This is an automatically translated article.
The article was professionally consulted by Specialist Doctor II Nguyen Quoc Viet - Interventional Cardiologist - Department of Medical Examination & Internal Medicine - Vinmec Danang International General Hospital.Electrocardiogram is a very valuable medical technique, used to diagnose and localize coronary artery occlusion in ischemic heart disease. On the other hand, the electrocardiogram also plays an important role in monitoring and evaluating the progress of coronary revascularization in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
1. What is an electrocardiogram?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a method of monitoring the activity, speed, and rhythm of the heart. When the heart contracts, it generates fluctuations in electrical current. An electrocardiogram is a curve that records these variations. Through the electrocardiogram, the doctor can see the heart's ability to eject blood, the rhythm and speed of the heart.The leads will examine different myocardial regions:
V1, V2: "look" in front of the interventricular septum. V3, V4: “look at” the anterior apex. V5, V6: “look at” the lower left ventricular wall. D1, aVL: “look at” the left ventricular superior wall. V7, V8, V9: “look at” the posterior wall of the left ventricle. D2, D3, aVF: “look at” the left ventricular inferior wall. V3R, V4R: “look at” the right ventricle.
Electrocardiogram ischemic myocardial
ST depression. T wave inversion becomes negative, symmetric Pathological Q wave: Q wave is > 2mm deep, > 0.04s wide, this is a late sign after myocardial infarction. If no ST segment elevation is detected, the ECG changes over time or upon recovery such as: ST depression, transient ST elevation, T wave reversal are also very valuable in diagnosing myocardial ischemia. . However, up to 20% of cases of myocardial ischemia have no ECG changes. Therefore, monitoring the evolution of electrocardiographic changes according to the progression of angina and symptoms of myocardial ischemia is extremely necessary.
The ischemic electrocardiogram will be repeated after 90 minutes in cases of thrombolysis or immediately after PCI to assess the extent of revascularization and reperfusion of the patient. coronary artery.
2. Electrocardiogram of acute myocardial infarction
Myocardial ischemia: high-positive or negative-pointed T waves, symmetrical. Signs of myocardial necrosis: Appearance of new Q waves (at least 40 ms wide or ≥ 1⁄4 R waves) in 1 of the following lead domains: D2, D3, and aVF; V1 to V6... ST segment elevation or depression in one of the above lead domains.
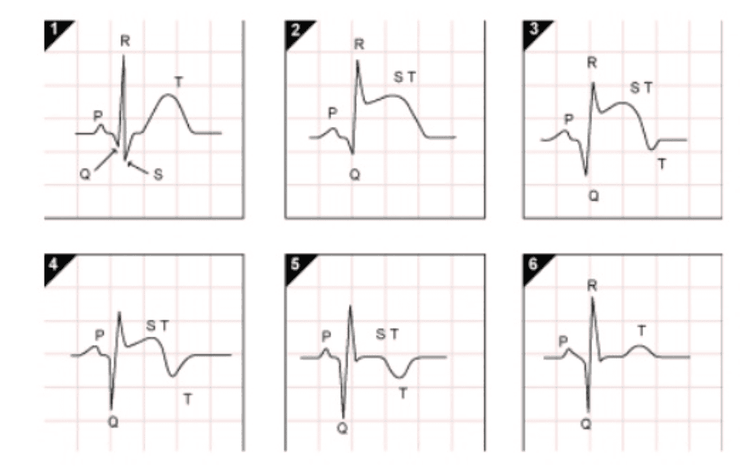
fulminant stage: in the first 24 hours, ST segment elevation, arch arch, high and sharp T intermingled with ST segment. Acute stage: in the first 1, 2 days, arch wave may appear, pathological Q wave may appear, QT lengthening, ST elevation decreased, T wave is more negative. Subacute phase: From a few days to a few weeks is the most common stage, the ST segment is lower, the T negative is deep, pointed, and symmetrical. Simultaneously, a distinct pathological Q wave and QT interval prolongation were observed. During this stage, arrhythmias or atrioventricular block are often present, especially in septal (interventricular) infarction. Chronic phase: From a few months to several years, ST returns to isoelectric, T may become positive again, and pathological Q is often permanent.
3. Types of myocardial infarction
The above signs are not always present in all the same leads, but only clearly seen in the lead where the electrode is placed (directly) on the infarcted myocardium, called imaging. direct. In contrast, leads with electrodes placed in the contralateral radial region of the infarct region will obtain contrasting, "mirrored" findings of these or indirect images.
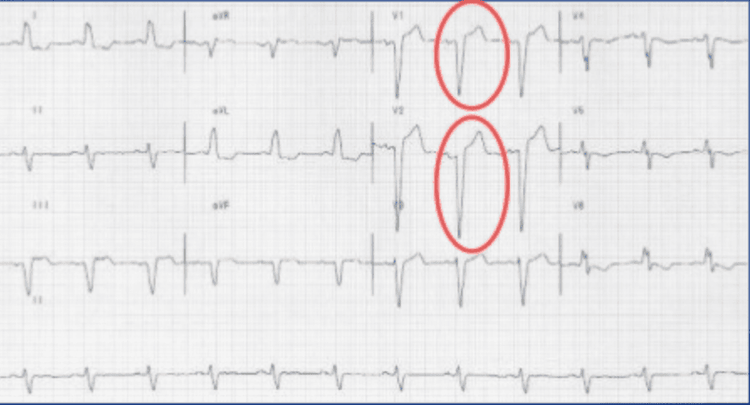
Anterior septal infarction: anterior wall of the left ventricle and anterior portion of the interventricular septum. Image of QS wave, ST elevation, negative T in V2, V3, V4. Sometimes T waves are low or negative in V5, V6, aVL, D1 (T1>T3) because the ischemic area spreads to the lateral (left) wall of the left ventricle. Lateral wall infarction of the anterior and lateral wall of the left ventricle. Deep and wide Q, ST elevation, and deep negative T in V5, V6, D1, aVL. ST segment depression, very high positive T at D3, sometimes aVF. Posterior infarction: in the posterior and inferior walls of the left ventricle. Deep, wide Q, ST elevation, deep negative T in D2, D3, aVF. Indirect images: T is high positive, can be pointed, symmetrical, ST can be depressed in V1, V2, V3, V4. Non-ST-elevated myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) or Subendocardial infarction (left ventricle): Primarily anterior-lateral: ST depression, sometimes T deformity in V5, V6, D1 , aVL. Sometimes the posterior wall is below the ST segment depression at D3, D2, aVF.
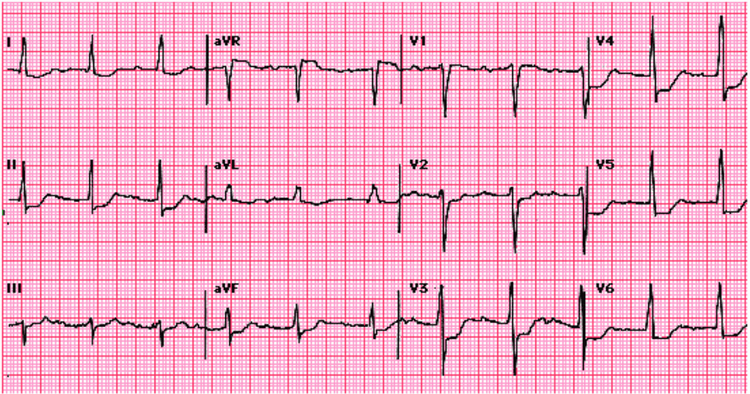
3.1. ST segment elevation in any position will indicate the location of myocardial infarction V1, V2: myocardial infarction in the anterior septum.
V3, V4: myocardial infarction in the anterior apex.
V1, V2, V3, V4: anterior apical myocardial infarction.
V5, V6: low lateral myocardial infarction.
D1, aVL: high lateral myocardial infarction.
V5, V6, D1, aVL: lateral myocardial infarction.
V3, V4, V5, V6: anterolateral myocardial infarction.
From V1 to V6, with D1, aVL: large anterior myocardial infarction.
D2, D3, aVF: myocardial infarction of the lower wall (diaphragm)
V7, V8, V9: myocardial infarction of the posterior wall.
D2, D3, aVF with V7, V8, V9: posterior inferior myocardial infarction.
V3R, V4R: right ventricular myocardial infarction.
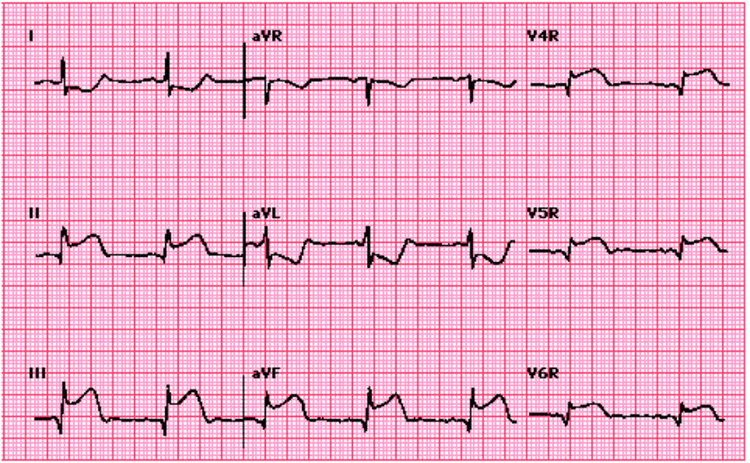
3.2. Case of electrocardiographic changes not due to coronary artery disease Acute pericarditis. Electrolyte disorders: hyperkalemia. Digoxin poisoning. WPW syndrome. Brugada syndrome. ST elevation in traumatic brain injury. Use a pacemaker. Electrocardiogram is a very valuable medical technique, used to diagnose and localize coronary artery occlusion in ischemic heart disease. In addition, they also play an important role in monitoring and evaluating the progress of coronary revascularization in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Therefore, the patient should choose reputable and well-qualified examination addresses to perform this method, thereby giving the results, the doctor will determine the best treatment regimen for the patient.
Vinmec International General Hospital is a prestigious hospital with high quality in examination, detection and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, including the implementation of methods of exploration, imaging, and treatment. prevention of cardiovascular diseases.

Vinmec Cardiology Department has always received much praise and satisfaction from domestic & international customers, being pioneers in successfully applying the world's most advanced techniques in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. .
A team of highly qualified and experienced experts: qualified doctors from Master's to Professor's and Doctor's degrees, reputable in medical treatment, surgery, interventional cardiac catheterization. Intensive training at home & abroad. In particular, Prof. TS.BS Vo Thanh Nhan - Cardiology Director of Vinmec Central Park was recognized as the first and only expert in Vietnam to be awarded the "Proctor" certificate on TAVI. State-of-the-art equipment, comparable to major hospitals in the world: The most modern operating room in the world; The most modern silent magnetic resonance imaging machine in Southeast Asia; The CT machine has a super-fast scanning speed of only 0.275s/round without the use of heart rate-lowering drugs; The 16-sequence PET/CT and SPECT/CT systems help detect damage to cardiovascular organs early even when there are no symptoms of the disease. Applying the most advanced advanced cardiovascular techniques in the world in treatment: Painless open-heart surgery; Percutaneous aortic intervention without general anesthesia; Treatment of mitral regurgitation through the catheter has a success rate of 95%; Ventricular-assisted artificial heart transplantation for patients with end-stage heart failure prolongs quality of life beyond 7 years. Cooperating with leading Cardiology Centers in Vietnam and the world such as: National Heart Institute, Cardiology Department of Hanoi Medical University, University of Paris Descartes - Georges Pompidou Hospital (France), University of Pennsylvania (France), University of Pennsylvania (France), University of Pennsylvania (France). United States)... with the aim of updating the most modern cardiovascular treatments in the world.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.