If a mother experiences bleeding (hemorrhage) during labor, it could represent a significant risk to her overall health and lead to life-threatening complications that need to be treated immediately. Bleeding can be classified into three periods: before, throughout, and after birth.
1. Causes of bleeding during labor and childbirth
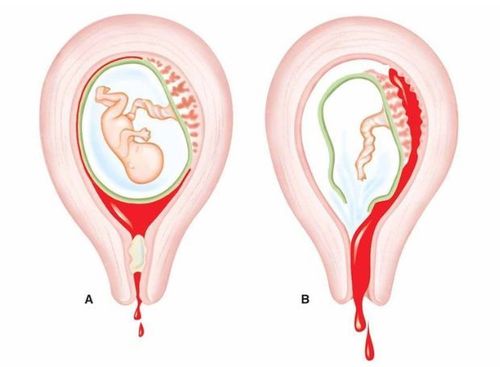
- Placenta previa: Normally, the placenta lies to the body and bottom of the uterus, but there are also cases where the placenta lies low to the lower part of the uterus. When the placenta lies low in the uterus, it may partly or entirely cover the cervix. The condition is called placenta previa. It may cause vaginal bleeding. It causes intermittent bleeding in the last months of pregnancy. When labor and delivery occur, the lower part of the uterus stretches (due to uterine contractions pushing the fetus down), causing the placenta to slip and peel off, causing severe bleeding, and the mother dies quickly.
- Uterine Atony: Generally, after giving birth, the uterine muscles contract, squeezing the blood vessels in the muscles, which has the effect of stopping bleeding, called "physiological hemostasis." Uterine atony is caused by excessive stretching of the uterine muscles during pregnancy or labor. Symptoms of uterine atony include significant bleeding immediately after the delivery of the placenta, which is the most common and noticeable sign. The uterus may feel soft and enlarged (flaccid), with minimal or absent contractions. It lacks the firm, well-contracted state (commonly called a "safe uterine mass") expected postpartum. If untreated, uterine atony can quickly lead to severe blood loss and potentially life-threatening shock. Uterine atony often occurs in the following cases:
- Prolonged Labor: over 12 hours for the second child or over 16 hours for the first child.
- Overdistended Uterus: An overly stretched uterus due to multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets), excessive amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios), or a large baby.
Multiple Births: Having multiple previous pregnancies can weaken uterine muscle tone over time. - Placental Complications (Abnormalities due to placental abruption and placental delivery):
- Retained Placental Tissue: If fragments of the placenta remain in the uterus after delivery, they can prevent uterine contraction, resulting in persistent bleeding. Bleeding can occur in either major or minor amounts, with bright red blood mixed with blood clots. Placental retention can be discovered early by checking the placenta and membranes. Heavy blood loss might induce shock if diagnosed too late or not at all.
- Placenta accreta: The placenta does not separate within 30 minutes after the fetus is delivered, or active treatment of the third stage of labor is unsuccessful. The placenta is firmly attached and does not bleed. Partial placenta accreta: after 30 minutes of delivery, the placenta does not entirely separate, bleeding more or less depending on the extent of the placenta. Complete placenta accreta: rare, no bleeding
- Genital tract trauma: tearing of the vulva, vagina, perineum, cervix, uterine rupture, genital tract hematoma
- Uterine rupture occurs when blood vessels at the rupture site break down, resulting in bleeding outside the vagina or into the abdominal cavity. This is one of the most serious obstetric complications, and if not recognized early, it can quickly lead to the mother's death. It frequently occurs after complicated procedures such as forceps while the position is still high, internal rotation of the fetus, or in women with old surgical scars
- Cervical tear, vaginal tear, vulva tear: During the delivery stage, uterine contractions push the fetus down, causing the cervix to open; the vagina, vulva, and the muscles in the vaginal area also stretch so that the fetus can pass through. If the labor time is too fast, the mother pushes too hard, too early when the cervix is not fully open, or the muscles in the vaginal area or vulva are not stretched enough, it will cause tears in these parts. The tear may be shallow or deep, resulting in severe bleeding or minor leaking that lasts for hours. If not detected, the mother will die.
- Coagulation disorder: Pre-existing or acquired blood clotting disorders can impair the body's ability to stop bleeding during and after childbirth. It may be primarily due to blood diseases, although it typically results from significant bleeding and fibrinogen loss. Conditions, like disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), can be especially harmful in the obstetric setting.
2. How can you detect irregular bleeding in pregnant women?
If there is bleeding before labor, the pregnant woman can detect it herself and go to the hospital for an examination; however, during or after delivering their infancy, because the pregnant woman is too tired and falls asleep (postpartum physiological sleep), she cannot detect it herself, so the pregnant woman must be closely monitored by the medical team for 3 to 6 hours after giving birth to detect and treat it immediately.
Trắc nghiệm: Dấu hiệu cảnh báo chuyển dạ thực sự
Chuyển dạ là quá trình thai phụ bước vào giai đoạn “đẻ đau” để kết thúc thời gian “mang nặng”. Thời gian và dấu hiệu chuyển dạ sẽ khác nhau tùy vào vào từng người và nhiều yếu tố. Theo dõi bài trắc nghiệm dưới đây sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn các dấu hiệu chuyển dạ một cách chính xác và an toàn.3. How to prevent bleeding during the delivering stage?
During and after birth, bleeding complications often occur quickly and unexpectedly, making it difficult to control the disease, so pregnant women should take the following measures to prevent complications:
- Regular prenatal check-ups as prescribed and scheduled by your doctor to detect blood diseases and other fetal abnormalities early.
- Visit a medical facility for prenatal care if you have blood diseases, blood clotting disorders, old surgical scars, huge fetuses, twins, triplets, polyhydramnios, or a placenta previa.
- During labor, pregnant women need to be calm, trust, and listen to the doctor's instructions.
Vinmec International General Hospital provides a comprehensive maternal healthcare program for pregnant women from the first few months of labor, including routine tests, periodic 3D and 4D ultrasounds, and detailed prenatal checkups to ensure the mother's stable medical condition and the fetus's healthy development. Pregnant women will no longer be alone when they enter labor because having a companion will always make the birthing experience more peaceful and joyful.
Pregnant women will be examined and their health evaluated under the personal guidance of skilled and qualified obstetricians, allowing moms to learn more about how to preserve their health throughout pregnancy and reduce difficulties for both mother and child.
To arrange an appointment, please call HOTLINE or make your reservation directly HERE. You may also download the MyVinmec app to schedule appointments faster and manage your reservations more conveniently.