Ultrasound is a common diagnostic technique used today and is significant in screening, detecting, diagnosing, and monitoring the treatment of various diseases, including cancer. So, can ultrasound detect stomach cancer?
1. What is Ultrasound?
Ultrasound is a widely used clinical method in medicine. It utilizes the characteristics of ultrasound waves—high-frequency sound waves—to examine organs in the digestive system, cardiovascular system, obstetrics, breast, thyroid, etc., through images recreated of the internal structures of the body. This helps doctors detect various pathological conditions.
Radiologist will use an ultrasound probe that both emits and receives signals. After applying gel to the skin area outside the organ to be examined (this gel helps improve image quality in ultrasound), the doctor will move the ultrasound probe close to the patient's skin and scan to examine the internal organs. The images received from the ultrasound probe will be displayed directly on the screen, helping the doctor detect abnormal pathological conditions.
Currently, there are many ultrasound techniques and applications that have been deployed to enhance diagnostic efficiency:
2D Ultrasound (Two-Dimensional Ultrasound): The most common ultrasound method today.
3D Ultrasound (Three-Dimensional Ultrasound) and 4D Ultrasound (Three-Dimensional Ultrasound in Real-Time): Increasingly deployed, often used in fetal ultrasound.
Doppler Ultrasound: Used to examine the heart and blood vessels.
Elastography: Evaluates the stiffness and hardness of the liver, thyroid, breast, etc.
Transvaginal Ultrasound: Helps examine gynecological diseases more accurately.
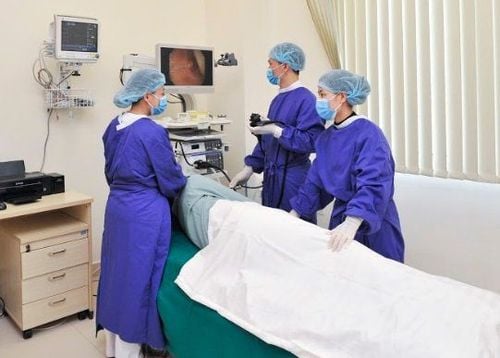
Endoscopic Ultrasound: A modern method combining endoscopy and ultrasound. Endoscopic ultrasound uses an endoscope with an attached ultrasound probe, helping diagnose and intervene in lesions in the digestive tract (esophagus, stomach, colon), liver, gallbladder, pancreas, or lesions outside the digestive tract with minimal invasiveness. This technique is particularly significant in early detection and diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancers such as stomach cancer or deep-seated tumors in the abdomen.
Biopsy of Suspected Lesions Under Ultrasound Guidance: Besides diagnosis, ultrasound also supports other techniques such as fine-needle aspiration (FNA) or biopsy of unclear lesions under ultrasound guidance, pleural fluid aspiration under ultrasound guidance, etc.
With the development of modern medicine, more and more new equipment and techniques are being applied. Ultrasound still proves its role with many advantages: simple, quick, easy to perform, painless, non-invasive, less harmful, and reasonably priced.
2. Can Ultrasound Detect Stomach Cancer?
Stomach cancer is quite common worldwide, with varying incidence rates in different regions, with Japan and China having the highest rates globally. In the US, about 26,240 new cases are recorded annually, and the number of deaths due to stomach cancer reaches up to 10,800 cases each year. The incidence of stomach cancer increases with age, with more than 75% of stomach cancer patients being 50 years old or older.
Early detection of stomach cancer is of great significance to timely treatment, reducing recurrence rates, distant metastasis, and mortality rates.
A common question is whether abdominal ultrasound can detect stomach cancer. It must be affirmed that ultrasound is not a test that can definitively diagnose stomach cancer. Early detection of stomach cancer through ultrasound is also more challenging because the stomach is a hollow organ, making it difficult for ultrasound to detect small, newly formed lesions. However, ultrasound still has certain values for stomach cancer:
Transabdominal Ultrasound: Can help detect lesions in the stomach, especially when the tumor is too large with characteristics suggesting malignancy. Detecting suspected lesions through ultrasound is a reason for doctors to prescribe additional necessary tests such as endoscopy, biopsy to confirm the diagnosis of stomach cancer.
Ultrasound also helps evaluate whether there are suspicious regional lymph nodes or detect distant metastatic lesions in patients already diagnosed or suspected of having stomach cancer.
It also helps quickly diagnose complications of stomach cancer such as intestinal obstruction, partial intestinal obstruction, etc.
Endoscopic Ultrasound: If ultrasound cannot show much value in detecting stomach cancer, endoscopic ultrasound is significant in evaluating stomach cancer at the site, region, especially when the tumor is in the early stage. Endoscopic ultrasound proves superior to other methods when ultrasound images of stomach cancer allow accurate determination of the extent of invasion of the primary stomach tumor through the layers of the stomach wall, the extent of invasion to surrounding tissues, and evaluate
3. How to Detect Stomach Cancer Early?
Early diagnosis of stomach cancer is challenging because symptoms at this stage are often very poor. Therefore, screening for stomach cancer is very meaningful for early detection and timely treatment.
Gastroscopy combined with biopsy of suspected lesions is considered the "core" method for definitive diagnosis of stomach cancer. In addition, some other tests also contribute to supporting the diagnosis.
3.1. Gastroscopy Combined with Biopsy for Pathological Examination
The development of medicine has produced many endoscopic machines with increasingly advanced and modern features for diagnosing stomach cancer.
Conventional Light Endoscopy: This is a common endoscopy in Vietnam with an accuracy rate of up to 90-96%. Gastroscopy allows the detection of abnormal lesions in the stomach, including suspected cancer lesions such as nodules, ulcers, and changes in mucosal color. Suspected stomach lesions will be biopsied and sent to the Pathology Department for histopathological examination to confirm the diagnosis.
Chromoscopy: Gastric adenocarcinoma often develops on a background of chronically inflamed epithelial cells. Early-stage stomach cancer lesions can be missed due to confusion with benign mucosal areas. Chromoscopy allows the detection of dysplastic mucosa through uneven staining, thereby guiding biopsy locations and accurate diagnosis. Magnifying endoscopy combined with chromoscopy can be used to highlight unclear dysplastic and malignant lesions in the gastric mucosa.
3.2. Endoscopic Ultrasound
As mentioned above, endoscopic ultrasound is significant in evaluating local and regional stomach cancer lesions, helping to accurately diagnose the disease stage.
The gastroscope is equipped with an ultrasound probe, allowing close access to the stomach tumor, overcoming the limitations of conventional transabdominal ultrasound such as image noise and gas interference. Endoscopic ultrasound helps distinguish lesions in the gastrointestinal wall or from external compression; it evaluates the size, structure, and invasion level of the stomach tumor with high accuracy.
3.3. Other Diagnostic Techniques for Stomach Cancer
Abdominal Ultrasound: Ultrasound can detect large stomach tumors and show abnormal abdominal lymph nodes or other organs suspected of distant metastasis, such as liver, peritoneal, and pleural metastases. Ultrasound also helps differentiate stomach cancer from other conditions.
Standing Abdominal X-ray, Barium Contrast X-ray: These can detect gastric lumen narrowing due to stomach tumors or external compression.
Computed Tomography (CT): Abdominal CT combined with endoscopic ultrasound helps accurately evaluate local and regional stomach cancer lesions. Whole-body CT helps screen for systemic secondary lesions, thereby assessing the disease stage.
PET/CT: PET/CT is superior to CT in detecting small lesions, helping to detect early stomach cancer and systemic secondary lesions.
These methods supplement gastroscopy, biopsy, and pathological examination. However, it should be emphasized that the definitive diagnosis of stomach cancer still relies on histopathological results.
In summary, ultrasound is a test that contributes to diagnosing and monitoring stomach cancer. However, ultrasound does not provide accurate results on whether a patient has stomach cancer, and its value in early detection of stomach cancer seems very low. Ultrasound images of stomach cancer are only clear for large stomach tumors or enlarged abdominal lymph nodes. Ultrasound does not help in early detection of stomach cancer but is considered a preliminary clinical method for doctors to base other techniques on for accurate cancer detection. Gastroscopy and biopsy of suspected lesions for pathological examination are considered the gold standard for accurate diagnosis of stomach cancer. Additionally, gastroscopy combined with ultrasound is an increasingly valuable technique in evaluating local and regional stomach cancer lesions.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.