This is an automatically translated article.
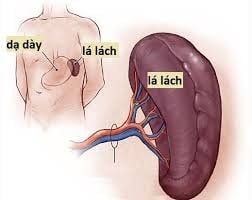
The article is professionally consulted by Master, Doctor Nguyen Van Phan - Head of Interventional Imaging Unit - Department of Diagnostic Imaging and Nuclear Medicine - Vinmec Times City International General Hospital.Background digitized hepatic angiography is an interventional procedure that uses iodine-containing contrast to image the splenic artery and vein. Digital splenic angiography erases background to help diagnose splenic diseases with angiogenesis, aneurysms and vascular malformations, thereby providing appropriate treatment.
1. When is the digitized splenic artery angiography indicated?
1.1 Designation
Splenic artery pseudoaneurysmGastrointestinal bleeding
Splenic rupture trauma
Hypersplenism syndrome
Splenic lymphoma
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Preoperative laparoscopic splenectomy .
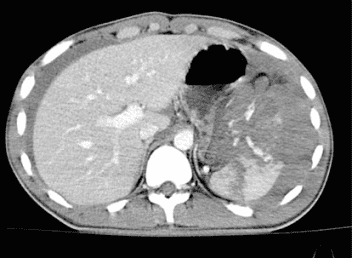
Bác sĩ sẽ chỉ định chụp các động mạch lách số hóa nền khi bệnh nhân bị chấn thương vỡ lách
1.2 Contraindications
● Severe and uncontrolled coagulopathy (prothrombin <60%, INR > 1.5, platelet count < 50 G/l): Need to be adjusted before intervention● Severe renal failure
● Allergic to contrast agent Photonic contains Iodine
● Pregnant women.
2. Digital splenic angiography with background erasure
2.1 Personnel
2 interventional radiologists 1 nurse 2 radiology technicians 1 anesthesiologist if the patient is uncooperative or the child is under 5 years old. 1 anesthesiologist
Máy chụp mạch số hóa xóa nền (DSA)
2.2 Vehicles and machines
● Digital erasure angiography (DSA)● Specialized high-pressure contrast agent pump.
Pacs image storage system.
● Lead jacket, apron, lead collar, x-ray shielding glasses.
2.3 Implementation steps
● Patients and guardians are explained about the procedure, benefits, risks of complications - possible complications. Sign a commitment to do the procedure, commit to using contrast agents containing iodine.● Fasting, drinking before 6 hours if anesthesia; 4 hours before anesthesia. You can drink water but not more than 50ml of water.
● At the intervention room: the patient lies on his back, installing a monitor to monitor breathing, pulse, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, SpO2.
● Disinfect the femoral artery puncture area, cover with a vascular intervention towel set.
● Local anesthesia of femoral artery puncture with Lidocaine 2%
● Fetal artery puncture. In special cases, a radial puncture can be performed if femoral artery puncture is not possible. Placement of an arterial catheter
● Thread the catheter onto a visceral angiogram to assess the overall splenic artery.
● Superior mesenteric angiogram to evaluate the splenic-portal venous system.
● Selective splenic artery scan, identify damaged blood vessels, use microcatheter to thread super selectively into the pedicle supplying blood to the lesion.
● Conduct embolization with materials suitable for indications through microcatheter.
● Take a scan to check the occlusion of the feeding vessels, continue selective embolization if necessary.
● Remove the catheter and open the catheter into the lumen.
● At the end of the procedure, compress the femoral artery or close the femoral artery.
● The patient lies on the hospital bed, immobilizes the leg on the side of the puncture, the nurse will monitor for bleeding complications ~ 8 hours if the bandage is pressed, ~ 2 hours if the femoral pulse is closed.
● Monitor pulse, temperature, blood pressure, respiratory indicators.
● Use pain relievers and antiemetics in case of need.
Dr. Nguyen Van Phan is an interventional radiologist and radiologist, with extensive experience in diagnosing and performing vascular interventions such as brain aneurysm implantation, brain stenting, and vascular malformations. cerebrovascular brain; embolization for the treatment of hemoptysis; treatment of liver tumors, uterine fibroids, benign prostatic hypertrophy, stem cell transplantation for treatment of cirrhosis, congenital biliary atrophy, Type II diabetes... Non-vascular interventions such as high-frequency ablation frequency (RFA) treatment of liver tumors, benign thyroid tumors; aspiration and drainage of abscesses, drainage and stenting of biliary tract, urinary kidney; aspiration cytology and biopsies of breast, thyroid, lymph nodes, soft tissue, biopsies of liver tumors, lung tumors, bone tumors ...
Currently, Vinmec International Hospital also applies dynamic imaging techniques digitized spleen circuit erase background. Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as if you want to be examined and treated at Vinmec International General Hospital, you can contact Vinmec Health System nationwide or register online. online HERE.
SEE MORE
Digital scan to erase the background and intervene on pancreatic duodenal vessels Digital scan to erase the background and stop the bleeding of the viscera Treating the tumor embolism of the lower viscera digitalized to erase the background