This article has been reviewed for professional accuracy by Dinh Van Loc, MD, Specialist Level II in Anesthesiology at the General Surgery Department of Vinmec Da Nang International Hospital. With over 23 years of experience in anesthesiology and resuscitation, Dr. Loc provides expert insights into post-surgical blood clots.
Blood clots after surgery can result from limited physical activity during recovery. If not promptly identified and treated, these clots can lead to severe complications such as pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
1. Causes of Blood Clots After Surgery
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when blood clots form in veins, often following surgery. This typically results from prolonged immobility during post-surgical bed rest. Reduced movement slows blood flow in deep veins, increasing the risk of clot formation.
Blood clots are most likely to form within the first three months after surgery, with the highest risk occurring between 2 to 10 days post-operation.
Surgery significantly increases the likelihood of clot formation compared to daily activities, primarily due to immobility.
Lack of movement slows circulation, promoting clotting. Muscle activity is critical to maintaining healthy blood flow and preventing clot stagnation.
During surgery, extended periods of immobility on the operating table increase the risk of clot formation. Post-surgery, pain, illness, or difficulty moving further exacerbate this risk.
Some types of surgery carry a higher risk of clot formation, such as:
Procedures involving arterial or venous repair, where the body forms clots to stop bleeding.
Surgeries requiring cardiopulmonary bypass (e.g., coronary artery bypass grafting [CABG]), as the heart temporarily stops during the procedure.
Personal medical history and lifestyle factors also influence clot risk. For example: Smoking increases clot formation risk, even without surgery.
2. Risk Factors for Blood Clots
Several medical conditions and factors increase the likelihood of developing blood clots after surgery, including:
Atrial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat).
Pregnancy, as clotting mechanisms are heightened in preparation for childbirth.
Certain cancers that make blood more prone to clotting.
Personal or family history of blood clots.
Use of hormone replacement therapy.
Smoking.
Obesity.
Prolonged immobility.
Heart valve issues.
Dehydration.
3. Prevention
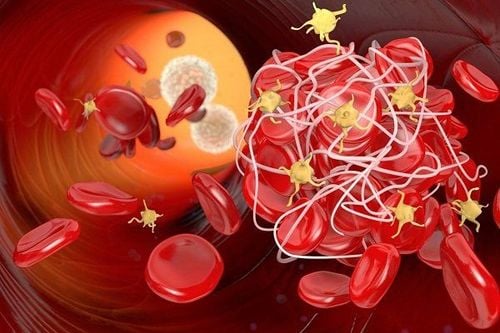
Preventing blood clots during and after surgery is essential. Here are some key prevention strategies:
Stay Mobile: Regular movement during recovery helps maintain blood flow and reduces clotting risk.
Hydration: Drink plenty of water to prevent blood thickening and improve circulation.
Medication: Physicians may prescribe blood-thinning medications. As always, prevention is better than cure.
Injections such as Lovenox or Heparin are commonly used during hospital stays after surgery to prevent the formation of blood clots. However, they are rarely prescribed for home use.
Recognize the symptoms of a blood clot
4. Treatment for Blood Clots

Treatment depends on the clot's location and severity. Common treatments include:
Medications
Warfarin (Coumadin) or Heparin to dissolve clots and prevent further formation or enlargement.
DVT Treatment
DVT typically occurs in the legs and is the most common post-surgical blood clot. Left untreated, DVT may resolve naturally but could also travel through blood vessels to the lungs, leading to life-threatening pulmonary embolism (PE).
Surgical Interventions
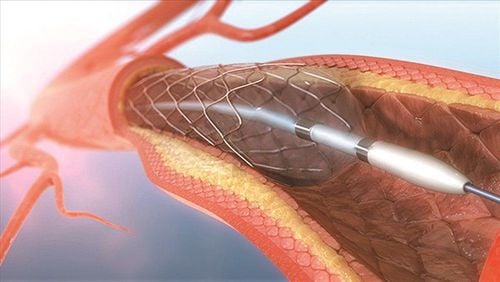
If clot migration poses a high risk or blood-thinning medications are unsafe, physicians may place an inferior vena cava (IVC) filter.
This device, inserted through a small incision in the groin or neck, catches clots before they reach the lungs. IVC filters can be temporary or permanent.
Final Advice
Blood clots after surgery can be a severe complication. If you experience unexplained pain or sudden discomfort after surgery, consult your healthcare provider immediately. It's better to address potential clotting issues early than to face life-threatening conditions like pulmonary embolism.
After surgery, it's always better to prioritize safety rather than regret, especially when there is a risk of blood clots.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.