Upper abdominal pain after eating is not an uncommon occurrence. Many people assume this is a sign of a stomach problem. So, the question is: is abdominal pain after eating caused by the stomach or not?
1. Is abdominal pain after eating caused by the stomach?
Feeling upper abdominal pain after eating is a common occurrence. Many people believe this is a symptom of a stomach problem and may sometimes be complacent about it. So the question is, is the abdominal pain after eating caused by the stomach? The belief that upper abdominal pain after eating is caused by the stomach cannot be entirely wrong, as in reality, when the stomach is damaged or has some problems, it will react with pain in the epigastric region (also known as the area above the umbilical and below the sternum). However, depending on the nature, location of the pain, and accompanying symptoms, doctors may have suspicions or make an accurate diagnosis of the cause of abdominal pain after eating.
According to doctors, upper abdominal pain after eating is one of the most common and characteristic symptoms of peptic ulcer disease, often accompanied by a range of other symptoms such as belching, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, abdominal distension, and discomfort.
Another serious cause of upper abdominal pain after eating is a perforated ulcer (or organ perforation) due to infection. Symptoms include severe upper abdominal pain, abdominal rigidity, vomiting, and sometimes vomiting blood along with bleeding.
Upper abdominal pain after eating in patients can sometimes stem from a particularly dangerous cause: stomach cancer. This disease progresses rapidly with the continuous growth of cancer cells, making early detection and intervention crucial.
2. What causes upper abdominal pain after eating?
Besides stomach problems, upper abdominal pain after eating can also be a symptom of the following conditions:
2.1. Bloating
Upper abdominal pain after eating can be caused by bloating, meaning there is more gas in the intestines than usual. This gas can be expelled through the mouth when burping or through the anus when passing gas.
In cases of bacterial or viral infections accompanied by diarrhea or constipation, patients may experience severe upper abdominal pain. Common symptoms include:
- Intermittent upper abdominal pain
- Pain leading to bloating
- The feeling of something moving in the stomach
- Frequent belching or passing gas
Upper abdominal pain after eating due to bloating is usually not serious and can be self-treated with over-the-counter (OTC) medications. To prevent this condition, people should develop habits of eating slowly and chewing thoroughly to reduce the amount of air swallowed, and limit consumption of foods that can cause gas in the abdomen.
2.2. Appendicitis
Appendicitis is a common condition and can also be a cause of upper abdominal pain after eating. If not treated promptly, appendicitis can progress to peritonitis and threaten the patient's life.
In the early stages of appendicitis, the most common symptom is a dull ache in the epigastric region (or upper abdominal pain). The pain then migrates and localizes to a more specific location, the lower right quadrant (also known as the right iliac fossa). Treatment in most cases of appendicitis is surgical removal.
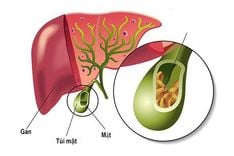
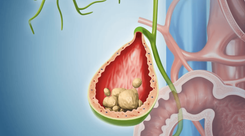
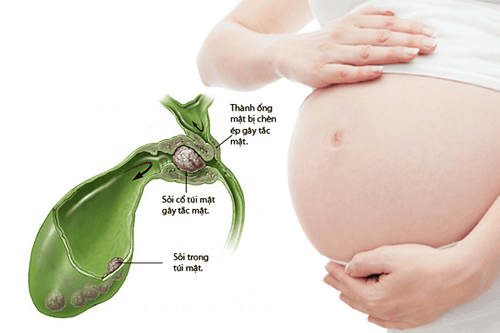
2.3. Gallstones
The gallbladder is an organ located in the upper right abdomen, just below the liver. Its function is to store bile produced by liver cells and then secrete it into the duodenum and small intestine to aid in digestion. An imbalance in the components of bile can lead to the formation of gallstones, which are hard, pebble-like, or muddy deposits.
Gallstones can block the gallbladder, resulting in severe pain in the upper right quadrant, accompanied by nausea, vomiting, fatigue, and weakness. If not treated promptly, gallstones can progress to affect the function of the liver or pancreas, with complications such as jaundice or pancreatitis that can be dangerous to health.
Most symptomatic cases of gallstones are treated by surgical removal of the gallbladder, and patients can live a normal healthy life even without this structure. To reduce the risk of recurrent upper abdominal pain after eating due to gallstones, doctors will recommend that patients should have a healthy lifestyle, a diet low in fat, and regular exercise.
2.4. Bowel obstruction
Upper abdominal pain after eating can be a consequence of a bowel obstruction. When this occurs, the flow of fluid and gas in the intestines is obstructed, reducing the ability to absorb and digest food, and causing the patient to feel extremely bloated, constipated, and experience severe vomiting.
However, the symptoms experienced depend on the location of the bowel obstruction. For example, vomiting is an early symptom of small bowel obstruction but a late symptom of large bowel obstruction. Additionally, patients may experience diarrhea if there is a partial bowel obstruction and constipation if there is a complete obstruction. Furthermore, a bowel obstruction can cause a high-grade fever if the bowel wall is perforated.
Bowel obstruction is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment to prevent bowel perforation or severe infection. Doctors will prescribe appropriate pain relievers, but in more severe cases, emergency surgery may be necessary to remove the cause of the bowel obstruction.
3. Treatment for Upper Abdominal Pain after eating
If the upper abdominal pain after eating is recent and mild, patients can try the following measures to relieve discomfort:
Use a clean cloth soaked in warm water and place it on the upper abdomen, or use a warm water bottle to roll around the painful area after eating.
Avoid cold drinks and opt for warm water. Adding a bit of ginger and honey to warm tea can be especially effective in relieving pain.
A traditional remedy involves boiling 10 grams of tangerine peel, fresh ginger, and 30 grams of rice in 350ml of water. Strain and drink the liquid.
If the pain is caused by a stomach issue, patients should adjust their diet and lifestyle, avoiding foods and drinks that harm the stomach. Increasing the intake of fruits and vegetables can support the digestive system.
Get plenty of rest, especially when experiencing abdominal pain. Avoid strenuous activities as they can worsen the pain.
According to doctors, adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, adequate rest, and stress management, can help control upper abdominal pain after eating. However, if the pain is severe, persistent, and doesn't respond to these measures, patients should seek medical attention for a proper diagnosis and treatment.
… HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.