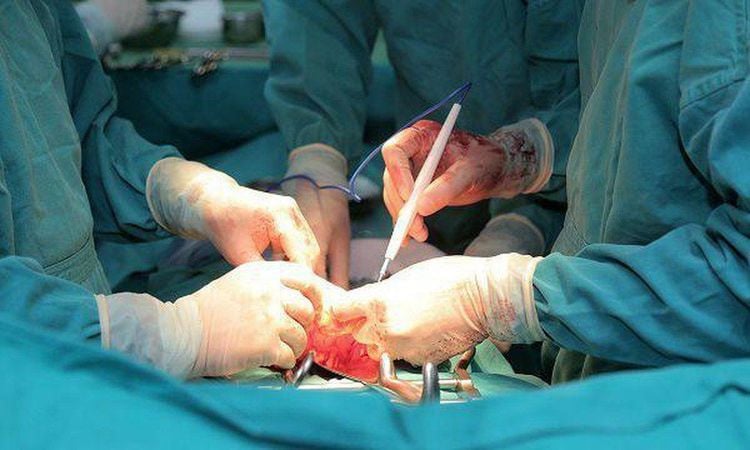
Thủ thuật cần thực hiện nhanh chóng để tránh tử vong
5. What living habits will help the patient limit the progression of heart compression syndrome?
After receiving treatment in a stable state, you should do the following to manage your recovery:Follow up with scheduled follow-up appointments Do not arbitrarily quit or use over-the-counter drugs are prescribed Call 911 or go to the hospital immediately if your symptoms get worse. If you have any questions, you should consult a medical professional for the most accurate advice. Cardiac tamponade is a fairly rare disease, about 2 people will have this condition, about 2 people will have this condition, but this is a disease with a high risk of death. Understanding the disease, minimizing risk factors, consulting a doctor if there are any suspicious signs will help you avoid the risk of death, limit complications and speed up recovery.
Master. Dr. Huynh Khiem Huy has more than 11 years of experience working in the field of cardiovascular resuscitation anesthesia; examination and resuscitation treatment after surgery for cardiovascular diseases in adults and children. Dr. Huy was former deputy head of the Department of Surgical Resuscitation at Tam Duc Heart Hospital before becoming a cardiologist in Cardiovascular Surgery, Cardiovascular Center - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital
Any questions should be asked by a doctor specialists as well as customers wishing to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online HERE.