This is an automatically translated article.
The article is expertly consulted by Master, Resident, Specialist I Trinh Le Hong Minh - Radiologist - Radiology Department - Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.Intervention of the splenic artery is an embolization technique, which can be selective or non-selective. The goal of this technique is to reduce circulating blood flow to the spleen or possibly induce active splenic necrosis.
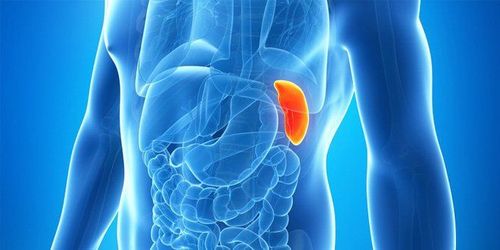
1. Structure and function of the spleen
The spleen of an adult and healthy person is usually 7-14cm long and weighs about 150-200g. The spleen consists of splenic parenchyma and supporting tissue. The main supporting tissue is the fibrous sheath, the fibrous raft, and the fibrous cord. The splenic parenchyma consists of white and red marrow.The spleen has a pyramidal shape with 3 faces, 3 edges, 1 base and 1 apex; The anterior (superior) margin is notched and palpable when the spleen is enlarged; The spleen has the diaphragm, kidney and stomach, the bottom is the colon, the remaining faces can be called visceral; The stomach surface near the lower border has the hilum of the spleen, in which the hilum of the spleen does not include arteries and veins. The hilum is also connected to the stomach by the gastrosplenic omentum, the tail of the pancreas by the pancreatic-splenic omentum. The spleen is the body's largest lymphatic organ, located in the path of blood circulation. The spleen is responsible for producing lymphocytes, destroying old blood cells, and retaining iron and protein and other substances needed to regenerate new cells.
The spleen also has the function of storing blood for the body, when the spleen contracts or dilates, it also participates in regulating blood volume in the circulation. The spleen is an infection-fighting part of the body, filtering bacteria and foreign objects in the blood.
2. Digital imaging technique to erase the splenic artery background
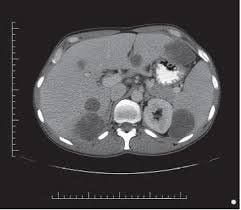
When the spleen is injured, has a tumor or other abnormality, the doctor may perform an X-ray to find out the cause. Digital angiography erasing the splenic artery background is one of the techniques used to examine the spleen.This is an endoscopic fluoroscopy technique widely used in radiology to produce images of blood vessels. Radiation-blocking structures such as bones are digitally removed from the image, so blood vessels are clearly shown.
The basic principle of this technique is to use fluorescent light and X-rays to take pictures of the blood vessels at the site to be examined before and after the contrast is injected into the blood vessels to be imaged. Finally, the computer erases the background image to make it clearer how the blood vessels are imaged.
This technique used for spleen will use catheter and microcatheter to be inserted into the splenic artery or branch. Next, the doctor will use vascular material to cause an embolism.
2.1 Indications and contraindications
Digital imaging technique to erase the background of the splenic artery is indicated and contraindicated for the following cases.Indications Pseudoaneurysm of the splenic artery Injury to rupture of the spleen High gastrointestinal bleeding with blood supply from the splenic artery Hypersplenism syndrome Chronic lymphocytic vascular disease Endoscopic preoperative splenectomy Splenic lymphoma Anti Indications Allergic to iodine contrast agents Pregnant women Patients with severe renal failure Blood clotting disorders The above contraindications are approximate only, depending on the case, the doctor will have different decisions about whether to take it or not. use this technique no.
2.2 Steps to take
2.2.1 Opening the way to the artery
First, the doctor will give local anesthetic to the patient and make an incision in the area to be examined. Then use a needle set to poke the right artery with enough common ground and then thread the guide wire through the needle. Finally, the tube is placed into the lumen of the vessel through the wire.2.2.2 Angiography and injury assessment
The doctor will continue to angiogram of the visceral trunk and superior mesenteric arteries using a standard catheter. Selective imaging of the splenic artery with microcatheters is required.2.2.3 Treatment interventions
To intervene in the treatment of lesions in the spleen, the doctor uses a microcatheter to select the branch of the artery that requires intervention. Then proceed to vascular occlusion with the appropriate material indicated through the microtubule.2.2.4 Evaluation after intervention
After the end of the intervention on the arteries, the doctor will conduct an angiogram to evaluate the circulation after the embolization. Finally close the vascular access and end the procedure.2.3 Commenting on results
Depending on the purpose of arterial intervention, the doctor will make different comments. A few cases can be reviewed:Aneurysm pseudoaneurysm node : After intervention, the pseudoaneurysm sac will be removed from the splenic artery circulation. Circulation behind the pseudobulb will remain normal. Vascular embolization to treat hypersplenism: Depending on the volume of the spleen that requires necrosis, the doctor will choose different target vessels. Hemostasis after injury: The bleeding site will be completely blocked and no longer drain the drug out of the vessel.
2.4 Some possible adverse events
Digital imaging technique to erase the splenic artery background can cause some complications such as: Hematoma at the site of opening the way into the lumen, pain after embolization or allergy to contrast agents. If a hematoma occurs, the patient should be bandaged to stop the bleeding immediately. Patients with pain after embolization may be due to necrosis of splenic tissue, anti-pain regimens from level 1 to level 3 can be applied.The case of drug allergy is quite rare, if this is the case, it is necessary to apply using the procedure for the diagnosis and management of adverse events with contrast agents.
Digital imaging technique to erase the background of the splenic artery is not only applied to the splenic artery but also in many cases such as cardiovascular or neurological applications.
Any questions that need to be answered by a specialist doctor as well as if you have a need for examination and treatment at Vinmec International General Hospital, please book an appointment on the website to be served.
Please dial HOTLINE for more information or register for an appointment HERE. Download MyVinmec app to make appointments faster and to manage your bookings easily.
SEE ALSOClassification of 5 degrees of splenic rupture in blunt abdominal trauma Aneurysms in the splenic artery: What you need to know Emergency Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm